Abstract
Aims
Observational studies and meta-analyses of randomized trials on dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i) reported discordant results on the risk of malignancies with this class of drugs. Aim of the present meta-analysis is the assessment of the effect of DPP4i treatment on the incidence of different types of cancer, collecting all available evidence from randomized controlled trials.
Methods
An extensive MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane database search for sitagliptin or vildagliptin or omarigliptin or saxagliptin or alogliptin or trelagliptin or anagliptin or linagliptin or gemigliptin or evogliptin or teneligliptin was performed up to September 30th, 2019. All trials performed on type 2 diabetes, with duration ≥ 24 weeks, and comparing of DPP4i with placebo or active drugs were collected. The study has been registered on PROSPERO (#153344). Mantel–Haenszel odds ratio (MH-OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) was calculated for all outcomes.
Results
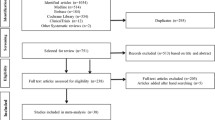
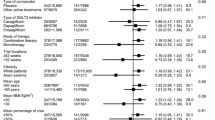
A total of 157 eligible trials were identified. DPP-4i were not associated with an increased risk of overall cancer (MH-OR 0.93 [0.86, 1.00]; p = 0.07), with no significant differences across individual molecules of the class. When compared with placebo/none, a lower risk of cancer with DPP-4i was observed in placebo-controlled trials (MH-OR 0.90 [0.82, 0.99], p = 0.030), whereas no significant differences have been detected with any other comparators. DPP-4i was associated with a significant reduction in colorectal cancer (MH-OR 0.70 [0.53, 0.94], p = 0.020).
Conclusions
Available data do not support the hypothesis of an association of DPP4i treatment with malignancies, with a possible beneficial effect for colon-rectal cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Koo DH, Han KD, Kim HJ, Park CY (2019) Middle-aged men with type 2 diabetes as potential candidates for pancreatic cancer screening: a 10-year nationwide population-based cohort study. Acta Diabetol [Epub ahead of print]
Pasquale V, Dugnani E, Liberati D et al (2019) Glucose metabolism during tumorigenesis in the genetic mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Acta Diabetol 56:1013–1022
Yang WS, Chen PC, Lin HJ et al (2017) Association between type 2 diabetes and cancer incidence in Taiwan: data from a prospective community-based cohort study. Acta Diabetol 54:455–461
Monami M, Dicembrini I, Mannucci E (2014) Thiazolidinediones and cancer: results of a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Acta Diabetol 51:91–101
Monami M, Lamanna C, Balzi D, Marchionni N, Mannucci E (2009) Sulphonylureas and cancer: a case-control study. Acta Diabetol 46:279–284
Rotella CM, Monami M, Mannucci E (2006) Metformin beyond diabetes: new life for an old drug. Curr Diabetes Rev 2:307–315
Overbeek JA, Bakker M, van der Heijden A, van Herk-Sukel MPP, Herings RMC, Nijpels G (2018) Risk of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors on site-specific cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes/Metab Res Rev 34:e3004
Capuano A, Sportiello L, Maiorino MI, Rossi F, Giugliano D, Esposito K (2013) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes therapy–focus on alogliptin. Drug Des Dev Ther 7:989–1001
Wang H, Liu X, Long M et al (2016) NRF2 activation by antioxidant antidiabetic agents accelerates tumor metastasis. Sci Transl Med 8:334ra51
Lee M, Sun J, Han M et al (2019) Nationwide trends in pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer risk among patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes receiving dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors. Diabetes Care 42:2057–2064
Abrahami D, Douros A, Yin H et al (2018) Incretin based drugs and risk of cholangiocarcinoma among patients with type 2 diabetes: population based cohort study. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 363:k4880
Noh Y, Jeon SM, Shin S (2019) Association between glucose-lowering treatment and cancer metastasis among patients with preexisting type 2 diabetes and incident malignancy. Int J Cancer 144:1530–1539
Elashoff M, Matveyenko AV, Gier B, Elashoff R, Butler PC (2011) Pancreatitis, pancreatic, and thyroid cancer with glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies. Gastroenterology 141:150–156
Faillie JL, Azoulay L, Patenaude V, Hillaire-Buys D, Suissa S (2014) Incretin based drugs and risk of acute pancreatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes: cohort study. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 348:g2780
Htoo PT, Buse JB, Gokhale M, Marquis MA, Pate V, Sturmer T (2016) Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on colorectal cancer incidence and its precursors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 72:1013–1023
Tseng CH (2017) Sitagliptin may reduce breast cancer risk in women with type 2 diabetes. Clin Breast Cancer 17:211–218
Hicks BM, Yin H, Yu OH, Pollak MN, Platt RW, Azoulay L (2016) Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues and risk of breast cancer in women with type 2 diabetes: population based cohort study using the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 355:i5340
Amritha CA, Kumaravelu P, Chellathai DD (2015) Evaluation of anti cancer effects of DPP-4 inhibitors in colon cancer—an invitro study. J Clin Diagn Research JCDR 9:Fc14-6
Femia AP, Raimondi L, Maglieri G, Lodovici M, Mannucci E, Caderni G (2013) Long-term treatment with Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, reduces colon carcinogenesis and reactive oxygen species in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced rats. Int J Cancer 133:2498–2503
Yorifuji N, Inoue T, Iguchi M et al (2016) The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin suppresses mouse colon tumorigenesis in type 2 diabetic mice. Oncol Rep 35:676–682
Lehrke M, Marx N, Patel S et al (2014) Safety and tolerability of linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a comprehensive pooled analysis of 22 placebo-controlled studies. Clin Ther 36:1130–1146
Engel SS, Round E, Golm GT, Kaufman KD, Goldstein BJ (2013) Safety and tolerability of sitagliptin in type 2 diabetes: pooled analysis of 25 clinical studies. Diabetes Ther Res Treat Educ Diabetes Related Disord 4:119–145
Hirshberg B, Parker A, Edelberg H, Donovan M, Iqbal N (2014) Safety of saxagliptin: events of special interest in 9156 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes/Metab Res Rev 30:556–569
Pinto LC, Rados DV, Barkan SS, Leitao CB, Gross JL (2018) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, pancreatic cancer and acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Sci Rep 8:782
Monami M, Dicembrini I, Martelli D, Mannucci E (2011) Safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Curr Med Res Opin 27(Suppl 3):57–64
Zhao M, Chen J, Yuan Y et al (2017) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Sci Rep 7:8273
Rosenstock J, Perkovic V, Johansen OE et al (2019) Effect of linagliptin vs placebo on major cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular and renal risk: the CARMELINA randomized clinical trial. JAMA 321:69–79
Rosenstock J, Kahn SE, Johansen OE et al (2019) Effect of linagliptin vs glimepiride on major adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: the CAROLINA randomized clinical trial. JAMA [Epub ahead of print]
Moses RG, Kalra S, Brook D et al (2014) A randomized controlled trial of the efficacy and safety of saxagliptin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes and inadequate glycaemic control on metformin plus a sulphonylurea. Diabetes Obes Metab 16:443–450
Oyama J, Murohara T, Kitakaze M et al (2016) The effect of sitagliptin on carotid artery atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes: the PROLOGUE randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med 13:e1002051
Funding
This research was performed as a part of the institutional activity of the unit, with no specific funding. All expenses, including salaries of the investigators, were covered by public research funds assigned to the unit. The manuscript was drafted and revised by the authors in accordance with ICJME standards for authorship. The corresponding author had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MM and EM were involved in design, data collection, analysis, and writing manuscript. ID, BN, and CM were involved in data collection and manuscript revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
ID has received speaking fees from Novonordisk; CM has no conflict of interest; BN is presently employee of Novo Nordisk; FT has no conflicts of interest to declare MM has received speaking fees from Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Eli-Lilly, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Novartis and research grants from Bristol Myers Squibb; EM has received consultancy fees from Merck and Novartis speaking fees from Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Eli-Lilly, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Novartis and research grants from Merck, Novartis, and Takeda. All the authors approved the final version of this manuscript. Dr. Matteo Monami is the person who takes full responsibility for the work as a whole, including the study design, access to data, and the decision to submit and publish the manuscript.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of article, informed consent is not necessary.
Additional information
Managed by Antonio Secchi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dicembrini, I., Nreu, B., Montereggi, C. et al. Risk of cancer in patients treated with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: an extensive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Diabetol 57, 689–696 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-020-01479-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-020-01479-8