Abstract
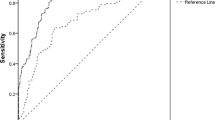
The aim of this study was to demonstrate that neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) increased before the onset of microalbuminuria in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), representing an important biochemical parameter with high sensitivity and specificity to make a precocious diagnosis of “normoalbuminuric” diabetic nephropathy (DN). Serum NGAL (sNGAL) and urinary NGAL (uNGAL) levels were evaluated in a cohort of fifty patients affected by T1DM. They had no signs of clinical nephropathy. Thirty-five healthy subjects (HS) were recruited. sNGAL levels were significantly higher compared with those measured in HS [193.7 (103.2–405.4) vs. 46.4 (39.8–56.2) ng/ml; p < 0.0001], as were uNGAL levels [25.5 (14.2–40.2) vs. 6.5 (2.9–8.5) ng/ml; p < 0.0001]. sNGAL was found to be directly correlated with glycated hemoglobin. uNGAL also positively correlated with albuminuria, whereas an inverse correlation was found with uric acid. After multivariate analysis, significance was maintained for the correlation between uNGAL and microalbuminuria. In ROC analysis, sNGAL showed a good diagnostic profile such as uNGAL. NGAL increases in patients with T1DM, even before diagnosis of microalbuminuria representing an early biomarker of “normoalbuminuric” DN with a good sensitivity and specificity. NGAL measurement could be useful for the evaluation of early renal involvement in the course of diabetes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Fioretto P, Mauer M (2007) Histopathology of diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 27:195–207
Fathy Manal A, Elkady Manal M, Fathy Hanan A, Awad Seham A, Elmenshawy Amal A (2009) Estimation of renal tubular markers for predicting early stage diabetic nephropathy in Egyptian children with type I diabetes mellitus. Res J Med Med Sci 4:207–211
MacIsaac RJ, Tsalamandris C, Panagiotopoulos S, Smith TJ, McNeil KJ, Jerums G (2004) Nonalbuminuric renal insufficiency in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27:195–200
Thomas MC, Burns WC, Cooper ME (2005) Tubular changes in early diabetic nephropathy. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 12:177–186
Mason RM, Wahab NA (2003) Extracellular matrix metabolism in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1358–1373
Wolf G (2000) Cell cycle regulation in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl 77:59–66
Pfleiderer S, Zimmerhackl LB, Kinne R, Manz F, Schuler G, Brandis M (1993) Renal proximal and distal tubular function is attenuated in diabetes mellitus type 1 as determined by the renal excretion of alpha 1-microglobulin and Tamm-Horsfall protein. Clin Investig 71:972–977
Yaqoob M, McClelland P, Patrick AW et al (1994) Evidence of oxidant injury and tubular damage in early diabetic nephropathy. QJM 87:601–607
Dunlop M (2000) Aldose reductase and the role of the polyol pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl 77:S3–S12
Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL et al (2000) Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature 404:787–789
Bolignano D, Donato V, Coppolino G et al (2008) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of kidney damage. Am J Kidney Dis 52:595–605
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R et al (2005) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365:1231–1238
Bachorzewska-Gajewska H, Malyszko J, Sitniewska E, Malyszko JS, Dobrzycki S (2006) Neutrophil-gelatinase-associated lipocalin and renal function after percutaneous coronary interventions. Am J Nephrol 26:287–292
Bolignano D, Lacquaniti A, Coppolino G, Campo S, Arena A, Buemi M (2008) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin reflects the severity of renal impairment in subjects affected by chronic kidney disease. Kidney Blood Press Res 31:255–258
Bolignano D, Lacquaniti A, Coppolino G et al (2009) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and progression of chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:337–344
Guo L, Cheng Y, Wang X et al (2012) Association between microalbuminuria and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus of the Beijing Han nationality. Acta Diabetol 49:65–71
Bolignano D, Coppolino G, Lacquaniti A, Buemi M (2010) From kidney to cardiovascular diseases: NGAL as a biomarker beyond the confines of nephrology. Eur J Clin Invest 40:273–276
Bolignano D, Lacquaniti A, Coppolino G et al (2009) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as an early biomarker of nephropathy in diabetic patients. Kidney Blood Press Res 32:91–98
Zachwieja J, Soltysiak J, Fichna P et al (2009) Normal-range albuminuria does not exclude nephropathy in diabetic children. Pediatr Nephrol 25:51–1445
Soggiu A, Piras C, Bonizzi L et al (2012) A discovery-phase urine proteomics investigation in type 1 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 49:453–464
Phillips AO (2003) The role of renal proximal tubular cells in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep 3:491–496
Mori K, Lee HT, Rapoport D et al (2005) Endocytic delivery of lipocalin-siderophore-iron complex rescues the kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 115:610–621
Kuwabara T, Mori K, Mukoyama M et al (2009) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels reflect damage to glomeruli, proximal tubules and distal nephrons. Kidney Int 75:285–294
Nielsen SE, Andersen S, Zdunek D, Hess G, Parving HH, Rossing P (2011) Tubular markers do not predict the decline in glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy. Kidney Int 79:1113–1118
Nielsen SE, Sugaya T, Hovind P, Baba T, Parving HH, Rossing P (2010) Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein predicts progression to nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 33:1320–1324
Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA et al (2000) Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ 321:405–412
Fukuhara M, Matsumura K, Wakisaka M et al (2007) Hyperglycemia promotes microinflammation as evaluated by C-reactive protein in the very elderly. Intern Med 46:207–212
Stern MP (1998) The effect of glycemic control on the incidence of macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes. Arch Fam Med 7:155–162
Nambi V (2005) The use of myeloperoxidase as a risk marker for atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 7:127–131
Elneihoum AM, Falke P, Hedblad B, Lindga¨rde F, Ohlsson K (1997) Leukocyte activation in atherosclerosis: correlation with risk factors. Atherosclerosis 131:79–84
Malyszko J, Bachorzewska-Gajewska H, Malyszko JS, Pawlak K, Dobrzycki S (2008) Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a marker of renal function in hypertensive and normotensive patients with coronary artery disease. Nephrology 13:153
Hovind P, Rossing P, Tarnow L, Johnson RJ, Parving HH (2009) Serum uric acid as a predictor for development of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes an inception cohort study. Diabetes 58:1668–1671
Mene P, Punzo G (2008) Uric acid: bystander or culprit in hypertension and progressive renal disease? J Hypertens 26:2085–2092
Siu YP, Leung KT, Tong MKH, Kwan TH (2006) Use of allopurinol in slowing the progression of renal disease through its ability in lowering serum uric acid level. Am J Kidney Dis 47:51–59
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Massimo Federici.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lacquaniti, A., Donato, V., Pintaudi, B. et al. “Normoalbuminuric” diabetic nephropathy: tubular damage and NGAL. Acta Diabetol 50, 935–942 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0485-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0485-7