Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study is to evaluate the effect of absolute stability (AS) versus relative stability (RS) performed through a minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in AO/OTA 12A1 and 12A2 fractures on healing and the time to radiographic union.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of all patients treated with plate fixation for AO/OTA type 12A1–A2 fractures at a single institution. Patients were grouped according to the type of stability used in their surgery. Time until radiographic union was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method, which was compared by long-rank test between both types of surgical techniques.
Results
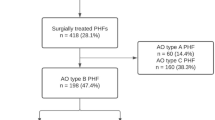
A total of 70 patients were included in this study with 35 patients in each group. The median follow-up was 9 (IQR 6–14) months. The median time to radiographic union was significantly lower in the AS group than in the RS group: 12 (interquartile range (IQR) 10–14) weeks versus 18 (IQR 16–19) weeks, respectively (p < 0.001). Non-union was seen in two cases (7%) in the relative stability group. Three patients in the RS group developed a post-operative radial nerve palsy.
Conclusion
The main finding of this study is that the median time to radiographic union was significantly shorter in the patients treated with AS compared to those with a RS technique. These findings support the recommendations of the AO foundation in that simple metaphyseal fractures (type A) that require surgical treatment should be treated with an AS construct. RS techniques should be reserved to multifragmentary fractures where fragment preservation of blood supply is paramount.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumgaertel F (2017) Bridge plating. In: AO principles of fracture management. Thieme, Thieme New York, 333, pp 241–52
An Z, Zeng B, He X et al (2010) Plating osteosynthesis of mid-distal humeral shaft fractures: minimally invasive versus conventional open reduction technique. Int Orthop 34:131–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-009-0753-x
Benegas E, Ferreira Neto AA, Gracitelli MEC et al (2014) Shoulder function after surgical treatment of displaced fractures of the humeral shaft: a randomized trial comparing antegrade intramedullary nailing with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 23:767–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2014.02.010
Hohmann E, Glatt V, Tetsworth K (2016) Minimally invasive plating versus either open reduction and plate fixation or intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25:1634–1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2016.05.014
Kim JW, Oh C-W, Byun Y-S et al (2015) A prospective randomized study of operative treatment for noncomminuted humeral shaft fractures: conventional open plating versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Orthop Trauma 29:189–194. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000232
Oh C-W, Byun Y-S, Oh J-K et al (2012) Plating of humeral shaft fractures: comparison of standard conventional plating versus minimally invasive plating. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 98:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2011.09.016
Wang C, Li J, Li Y et al (2015) Is minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture advantageous compared with the conventional open technique? J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24:1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.07.032
Kulkarni VS, Kulkarni MS, Kulkarni GS et al (2017) Comparison between antegrade intramedullary nailing (IMN), open reduction plate osteosynthesis (ORPO) and minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in treatment of humerus diaphyseal fractures. Injury 48(Suppl 2):S8–S13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1383(17)30487-4
Matsunaga FT, Tamaoki MJS, Matsumoto MH et al (2017) Minimally invasive osteosynthesis with a bridge plate versus a functional brace for humeral shaft fractures: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Jt Surg Am 99:583–592. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.16.00628
Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, Chow SP (2007) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in the treatment of proximal humeral fracture. Int Orthop 31:657–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-006-0242-4
Rancan M, Dietrich M, Lamdark T et al (2010) Minimal invasive long PHILOS®-plate osteosynthesis in metadiaphyseal fractures of the proximal humerus. Injury 41:1277–1283
Gallucci GL, Boretto JG, Alfie VA et al (2015) Posterior minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of distal third humeral shaft fractures with segmental isolation of the radial nerve. Chir Main 34:221–226
Gallucci G, Boretto J, Vujovich A et al (2014) Posterior minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fractures. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg 18:25–30
Zogaib RK, Morgan S, Belangero PS et al (2014) Minimal invasive ostheosintesis for treatment of diaphiseal transverse humeral shaft fractures. Acta Ortop Bras 22:94–98. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-78522014220200698
van de Wall BJM, Theus C, Link BC et al (2019) Absolute or relative stability in plate fixation for simple humeral shaft fractures. Injury 50:1986–1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2019.08.004
Marsh JL, Slongo TF, Agel J et al (2007) Fracture and dislocation classification compendium - 2007: orthopaedic trauma association classification, database and outcomes committee. J Orthop Trauma 21:S1-133. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131-200711101-00001
Hoppenfeld S, de Boer P, Buckley R (2017) The Humerus. Surgical exposures in orthopaedics, 5th edn. Wolters Kluwer, Philadelphia, pp 162–219
Apivatthakakul T, Phornphutkul C, Laohapoonrungsee A, Sirirungruangsarn Y (2009) Less invasive plate osteosynthesis in humeral shaft fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol 21:602–613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00064-009-2008-9
John J (1984) Grading of muscle power: comparison of MRC and analogue scales by physiotherapists. medical research council. Int J Rehabil Res 7:173–181
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P-A (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae
Eastaugh-Waring SJ, Joslin CC, Hardy JRW, Cunningham JL (2009) Quantification of fracture healing from radiographs using the maximum callus index. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:1986–1991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-0775-0
Gautier E, Sommer C (2003) Guidelines for the clinical application of the LCP. Injury 34(Suppl 2):B63-76
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M et al (2014) The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int J Surg 12:1495–1499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.07.013
Wenger R, Oehme F, Winkler J et al (2017) Absolute or relative stability in minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis of simple distal meta or diaphyseal tibia fractures? Injury 48:1217–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2017.03.005
Yang K-H, Won Y, Kang D-H et al (2015) Role of appositional screw rixation in minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal tibial rracture. J Orthop Trauma 29:e331–e335
Claessen FMAP, Peters RM, Verbeek DO et al (2015) Factors associated with radial nerve palsy after operative treatment of diaphyseal humeral shaft fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24:e307–e311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.07.012
Hak DJ (2009) Radial nerve palsy associated with humeral shaft fractures. Orthopedics 32:111
Bumbasirević M, Lesić A, Bumbasirević V et al (2010) The management of humeral shaft fractures with associated radial nerve palsy: a review of 117 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:519–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-0951-4
Lee H-J, Oh C-W, Oh J-K et al (2013) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture: a reproducible technique with the assistance of an external fixator. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133:649–657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-013-1708-7
Lee T, Yoon J (2016) Newly designed minimally invasive plating of a humerus shaft fracture; a different introduction of the plate. Int Orthop 40:2597–2602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-3097-8
Ji F, Tong D, Tang H et al (2009) Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) technique applied in the treatment of humeral shaft distal fractures through a lateral approach. Int Orthop 33:543–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0522-2
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Sebastián Marciano MD for his statistical assistance.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest either financial or non-financial.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by our Institution Research Ethics Committee. We certify that the study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rellán, I., Gallucci, G.L., Donndorff, A.G. et al. Time until union in absolute vs. relative stability MIPO plating in simple humeral shaft fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 32, 191–197 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-02920-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-02920-6