Abstract
Purpose
To develop a deep learning-based cascaded HRNet model, in order to automatically measure X-ray imaging parameters of lumbar sagittal curvature and to evaluate its prediction performance.
Methods
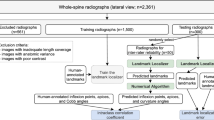
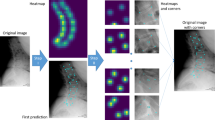
A total of 3730 lumbar lateral digital radiography (DR) images were collected from picture archiving and communication system (PACS). Among them, 3150 images were randomly selected as the training dataset and validation dataset, and 580 images as the test dataset. The landmarks of the lumbar curve index (LCI), lumbar lordosis angle (LLA), sacral slope (SS), lumbar lordosis index (LLI), and the posterior edge tangent angle of the vertebral body (PTA) were identified and marked. The measured results of landmarks on the test dataset were compared with the mean values of manual measurement as the reference standard. Percentage of correct key-points (PCK), intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC), Pearson correlation coefficient (r), mean absolute error (MAE), mean square error (MSE), root-mean-square error (RMSE), and Bland–Altman plot were used to evaluate the performance of the cascade HRNet model.
Results
The PCK of the cascaded HRNet model was 97.9–100% in the 3 mm distance threshold. The mean differences between the reference standard and the predicted values for LCI, LLA, SS, LLI, and PTA were 0.43 mm, 0.99°, 1.11°, 0.01 mm, and 0.23°, respectively. There were strong correlation and consistency of the five parameters between the cascaded HRNet model and manual measurements (ICC = 0.989–0.999, R = 0.991–0.999, MAE = 0.63–1.65, MSE = 0.61–4.06, RMSE = 0.78–2.01).
Conclusion
The cascaded HRNet model based on deep learning algorithm could accurately identify the sagittal curvature-related landmarks on lateral lumbar DR images and automatically measure the relevant parameters, which is of great significance in clinical application.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data and material availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Le Huec JC, Thompson W, Mohsinaly Y, Barrey C, Faundez A (2019) Sagittal balance of the spine. Eur Spine J 28(9):1889–1905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-019-06083-1
Makirov SK, Yuz AA, Jahaf MT, Nikulina AA (2015) Quantitative evaluation of the lumbosacral sagittal alignment in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Int J Spine surg 9:68. https://doi.org/10.14444/2068
Chun SW, Lim CY, Kim K, Hwang J, Chung SG (2017) The relationships between low back pain and lumbar lordosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J Official J North Am Spine Soc 17(8):1180–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2017.04.034
Youn YH, Cho KJ, Na Y, Kim JS (2022) Global sagittal alignment and clinical outcomes after 1–3 short-segment lumbar fusion in degenerative spinal diseases. Asian Spine J 16(4):551–559. https://doi.org/10.31616/asj.2021.0182
Berven S, Wadhwa R (2018) Sagittal alignment of the lumbar spine. Neurosurg Clin N Am 29(3):331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2018.03.009
Caprariu R, Popa I, Oprea M, Niculescu M, Poenaru D, Birsasteanu F (2021) Reduction of spondylolisthesis and sagittal balance correction by anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF). Int Orthop 45(4):997–1001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04900-7
Chang HS (2018) Influence of lumbar lordosis on the outcome of decompression surgery for lumbar canal stenosis. World Neurosurg 109:e684–e690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.10.055
Cheung JPY (2020) The importance of sagittal balance in adult scoliosis surgery. Ann Trans Med 8(2):35. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.10.19
Wang XD, Ma L, Wang DH, Yan JT (2020) Relationships among the lumbar lordosis index, sacral horizontal angle, and chronic low back pain in the elderly aged 60–69 years: a cross-sectional study. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 33(1):29–33. https://doi.org/10.3233/bmr-181382
Hong JY, Suh SW, Modi HN, Hur CY, Song HR, Park JH (2010) Reliability analysis for radiographic measures of lumbar lordosis in adult scoliosis: a case-control study comparing 6 methods. Eur Spine J 19(9):1551–1557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-010-1422-x
Cho BH, Kaji D, Cheung ZB, Ye IB, Tang R, Ahn A, Carrillo O, Schwartz JT, Valliani AA, Oermann EK, Arvind V, Ranti D, Sun L, Kim JS, Cho SK (2020) Automated measurement of lumbar lordosis on radiographs using machine learning and computer vision. Glob Spine J 10(5):611–618. https://doi.org/10.1177/2192568219868190
Chan AC, Morrison DG, Nguyen DV, Hill DL, Parent E, Lou EH (2014) Intra- and interobserver reliability of the cobb angle-vertebral rotation angle-spinous process angle for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine Deform 2(3):168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspd.2014.02.006
Serong S, Schutzbach M, Zovko I, Jäger M, Landgraeber S, Haversath M (2020) Evaluation of intra-and interobserver reliability in the assessment of the critical trochanter angle. Eur J Med Res 25(1):67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-020-00469-4
Marques C, Granström E, MacDowall A, Moreira NC, Skeppholm M, Olerud C (2020) Accuracy and reliability of X-ray measurements in the cervical spine. Asian Spine J 14(2):169–176. https://doi.org/10.31616/asj.2019.0069
Galbusera F, Niemeyer F, Wilke HJ, Bassani T, Casaroli G, Anania C, Costa F, Brayda-Bruno M, Sconfienza LM (2019) Fully automated radiological analysis of spinal disorders and deformities: a deep learning approach. Eur Spine J 28(5):951–960
Lafage R, Ferrero E, Henry JK, Challier V, Diebo B, Liabaud B, Lafage V, Schwab F (2015) Validation of a new computer-assisted tool to measure spino-pelvic parameters. Spine J Official J North Am Spine Soc 15(12):2493–2502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2015.08.067
Liao S, Zhan Y, Dong Z, Yan R, Gong L, Zhou XS, Salganicoff M, Fei J (2016) Automatic lumbar spondylolisthesis measurement in ct images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(7):1658–1669. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2016.2523452
Krishnaraj A, Barrett S, Bregman-Amitai O, Cohen-Sfady M, Bar A, Chettrit D, Orlovsky M, Elnekave E (2019) Simulating dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in CT using deep-learning segmentation cascade. J Am College Radiol JACR 16(10):1473–1479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2019.02.033
Fang Y, Li W, Chen X, Chen K, Kang H, Yu P, Zhang R, Liao J, Hong G, Li S (2021) Opportunistic osteoporosis screening in multi-detector CT images using deep convolutional neural networks. Eur Radiol 31(4):1831–1842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07312-8
Dong Q, Luo G, Lane NE, Lui LY, Marshall LM, Kado DM, Cawthon P, Perry J, Johnston SK, Haynor D, Jarvik JG, Cross NM (2022) Deep learning classification of spinal osteoporotic compression fractures on radiographs using an adaptation of the genant semiquantitative criteria. Acad Radiol 29(12):1819–1832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2022.02.020
Zhou S, Zhou F, Sun Y, Chen X, Diao Y, Zhao Y, Huang H, Fan X, Zhang G, Li X (2022) The application of artificial intelligence in spine surgery. Front Surg. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2022.885599
Hallinan J, Zhu L, Yang K, Makmur A, Algazwi DAR, Thian YL, Lau S, Choo YS, Eide SE, Yap QV, Chan YH, Tan JH, Kumar N, Ooi BC, Yoshioka H, Quek ST (2021) Deep learning model for automated detection and classification of central canal, lateral recess, and neural foraminal stenosis at lumbar spine MRI. Radiology 300(1):130–138. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2021204289
Cina A, Bassani T, Panico M, Luca A, Masharawi Y, Brayda-Bruno M, Galbusera F (2021) 2-step deep learning model for landmarks localization in spine radiographs. Sci Rep 11(1):9482. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89102-w
Lee HM, Kim YJ, Cho JB, Jeon JY, Kim KG (2022) Computer-aided diagnosis for determining sagittal spinal curvatures using deep learning and radiography. J Digit Imaging 35(4):846–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00592-0
Du Y, Fu Y, Wang L (2016) Representation learning of temporal dynamics for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process Public IEEE Signal Process Soc 25(7):3010–3022. https://doi.org/10.1109/tip.2016.2552404
Wang J, Sun K, Cheng T, Jiang B, Deng C, Zhao Y, Liu D, Mu Y, Tan M, Wang X, Liu W, Xiao B (2021) Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(10):3349–3364. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2020.2983686
Zhou S, Yao H, Ma C, Chen X, Wang W, Ji H, He L, Luo M, Guo Y (2022) Artificial intelligence X-ray measurement technology of anatomical parameters related to lumbosacral stability. Eur J Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.110071
Payer C, Štern D, Bischof H, Urschler M (2019) Integrating spatial configuration into heatmap regression based CNNs for landmark localization. Med Image Anal 54:207–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.03.007
Chen HC, Lin CJ, Wu CH, Wang CK, Sun YN (2010) Automatic Insall-Salvati ratio measurement on lateral knee x-ray images using model-guided landmark localization. Phys Med Biol 55(22):6785–6800. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/55/22/012
Larson DB, Chen MC, Lungren MP, Halabi SS, Stence NV, Langlotz CP (2018) Performance of a deep-learning neural network model in assessing skeletal maturity on pediatric hand radiographs. Radiology 287(1):313–322. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017170236
Zhou L, Wang Z, Luo Y, Xiong Z (2019) Separability and compactness network for image recognition and superresolution. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(11):3275–3286. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2018.2890550
Han W, Zhu H, Qi C, Li J, Zhang D (2022) High-resolution representations network for single image dehazing. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22062257
Saunders SL, Leng E, Spilseth B, Wasserman N, Metzger GJ, Bolan PJ (2021) Training convolutional networks for prostate segmentation with limited data. IEEE Access Pract Innov Open Solut 9:109214–109223. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3100585
Ye Q, Shen Q, Yang W, Huang S, Jiang Z, He L, Gong X (2020) Development of automatic measurement for patellar height based on deep learning and knee radiographs. Eur Radiol 30(9):4974–4984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-06856-z
Koo TK, Li MY (2016) A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med 15(2):155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012
Yang W, Ye Q, Ming S, Hu X, Jiang Z, Shen Q, He L, Gong X (2020) Feasibility of automatic measurements of hip joints based on pelvic radiography and a deep learning algorithm. Eur J Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109303
Anvari A, Halpern EF, Samir AE (2018) Essentials of statistical methods for assessing reliability and agreement in quantitative imaging. Acad Radiol 25(3):391–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2017.09.010
Korez R, Putzier M, Vrtovec T (2020) A deep learning tool for fully automated measurements of sagittal spinopelvic balance from X-ray images: performance evaluation. Eur Spine J Official Public Eur Spine Soc Eur Spin Deform Soc Eur Sect Cervic Spine Res Soc 29(9):2295–2305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-020-06406-7
Weng CH, Wang CL, Huang YJ, Yeh YC, Fu CJ, Yeh CY, Tsai TT (2019) Artificial Intelligence for Automatic Measurement of Sagittal Vertical Axis Using ResUNet Framework. J Clinic Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111826
Wang L, Xu Q, Leung S, Chung J, Chen B, Li S (2019) Accurate automated Cobb angles estimation using multi-view extrapolation net. Med Image Anal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.101542
Yeh YC, Weng CH, Huang YJ, Fu CJ, Tsai TT, Yeh CY (2021) Deep learning approach for automatic landmark detection and alignment analysis in whole-spine lateral radiographs. Sci Rep 11(1):7618. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87141-x
Acknowledgements
Hangzhou Jianpei Technology Co., Ltd., employees are gratefully acknowledged for providing practical and technical resources.
Funding
This study was supported by the Talent Innovation and Entrepreneurship project of Lanzhou city (2020-RC-53, the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China (22JR5RA659, 21JR11RA204), and the Scientific Research Project of health industry in Gansu Province (GSWSKY2022-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW contributed to conceptualization and writing—original draft. YW, LH, and GC were involved in data curation. YW, XC, and FD contributed to formal analysis. SZ was involved in funding acquisition, project administration, and supervision. XC and FD contributed to investigation. YW and XC were involved in methodology. LH and GC contributed to resources and provided software. YZ, CM, and HY were involved in validation. XC contributed to visualization. YW, XC, and SZ were involved in writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Gansu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (IRB no. 2020–112-01).
Informed consent
Because of the retrospective analysis of imaging data, patients’ informed consent was waived.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Chen, X., Dong, F. et al. Performance evaluation of a deep learning-based cascaded HRNet model for automatic measurement of X-ray imaging parameters of lumbar sagittal curvature. Eur Spine J (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07937-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07937-5