Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this retrospective analysis is to determine whether disc prosthesis replacement can be equivalent or superior compared with the disc interbody fusion.
Methods
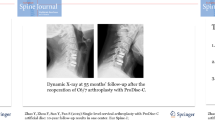
Between January, 2005 and June, 2011 we performed microdiscetomy by the anterior approach in 176 patients. We subdivided the total set of patients into two groups. Group A is made up of 84 patients in whom the prosthetic disc was implanted; Group B is made up of 92 patients in whom disc fusion was performed.
Results
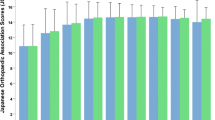
In both groups, the radicular pain disappeared and the signs of spinal cord compression improved or remained stable. Patients of Group A required significantly fewer days of hospitalization and shorter absence from work, and had significant lower scores in the Neck Disability Index (NDI) at 12 months.
Conclusions
Our experience demonstrates that the use of disc prosthesis is a safe and effective alternative to interbody fusion.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohlman HH, Emery SE, Goodfellow DB, Jones PK (1993) Robinson anterior cervical discectomy and arthrodesis for cervical radiculopathy. Long term follow-up of one hundred and twenty-two patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75:1298–1307
DiAngelo DJ, Roberston JT, Metcalf NH (2003) Biomechanical testing of an artificial cervical joint and an anterior cervical plate. J Spinal Disord Tech 16(4):314–323
Sasso RC, Anderson PA, Riew KD, Heller JG (2011) Results of cervical arthroplasty compared with anterior discectomy and fusion: four-year clinical outcomes in a prospective, randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93:1684–1692
Heller JG, Sasso RC, Papadopoulos SM et al (2008) Comparison of Bryan cervical disc arthroplasty with anterior cervical decompression and fusion. Spine 34(2):101–107
Goffin J, Van Calenbergh F, van Loon J et al (2003) Intermediate follow-up after treatment of degenerative disc disease with the Bryan cervical disc prosthesis: single-level and bi-level. Spine 28:2673–2678
Harris OA, Runnels JB, Matz PG (2001) Clinical factors associated with unexpected critical care management and prolonged hospitalization after elective cervical spine surgery. Crit Care Med 29(10):1898–1902
Mummaneni PV, Burkus JK, Haid RW, Traynelis VC, Zdeblick TA (2007) Clinical and radiographic analysis of cervical disc arthroplasty compared with allograft fusion: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Neurosurg Spine 6(3):198–209
Mummaneni PV, Robinson JC, Haid RW Jr (2007) Cervical arthroplasty with the prestige LP cervical disc. Neurosurgery 60(4 Suppl 2):310–314
Pickett GE, Mitsis DK, Sekhon LH, Sears WR, Duggal Neil (2004) Effects of a cervical prosthesis on segmental and cervical spine alignment. Neurosurg Focus 17(3):E5
Hunter LY, Braunstein EM, Bailey RW (1990) Radiographic changes following anterior cervical fusion Spine 5:399–401
Fuller DA, Kirkpatrick JS, Emery SE et al (1998) A kinematic study of the cervical spine before and after segmental arthrodesis. Spine 23:1649–1656
Hilibrand AS, Carlson GD, Palumbo MA et al (1999) Radiculopathy and myelopathy at segments adjacent to the site of a previous anterior cervical arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81:519–528
Bartels R, Donks R (2005) Fusion around cervical disc prosthesis: case report. Neurosurg 57(1):E194
Sukhomel P, Jurak L, Benes V 3rd et al (2010) Cinical results and development heterotopic ossification total cervical disc replacement during a 4-year follow-up. Eur Spine J 19(2):307–315
Huppert J, Beaurain J, Steib JP et al (2011) Comparison between single- and multi-level patients: clinical and radiological outcomes 2 years after cervical disc replacement. Eur Spine J 20(9):1417–1426
Bryan VE Jr (2002) Cervical motion segment replacement. Eur Spine J 11(Suppl 2):S92–S97
Gore DR (2001) Roentgenographic findings in the cervical spine in asymptomatic persons: a ten-year follow-up. Spine 26:2463–2466
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cappelletto, B., Giorgiutti, F., Veltri, C. et al. Disc prosthesis replacement and interbody fusion in the treatment of degenerative cervical disc disease: comparative analysis of 176 consecutive cases. Eur Spine J 22 (Suppl 6), 894–899 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3023-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3023-y