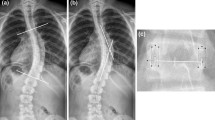
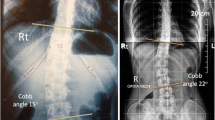
Abstract
The deformity in idiopathic scoliosis (IS) is three dimensional in nature and effective correction involves all three planes. Even though the vertebral translation (VT) is an accepted element in the deformity along with vertebral rotation(VR) as reported by Asher and Cook (Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20(12):1386–1391, 1995), Kotwicki et al. (Study Health Technol Inf 123:164–168, 2006) and Kotwicki and Napiontek (Pediatr Orthop 28(2):225–229, 2008), rib hump (rib hump index (RI)) and Cobb angle as reported by Aaro and Dahlborn (Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 6(6):567–572, 1981), it was assumed that VT was represented by adequately by Cobb angle and it was not analysed individually. We hypothesized that the Cobb angle and the VT measured in axial plane on CT scan and may not represent the same measurement and factors like coronal plane vertebral tilt,VR and vertebral deformation might affect them in different ways. Hence, VT should be considered as a separate variable and its relationship with VR, RI and Cobb angle should be investigated. Since the newer implants depend on curve translation and derotation for correction studying the role of VT and the relationships is important. VT, VR and RI were measured in CT scans of 75 patients with IS and correlated with Cobb angle. Regression analysis was used to identify the influence of the variables on each other. All the variables significantly correlated with one another but the correlation of Cobb and VT is not perfectly linear and it cannot be used to represent VT. VT influences RI much more than Cobb angle or VR. VT, therefore, merits further study treating it as an independent variable.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuklo T, Potter BK, Lawrence L (2005) Vertebral rotation and thoracic torsion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: what is the best radiographic correlate? J Spinal Disord Tech 18(2):139–147
Skalli W, Lavaste F, Descrimes J (1995) Quantification of three-dimensional vertebral rotations in scoliosis: what are the true values? Spine 20(5):546–553
Grivas TB, Samelis P, Chadziargiropoulos T, Polyzois B (2002) Study of the rib cage deformity in children with 10 degrees-20 degrees of Cobb angle late onset idiopathic scoliosis, using rib-vertebra angles–aetiologic implications. Study Health Tech Inf 91:20–24
Patel A, Schwab F, Lafage V, Patel A, Obeidat MM, Farcy JP (2010) Computed tomographic validation of the porcine model for thoracic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35(1):18–25
Grivas TB, Dangas S, Polyzois BD, Samelis P (2002) The double rib contour sign (DRCS) in lateral spinal radiographs: aetiologic implications for scoliosis. Study Health Tech Inf 88:38–43
Grivas TB, Vasiliadis ES, Mihas C, Savvidou O (2007) The effect of growth on the correlation between the spinal and rib cage deformity:implications on idiopathic scoliosis pathogenesis. Scoliosis 2:11
Stokes IAF, Bigalow LC, Moreland MS (1986) Measurement of axial rotation of vertebrae in scoliosis. Spine 11:213–218
Kotwicki T, Krawczynski A, Lorkowska M, Frydryk K (2004) Clinical and radiological assessment of spinal rotation, International Research Society of spinal deformities, 207–211
Ho EKW, Upadlyay SS, Chan FL, Hsu LC, Leong JC (1993) New methods of measuring vertebral rotation from computed tomographic scans. Spine 18:1173–1177
Ho E, Upadhyay SS, Chan FL, Hsu L, Leong J (1993) New methods of measuring vertebral rotation from computed tomographic scans: an intraobserver and interobserver study on girls with scoliosis. Spine 18(9):1173–1177
Aaro S, Dahlborn M, Svensson L (1978) Estimation of vertebral rotation in structural scoliosis by computer tomography. Acta Radiol Diagn 19:990–992
Aaro S, Dahlborn M (1981) Estimation of vertebral rotation and the spinal and rib cage deformity in scoliosis by computer tomography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 6(5):460–467
Aaro S, Dahlborn M (1981) The longitudinal axis rotation of the apical vertebra, the vertebral, spinal, and rib cage deformity in idiopathic scoliosis studied by computer tomography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 6(6):567–572
Asher MA, Cook LT (1995) The transverse plane evolution of the most common adolescent idiopathic scoliosis deformities a cross-sectional study of 181 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20(12):1386–1391
Kotwicki T, Napiontek M, Nowakowski A (2006) Transverse plane of apical vertebra of structural thoracic curve: vertebra displacement versus vertebral deformation. Study Health Technol Inf 123:164–168
Kotwicki T, Napiontek MJ (2008) Intravertebral deformation in idiopathic scoliosis: a transverse plane computer tomographic study. Pediatr Orthop 28(2):225–229
Lenke LG, Dobbs MB (2007) Management of juvenile idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:55–63
Lenke LG, Betz RR, Harms J, Bridwell KH, Clements DH, Lowe TG, Blanke K (2001) Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:1169–1181
Ho EKW, Upadlyay SS, Ferris L et al (1992) A comparative study of computed tomographic and plain radiographic methods to measure vertebral rotation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 17:771–774
Göçen S, Aksu MG, Baktiroğlu L, Ozcan OJ (1998) Evaluation of computed tomographic methods to measure vertebral rotation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: an intraobserver and interobserver analysis. Spinal Disord 11(3):210–214
Lam GC, Hill DL, Le LH, Raso JV, Lou EH (2008) Vertebral rotation measurement: a summary and comparison of common radiographic and CT methods. Scoliosis 3:16
Thulbourne T, Gillespie R (1976) The rib hump in idiopathic scoliosis. measurement, analysis and response to treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br 58(1):64–71
Götze HG (1975) Significance of the rotation index for the prognostic evaluation of idiopathic thoracic scoliosis. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 113(4):563–565
Acaroglu E, Yazici M, Deviren V, Alanay A, Cila A, Surat A (2001) Does transverse apex coincide with coronal apex levels (regional or global) in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26(10):1143–1146
George K, Rippstein J (1961) A comparative study of the two popular methods of measuring scoliotic deformity of the Spine. J Bone Joint Surg 43:809–818
Lindahl O, Movin A (1968) Measurement of the deformity in scoliosis. Acta Orthop Scand 39(3):291–302
Acknowledgments
None.
Conflict of interest
All authors have contributed equally to this study and have no conflict of interest. All authors declare that they have no commercial interest which may pose a conflict of interest to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Easwar, T.R., Hong, JY., Yang, J.H. et al. Does lateral vertebral translation correspond to Cobb angle and relate in the same way to axial vertebral rotation and rib hump index? A radiographic analysis on idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 20, 1095–1105 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-1702-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-1702-0