Abstract
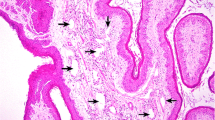
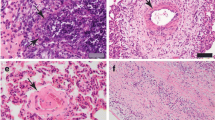
Eosinophil efferocytosis, a process of engulfment and removal of apoptotic eosinophils by professional phagocytes, has been described in several chronic inflammatory disorders (such as asthma) in human medicine. Eosinophil efferocytosis was recognized in naturally occurring chronic inflammatory disorders affecting lymphatic vessels of the bovine rumen. Twelve adult Holstein–Friesian dairy cows that were conventionally slaughtered exhibited regional emphysematous thickening of the ruminal submucosa. Histopathology revealed multiple emphysematous eosinophilic lymphangitis, characterized by cystic dilations of submucosal lymphatics in association with fibrous proliferation, neovascularization, and infiltration by large numbers of eosinophils, macrophages, multinucleated giant cells, and smaller numbers of mast cells. Neither parasites nor other pathogenic organisms were identified in the inflammatory lesions. The composition of gaseous constituents within dilated lymphatics was not known. Based on the histopathological findings, an allergic pathogenesis was considered to be possibly implicated in this disorder. In the inflamed lesions of seven cows, macrophages, and giant cells frequently phagocytized and disposed of large numbers of apoptotic eosinophils, demonstrating high efferocytic activity on promoting the resolution of this lymphangitis. From perspectives of cellular kinetics, eosinophil efferocystois by these professional phagocytes indicated a regularized pattern of progress steps toward the degradation of apoptotic eosinophils as follows: first, nuclei of apoptotic eosinophils were displaced and disintegrated, then, cytoplasmic granules were agglomerated and dissolved, and finally, cell bodies totally disappeared from cytoplasmic vacuoles (efferosomes) of phagocytes. It is revealed that older eosinophils undergoing constitutive, spontaneous apoptosis in inflammatory lesions were cleared via the lymphatic system in cattle.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolmaleki F, Farahani N, Hayat SMG et al (2018) The role of efferocytosis in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 9:1645
Bagaitkar J, Huang J, Zeng MY et al (2018) NADPH oxidase activation regulates apoptotic neutrophil clearance by murine macrophages. Blood 131:2367–2378
Baker IK, van Dreumel AA, Palmer N (1993) Infectious and parasitic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In: Jubb KVF, Kennedy PC, Palmer N (eds) Pathology of domestic animals, vol 2, 4th edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 141–318
Barnig C, Frossard N, Levy BD (2018) Towards targeting resolution pathways of airway inflammation in asthma. Pharmacol Therap 186:98–113
Boada-Romero E, Martinez J, Heckmann BL et al (2020) Mechanisms and physiology of the clearance of dead cells by efferocytosis. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:398–414
Canton J (2018) Macropinocytosis: new insights into its underappreciated role in innate immune cell surveillance. Front Immunol 9:2286
Colucci-Guyon E, Tinevez JY, Renshaw SA et al (2011) Strategies of professional phagocytes in vivo: unlike macrophages, neutrophils engulf only surface-associated microbes. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 18):3053–3059
Condon ND, Heddleston JM, Chew TL et al (2018) Macropinosome formation by tent pole ruffling in macrophages. J Cell Biol 217:3873–3885
Diab SS, Rodriguez-Bertos A, Uzal FA (2013) Pathology and diagnostic criteria of Clostridium difficile enteric infection in horses. Vet Pathol 50:1028–1036
Doran AC, Yurdagul A Jr, Tabas I (2020) Efferocytosis in health and disease. Nature Rev Immunol 20:254–267
Elishmereni M, Alenius HT, Bradding P et al (2011) Physical interactions between mast cells and eosinophils: a novel mechanism enhancing eosinophil survival in vitro. Allergy 66:376–385
Elliott MR, Koster KM, Murphy PS (2017) Efferocytosis signaling in the regulation of macrophage inflammatory responses. J Immunol 198:1387–1394
Felton JM, Lucas CD, Dorward DA et al (2018) Mer-mediated eosinophil efferocytosis regulates resolution of allergic airway inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 142:1884–1893
Felton JM, Lucas CD, Rossi AG et al (2014) Eosinophils in the lung – modulating apoptosis and efferocytosis in airway inflammation. Front Immunol 5:302
Gachanja NN, Dorward DA, Rossi AG et al (2021) Assays of eosinophil apoptosis and phagocytic uptake. Methods Mol Biol 2241:113–132
Gangwar RS, Friedman S, Seaf M et al (2016) Mast cells and eosinophils in allergy: close friends or just neighbors. Eur J Pharmacol 778:78–83
Greenlee-Wacker M (2016) Clearance of apoptotic neutrophils and resolution of inflammation. Immunol Rev 273:357–370
Hanna P, Kassir R, Tarek D et al (2016) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis presenting as bowel perforation, a rare case. Int J Surg Case Rep 20:7–9
Haslett C (1999) Granulocyte apoptosis and its role in the resolution and control of lung inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169:S5–S11
Haslett C, Savill JS, Whyte MK et al (1994) Granulocyte apoptosis and the control of inflammation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 345(1313):327–333
Hayat SMG, Bianconi V, Pirro M et al (2019) Efferocytosis: molecular mechanisms and pathophysiological perspective. Immunol & Cell Biol 97:124–133
Ilmarinen P, Kankaanranta H (2014) Eosinophil apoptosis as a therapeutic target in allergic asthma. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 114:109–117
Ilmarinen P, Moilanen E, Kankaanranta H (2014) Regulation of spontaneous eosinophil apoptosis—a neglected area of importance. J Cell Death 7:1–9
Kancherla D, Vattikuti S, Vipperla, (2015) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: is surgery always indicated? Cleve Clin J Med 82:151–152
Karl-Heinz K (2000) Professional phagocytes: predators and prey of microorganisms. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 130:97–100
Kinjo M (2016) Lurking in the wall: pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis with scleroderma. Am J Med 129:382–383
Korns D, Frash SC, Fernandez-Boyanapolli R, Henson PM, Bratton D (2011) Modulation of macrophage efferocytosis in inflammation. Front Immunol 2:57
Kourtzelis I, Hajishengallis G, Chavakis T (2020) Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells in resolution of inflammation. Front Immunol 11:553
Krystel-Whittemore M, Dileepan KN, Wood JG (2015) Mast cell: a multi-functional master cell. Front Immunol 6:620
Lam AL, Heit B (2021) Having an old friend for dinner: the interplay between apoptotic cells and efferocytes. Cells 10:1265
Leitch A, Duffin R, Haslett C et al (2008) Relevance of granulocyte apoptosis to resolution of inflammation at the respiratory mucosa. Mucosal Immunol 1:350–363
Linton MF, Babaev VR, Huang J et al (2016) Macrophage apoptosis and efferocytosis in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ J 80:2259–3226
Martin CJ, Peters KN, Behar SM (2014) Macrophages clean up: efferocytosis and microbial control. Curr Opin Microbiol 0: 17–23
McCubbrey AL, Curtis JL (2013) Efferocytosis and lung disease. Chest 146:1750–1757
Metcalfe DD, Pawankar R, Ackerman SJ et al (2016) Biomarkers of the involvement of mast cells, basophils and eosinophils in asthma and allergic diseases. World Allergy Organ 9:7
Minai-Fleminger Y, Levi-Schaffer F (2009) Mast cells and eosinophils: the two key effector cells in allergic inflammation. Inflamm Res 58:631–638
Monks J, Smith-Steinhart C, Kruk ER et al (2008) Epithelial cells remove apoptotic epithelial cells during post-lactation involution of the mouse mammary gland. Biol Rep 78:586–594
Ohfuji S (2015) Emphysematous eosinophilic lymphangitis in the ruminal submucosa of cattle. Vet Pathol 52:1163–1166
Ohfuji S (2016) Pathology of emphysematous reticulitis in cattle: report of two cases and comparative overview of similar or identical conditions. Comp Clin Pathol 25:805–813
Ohfuji S (2017) Emphysematous lymphangitis in the colon of a steer. Comp Clin Pathol 26:1105–1109
Olave C, Morales N, Uberti B et al (2018) Tamoxifen induces apoptotic neutrophil efferocytosis in horses. Vet Res Comm 42:57–63
Pietrangelo A, Oumet M (2019) Death eaters rely on metabolic signaling to wield anti-inflammatory responses. Cell Metab 29:234–236
Proto JD, Doran AC, Gusarova G et al (2018) Regulatory T cells promote macrophage efferocytosis during inflammation resolution. Immunity 49:666–677
Rabinovitch M (1995) Professional and non-professional phagocytes: an introduction. Trends Cell Biol 5:85–87
Racoosin EL, Swanson JA (1993) Macropinosome maturation and fusion with tubular lysosomes in macrophages. J Cell Biol 121:1011–1020
Ramsey DB, Stephen S, Borum M et al (2010) Mast cells in gastrointestinal disease. Gastroenterol & Hepatol (NY) 6:772–777
Robb CT, Regan KH, Dorward DA et al (2016) Key mechanisms governing resolution of lung inflammation. Semin Immunopathol 38:425–448
Rocha JF, Daoualibi Y, De Lorenzo Ć et al (2018) Emphysematous and granulomatous submucosal rumenitis in a feedlot Nellore steer. Acta Scie Vet 46(Suppl 1):266
Savill J (1997) Apoptosis in resolution of inflammation. J Leuk Biol 61:375–380
Scott RS, McMahon EJ, Pop SM et al (2001) Phagocytosis and clearance of apoptotic cells is mediated by MER. Nature 411:207–211
Šoštarić B, Mihaljević Ž, Kompes G et al (2010) Intestinal emphysema in pigs-case studies. Vet Stan 41:79–84
Tajbackhsh A, Rezaee M, kovanen PT, et al (2018) Efferocytosis in atherosclerotic lesions: malfunctioning regulatory pathways and control mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 188:12–25
Thorp E, Tabas I (2009) Mechanisms and consequences of efferocytosis in advanced atherosclerosis. J Leuk Biol 86:1089–1095
Uzal FA, Plattner BL, Hostetter JM (2016) Alimentary system. In: Maxie MG (ed) Jubb, Kennedy, and Palmers’ pathology of domestic animals, vol 2, 6th edn. Elsevier, St. Louis, pp 1–257
Yin C, Argintaru D, Heit B (2019) Rab17 mediates intermixing of phagocytosed apoptotic cells with recycling endosomes. Small GTPases 10:218–226
Yurdagul Jr. A (2021) Metabolic consequences of efferocytosis and its impact on atherosclerosis. Immunometab 3: e210017
Yurdagul A Jr, Subramanian M, Wang X et al (2020) Macrophage metabolism of apoptotic cell-derived arginine promotes continual efferocytosis and resolution of injury. Cell Metab 31:518–533
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohfuji, S. Eosinophil efferocytosis during emphysematous eosinophilic lymphangitis in the bovine rumen: histopathological evaluation with special focus on cellular kinetics of professional phagocytes. Comp Clin Pathol 31, 73–80 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03307-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03307-z