Abstract
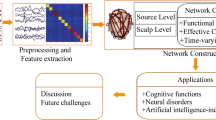
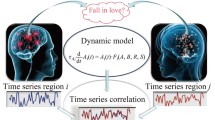
In this paper, electroencephalography data are used to establish a functional network connecting correlated human brain regions. Through analysis, it is found that the resulting network shows statistical characteristics of a complex network: its clustering coefficient is orders of magnitude larger than that of the equivalent random network, which is typical of a small-world network, and the distribution of degree is close to that of a scale-free network. All these characteristics reflect important functional information about brain states. For alcohol addicts, the characteristic indices of their brains are obviously different from those of the control group. The information entropy and standard information entropy of the brain neural network are also defined to measure the characteristics of the complex network. This gives a new criterion for clinical diagnosis and treatment of encephalopathy. Calculation results indicate that the brain neural network information entropy of alcohol addicts is quite distinct from that of the control group.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balenzuela P, Rué P, Boccaletti S (2014) Collective stochastic coherence and synchronizability in weighted scale-free networks. New J Phys 16:331–344
Diykh M, Li Y (2016) Complex networks approach for EEG signal sleep stages classification. Expert Syst Appl 63:241–248
Dodel S, Herrmann JM (2002) Functional connectivity by cross-correlation clustering. Neurocomputing 44:1065–1070
Eguiluz VM, Cecchi G, Chialvo DR (2003) Scale-free structure of brain functional networks. Phys Rev Lett 94:273–278
Friston KJ (2005) Models of brain function in neuroimaging. Annu Rev Psychol 56:57–87
Friston K, Phillips J, Chawla D (1999) Revealing interactions among brain systems with nonlinear PCA. Hum Brain Mapp 8:92–105
Horwitz B (2003) The elusive concept of brain connectivity. Neuroimage 19:466–470
Ingber L (2012) Columnar electromagnetic influences on short-term memory at multiple scales. Soc Sci Electr Publ 343:138–153
Ingber L (2016) Statistical mechanics of neocortical interactions: large-scale EEG influences on molecular processes. J Theor Biol 395:144–152
Ingber L, Nunez PL (1990) Multiple scales of statistical physics of the neocortex: application to electroencephalography. Math Comput Model 13:83–95
Mcintosh AR, Bookstein FL, Haxby JV (1996) Spatial pattern analysis of functional brain images using partial least squares. Neuroimage 3:143–157
Penny WD, Stephan KE, Mechelli A (2004) Modelling functional integration: a comparison of structural equation and dynamic causal models. Neuroimage 23:264–274
Power J, Cohen A, Nelson S (2011) Functional network organization of the human brain. Neuron 72:665–678
Shamshiri EA, Tierney TM, Centeno M (2017) Interictal activity is an important contributor to abnormal intrinsic network connectivity in paediatric focal epilepsy. Hum Brain Mapp 38:221–236
Sun G, Bin S (2018) A new opinion leaders detecting algorithm in multi-relationship online social networks. Multimed Tools Appl 77:4295–4307
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Humanity and Social Science Youth foundation of Ministry of Education of China under Grant no. 15YJC860001. This research is also supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China under Grant no. ZR2017MG011 and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project under Grant nos. 2016T90606 and 2018T110663.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bin, S., Sun, G. & Chen, CC. Analysis of functional brain network based on electroencephalography and complex network. Microsyst Technol 27, 1525–1533 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04424-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04424-0