Abstract
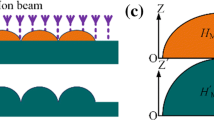
A cost-effective fabrication method for high quality and high fill-factor aspheric microlens arrays (MLAs) is developed. In this method, the complex shape of aspheric microlens is pre-modeled via dose modulation in a digital micromirror device (DMD) based maskless projection lithography system. Digital masks for several bottom layers are replaced from circle to hexagon for the purpose of enhancing the fill-factor of MLAs, then a low temperature thermal reflow process is conducted, after which the average surface roughness of microlens is improved to ~ 0.427 nm while the pre-modeled profile keeps unchanged. Experimental results show that the fabricated aspheric MLAs have almost 100% fill-factor, high shape accuracy and high surface quality. The presented method may provide a promising approach for rapidly fabricating high quality and high fill-factor aspheric microlens in a simple and low-cost way.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y et al (2015) Reducing optical losses in organic solar cells using microlens arrays: theoretical and experimental investigation of microlens dimensions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(5):3723–3730
Chung CK, Hong YZ (2007) Fabrication and analysis of the reflowed microlens arrays using JSR THB-130 N photoresist with different heat treatments. Microsyst Technol 13(5–6):523–530
Hahn DV et al (2010) Fiber optic bundle array wide field-of-view optical receiver for free space optical communications. Opt Lett 35(21):3559–3561
Huang S et al (2017) Improved slicing strategy for digital micromirror device-based three-dimensional lithography with a single scan. Micro Nano Lett 12(1):49–52
Huang S et al (2018) Fabrication of high quality aspheric microlens array by dose-modulated lithography and surface thermal reflow. Opt Laser Technol 100:298–303
Li L, Allen YY (2012) Design and fabrication of a freeform microlens array for a compact large-field-of-view compound-eye camera. Appl Opt 51(12):1843–1852
Lin CP, Yang H, Chao CK (2003) Hexagonal microlens array modeling and fabrication using a thermal reflow process. J Micromech Microeng 13(5):775
Park MK et al (2014) Design and fabrication of multi-focusing microlens array with different numerical apertures by using thermal reflow method. J Opt Soc Korea 18(1):71–77
Vekshin MM et al (2010) Glass microlens arrays for Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensors. Meas Sci Technol 21(5):3–143
Wu CY, Chiang TH, Hsu CC (2008) Fabrication of microlens array diffuser films with controllable haze distribution by combination of breath figures and replica molding methods. Opt Express 16(24):19978–19986
Wu D et al (2009) 100% fill-factor aspheric microlens arrays (AMLA) with sub-20-nm precision. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett 21(20):1535–1537
Yang H et al (2004) High fill-factor microlens array mold insert fabrication using a thermal reflow process. J Micromech Microeng 14(8):1197
Zhong K, Zhang H, Gao Y (2017) Fabrication of high fill-factor aspheric microlens array by digital maskless lithography. Optik-Int J Light Electron Opt 142:243–248
Zhu Z, To S, Zhang S (2015) Large-scale fabrication of micro-lens array by novel end-fly-cutting-servo diamond machining. Opt Express 23(16):20593–20604
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51475442), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and partially carried out at the University of Science and Technology of China Center for Micro and Nanoscale Research and Fabrication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Li, M., Qiu, J. et al. Fabrication of high fill-factor aspheric microlens array by dose-modulated lithography and low temperature thermal reflow. Microsyst Technol 25, 1235–1241 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4226-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4226-2