Abstract
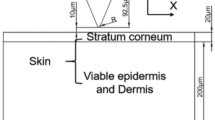
The microelectromechanical systems process including cutting, isotropic wet-etching and sputtering was used to fabricate a pyramid micro-needle electrode, which could be applied in long-term electroencephalogram (EEG) measurement. A penetrating testing and comfort survey was presented to optimize the parameters of applying force and penetrating depth in order to make user comfort, safe and free of pain and bleeding. To investigate the performance of the micro-needle electrode, three micro-needle electrodes with different arrays were deployed to perform skin–electrode contact impedance experiments. Moreover, the impedances in time domain were measured to verify the feasibility of long time measurement. At last, EEG signals were recorded directly by three pairs of standard wet/micro-needle electrodes and the power spectrum density (PSD) was presented between standard wet electrode and micro-needle electrode to estimate signal quality. Based on the results of EEG signals and the PSD, the micro-needle electrode can be as a biopotential electrode for recording EEG with low skin–electrode contact impedance.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang CL, Chang CW, Hsu CM, Luo CH, Chiou JC (2009) Power-efficient wireless sensor for physiological signal acquisition. JMicro/NanolithMEMS MOEMS 8:021120
Chi YM, Cauwenberghs G (2010) Wireless non-contact EEG/ECG electrodes for body sensor networks. In: IEEE international conferences. (BSN), 2010, pp 297–301
Chi YM, Jung TP, Cauwenberghs G (2010) Dry-contact and noncontact biopotential electrodes: methodological review. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 3:106–119
Dias N, Carmo J, Da Silva AF, Mendes P, Correia J (2010) New dry electrodes based on iridium oxide (IrO) for non-invasive biopotential recordings and stimulation. Sens Actuators A 164(1):28–34
Gargiulo G, Calvo RA, Bifulco P, Cesarelli M, Jin C, Mohamed A, Van Schaik A (2010) A new EEG recording system for passive dry electrodes. Clin Neurophysiol 121(5):686–693
Grozea C, Voinescu CD, Fazli S (2011) Bristle-sensors low-cost flexible passive dry EEG electrodes for neurofeedback and BCI applications. J Neural Eng 8:025008
Jones KE, Campbell PK, Normann RA (1992) A glass/silicon composite intracortical electrode array. Ann Biomed Eng 20(4):423–437
Lee SM, Sim KS, Kim KK, Lim YG, Park KS (2010) Thin and flexible active electrodes with shield for capacitive electrocardiogram measurement. Med Biol Eng Comput 48(5):447–457
Lin CT, Ko LW, Chiou JC, Duann JR, Huang RS, Liang SF, Chiu TW, Jung TP (2008) Noninvasive neural prostheses using mobile and wireless EEG. Proc IEEE 96(7):1167–1183
Lin CT, Liao LD, Liu YH, Wang IJ, Lin BS, Chang JY (2011) Novel dry polymer foam electrodes for long-term EEG measurement. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(99):1200–1207
McAdams E (2011) Biomedical Electrodes For Biopotential Monitoring and Electrostimulation. In: Bio-medical CMOS ICs. Massachusetts, pp 31–124
Miller HA, Harrison DC (1974) Biomedical electrode technology: theory and practice. Academic Press, New York
Ng W, Seet H, Lee K, Ning N, Tai W, Sutedja M, Fuh J, Li X (2009) Micro-spike EEG electrode and the vacuum-casting technology for mass production. J Mater Process Technol 209(9):4434–4438
Searle A, Kirkup L (2000) A direct comparison of wet, dry and insulating bioelectric recording electrodes. Physiol Meas 21:271
Spence AP, Lenn RC (1982) Basic human anatomy. Benjamin-Cummings Publishing Company, USA
Spinelli E, Haberman M (2010) Insulating electrodes: a review on biopotential front ends for dielectric skin-electrode interfaces. Physiol Meas 31:S183–S189
Yu L, Tay F, Guo D, Xu L, Yap K (2009) A microfabricated electrode with hollow microneedles for ECG measurement. Sens Actuators A 151(1):17–22
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51035005, 61176104), the Science and Technology Department of Shanghai (No. 11JC1405700, 11DZ2290203), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (2009) and Shanghai Jiao Tong University Innovation Fund for Postgraduates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LF., Liu, JQ., Yan, XX. et al. A MEMS-based pyramid micro-needle electrode for long-term EEG measurement. Microsyst Technol 19, 269–276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1638-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1638-2