Abstract
Background
Several methods have been used to predict the optimal depth of central venous catheter (CVC) tip position when using the anatomical landmark technique. In the present study, we devised a simple formula to predict CVC depth using ultrasound images and chest X-ray (CXR) in patients undergoing ultrasound-guided subclavian venous catheterization.
Methods
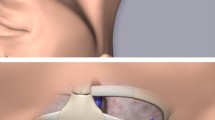
Central venous catheterization via the subclavian vein was performed under ultrasound guidance. We measured five parameters to determine the distance between the needle insertion point and the CVC tip: insertion point to vein puncture point (A), insertion point to a skin point indicating a vertical position above the vein puncture point (B), insertion point to the clavicular notch (C), clavicular notch to the carina (D), and catheter tip to carina (E). Catheter insertion depth was then determined as follows: calculated catheter insertion depth = A − B + C + D; actual catheter insertion depth = (A − B + C + D) + E.
Results
The calculated CVC insertion depth (mean ± SD) was 15.4 ± 1.5 cm from the needle insertion point to the carina [95 % confidence interval (CI) 15.0–15.9 cm]. Actual depth was 15.4 ± 1.5 cm (95 % CI 15.0–15.9 cm). No significant difference was observed between the calculated CVC insertion depth and the actual distance from the needle insertion point to the carina (p = 0.940).
Conclusions
The appropriate length of a CVC inserted through the subclavian vein can be estimated by a formula using ultrasound images and CXR.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDonough JJ, Altemeier WA. Subclavian venous thrombosis secondary to indwelling catheters. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1971;133:397–400.
Borja AR. Current status of infraclavicular subclavian vein catheterization. Ann Thorac Surg. 1972;13:615–24.
Johnson CL, Lazarchick J, Lynn HB. Subclavian venipuncture: preventable complications; report of two cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1970;45:712–9.
Collier PE, Blocker SH, Graff DM, Doyle P. Cardiac tamponade from central venous catheters. Am J Surg. 1998;176:212–4.
Collier PE, Goodman GB. Cardiac tamponade caused by central venous catheter perforation of the heart: a preventable complication. J Am Coll Surg. 1995;181:459–63.
Defalque RJ, Campbell C. Cardiac tamponade from central venous catheters. Anesthesiology. 1979;50:249–52.
Stonelake PA, Bodenham AR. The carina as a radiological landmark for central venous catheter tip position. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96:335–40.
Albrecht K, Nave H, Breitmeier D, Panning B, Troger HD. Applied anatomy of the superior vena cava-the carina as a landmark to guide central venous catheter placement. Br J Anaesth. 2004;92:75–7.
Chalkiadis GA, Goucke CR. Depth of central venous catheter insertion in adults: an audit and assessment of a technique to improve tip position. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1998;26:61–6.
Peres PW. Positioning central venous catheters—a prospective survey. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1990;18:536–9.
Jeon Y, Ryu HG, Yoon SZ, Kim JH, Bahk JH. Transesophageal echocardiographic evaluation of ECG-guided central venous catheter placement. Can J Anaesth. 2006;53:978–83.
Ryu HG, Bahk JH, Kim JT, Lee JH. Bedside prediction of the central venous catheter insertion depth. Br J Anaesth. 2007;98:225–7.
Kim MC, Kim KS, Choi YK, Kim DS, Kwon MI, Sung JK, Moon JY, Kang JM. An estimation of right- and left-sided central venous catheter insertion depth using measurement of surface landmarks along the course of central veins. Anesth Analg. 2011;112:1371–4.
Fragou M, Gravvanis A, Dimitriou V, Papalois A, Kouraklis G, Karabinis A, Saranteas T, Poularas J, Papanikolaou J, Davlouros P, Labropoulos N, Karakitsos D. Real-time ultrasound-guided subclavian vein cannulation versus the landmark method in critical care patients: a prospective randomized study. Crit Care Med. 2011;39:1607–12.
Czepizak CA, O’Callaghan JM, Venus B. Evaluation of formulas for optimal positioning of central venous catheters. Chest. 1995;107:1662–4.
Uchida Y, Sakamoto M, Takahashi H, Matsuo Y, Funahashi H, Sasano H, Sobue K, Takeyama H. Optimal prediction of the central venous catheter insertion depth on a routine chest X-ray. Nutrition. 2011;27:557–60.
Bodenham AR. Ultrasound-guided subclavian vein catheterization: beyond just the jugular vein. Crit Care Med. 2011;39:1819–20.
Schuster M, Nave H, Piepenbrock S, Pabst R, Panning B. The carina as a landmark in central venous catheter placement. Br J Anaesth. 2000;85:192–4.
Caruso LJ, Gravenstein N, Layon AJ, Peters K, Gabrielli A. A better landmark for positioning a central venous catheter. J Clin Monit Comput. 2002;17:331–4.
Rutherford JS, Merry AF, Occleshaw CJ. Depth of central venous catheterization: an audit of practice in a cardiac surgical unit. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1994;22:267–71.
Conflict of interest
There are no competing interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, HJ., Kim, B.G., Na, HS. et al. Estimation of catheter insertion depth during ultrasound-guided subclavian venous catheterization. J Anesth 29, 724–727 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-015-2012-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-015-2012-1