Abstract
Background
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common causes of cancer deaths worldwide; however, reliable and non-invasive screening methods for GC are not established. Therefore, we conducted this study to develop a biomarker for GC detection, consisting of urinary microRNAs (miRNAs).
Methods
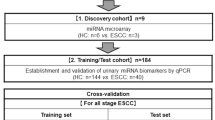
We matched 306 participants by age and sex [153 pairs consisting of patients with GC and healthy controls (HCs)], then randomly divided them across three groups: (1) the discovery cohort (4 pairs); (2) the training cohort (95 pairs); and (3) the validation cohort (54 pairs).
Results
There were 22 urinary miRNAs with significantly aberrant expressions between the two groups in the discovery cohort. Upon multivariate analysis of the training cohort, urinary expression levels of miR-6807-5p and miR-6856-5p were significantly independent biomarkers for diagnosis of GC, in addition to Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) status. A diagnostic panel that combined these 2 miRNAs and H. pylori status distinguished between HC and GC samples with an area under the curve (AUC) = 0.736. In the validation cohort, urinary miR-6807-5p and miR-6856-5p showed significantly higher expression levels in the GC group, and the combination biomarker panel of miR-6807-5p, miR-6856-5p, and H. pylori status also showed excellent performance (AUC = 0.885). In addition, this biomarker panel could distinguish between HC and stage I GC patients with an AUC = 0.748. Urinary expression levels of miR-6807-5p and miR-6856-5p significantly decreased to undetectable level after curative resection of GC.
Conclusions
This novel biomarker panel enables early and non-invasive detection of GC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fitzmaurice C, Akinyemiju TF, Al Lami FH, et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:1553–688.
Tashiro A, Sano M, Kinameri K, et al. Comparing mass screening techniques for gastric cancer in Japan. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:4873–4.
Jun JK, Choi KS, Lee HY, et al. Effectiveness of the Korean National cancer screening program in reducing gastric cancer mortality. Gastroenterology. 2017;152:1319–28 e7.
Feng F, Tian Y, Xu G, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19-9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2017;17:737.
Calin GA, Croce CM. Chromosomal rearrangements and microRNAs: a new cancer link with clinical implications. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:2059–66.
Xiao C, Rajewsky K. MicroRNA control in the immune system: basic principles. Cell. 2009;136:26–36.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66.
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:5003–8.
Liu R, Zhang C, Hu Z, et al. A five-microRNA signature identified from genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling serves as a fingerprint for gastric cancer diagnosis. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:784–91.
Liu H, Zhu L, Liu B, et al. Genome-wide microRNA profiles identify miR-378 as a serum biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012;316:196–203.
Li C, Li JF, Cai Q, et al. miRNA-199a-3p in plasma as a potential diagnostic biomarker for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(Suppl 3):S397–405.
Zeng Z, Wang J, Zhao L, et al. Potential role of microRNA-21 in the diagnosis of gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e73278.
Zhu C, Ren C, Han J, et al. A five-microRNA panel in plasma was identified as potential biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014;110:2291–9.
Shin VY, Ng EK, Chan VW, et al. A three-miRNA signature as promising non-invasive diagnostic marker for gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:202.
Zhou X, Zhu W, Li H, et al. Diagnostic value of a plasma microRNA signature in gastric cancer: a microRNA expression analysis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11251.
Qiu X, Zhang J, Shi W, et al. Circulating MicroRNA-26a in plasma and its potential diagnostic value in gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0151345.
Azarbarzin S, Feizi MAH, Safaralizadeh R, et al. The value of MiR-383, an intronic MiRNA, as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in intestinal-type gastric cancer. Biochem Genet. 2017;55:244–52.
Kao HW, Pan CY, Lai CH, et al. Urine miR-21-5p as a potential non-invasive biomarker for gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:56389–97.
Hung PS, Chen CY, Chen WT, et al. miR-376c promotes carcinogenesis and serves as a plasma marker for gastric carcinoma. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0177346.
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, et al. Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:9067–72.
Vandenbroucke JP, von Elm E, Altman DG, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration. Epidemiology. 2007;18:805–35.
Shimura T, Dagher A, Sachdev M, et al. Urinary ADAM12 and MMP-9/NGAL complex detect the presence of gastric cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2015;8:240–8.
Shimura T, Ebi M, Yamada T, et al. Urinary kallikrein 10 predicts the incurability of gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:29247–57.
Shimura T, Iwasaki H, Kitagawa M, et al. Urinary cysteine-rich protein 61 and trefoil factor 3 as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Transl Oncol. 2019;12:539–44.
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C. TNM classification of malignant tumours. 7th ed. Hoboken: Wiley; 2009.
Thery C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006; Chapter 3:Unit 3 22.
Mestdagh P, Van Vlierberghe P, De Weer A, et al. A novel and universal method for microRNA RT-qPCR data normalization. Genome Biol. 2009;10:R64.
Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, et al. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem. 2010;56:1733–41.
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–9.
Mall C, Rocke DM, Durbin-Johnson B, et al. Stability of miRNA in human urine supports its biomarker potential. Biomark Med. 2013;7:623–31.
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:784–9.
Miah S, Dudziec E, Drayton RM, et al. An evaluation of urinary microRNA reveals a high sensitivity for bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:123–8.
Mengual L, Lozano JJ, Ingelmo-Torres M, et al. Using microRNA profiling in urine samples to develop a non-invasive test for bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013;133:2631–41.
Cardenas-Gonzalez M, Srivastava A, Pavkovic M, et al. Identification, confirmation, and replication of novel urinary MicroRNA biomarkers in lupus nephritis and diabetic nephropathy. Clin Chem. 2017;63:1515–26.
Erbes T, Hirschfeld M, Rucker G, et al. Feasibility of urinary microRNA detection in breast cancer patients and its potential as an innovative non-invasive biomarker. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:193.
Debernardi S, Massat NJ, Radon TP, et al. Noninvasive urinary miRNA biomarkers for early detection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5:3455–66.
Acknowledgements
We thank Yukimi Hashidume-Itoh for handling of urine sample and Takako Onodera for data management of enrolled patients in this study (Department of Gastroenterology and Metabolism, Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences). We also thank Masahide Ebi at Aichi Medical University, Tomonori Yamada at Nagoya Daini Red Cross Hospital and other clinical colleagues who assisted for the sample collection. This study was supported, in part, by Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development under Grant Number JP19lm0203005j0003 (to T. S.) and the Takeda Science Foundation (to T. S.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwasaki, H., Shimura, T., Yamada, T. et al. A novel urinary microRNA biomarker panel for detecting gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol 54, 1061–1069 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01601-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01601-w
Keywords
Profiles
- Yusuke Okuda View author profile