Abstract
Background
Serum biomarkers currently available for gastric cancers are not sufficiently sensitive and specific.
Methods
We used matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MS) to generate comparative peptide profiles of serum samples obtained from gastric cancer patients (n = 81) and age- and sex-matched healthy controls (n = 66).
Results
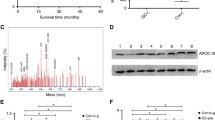
Because of initial screening and further validation, we found that the intensities of a 2209 m/z MS peak were increased in the preoperative sera obtained from gastric cancer patients, and we identified this peak, a 2209 Da peptide, as a high molecular weight (HMW) kininogen fragment. Receiver operating characteristic analyses showed that the area under the curve (AUC) for the 2209 Da peptide (AUC = 0.715) was greater than those for conventional tumor markers (carcinoembryonic antigen AUC = 0.593, carbohydrate antigen 19-9 AUC = 0.527) used for the detection of stage I gastric cancers. Inverse correlations were observed between the levels of intact HMW kininogen and the 2209 Da peptide, suggesting that the upregulation of some protease activities is responsible for the overproduction of a kininogen fragment in gastric cancer patients.
Conclusions
Serum levels of the 2209 Da peptide identified in this study have a greater diagnostic ability than those of conventional tumor markers used for the early detection of gastric cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodman KJ, Cockburn M. The role of epidemiology in understanding the health effects of Helicobacter pylori. Epidemiology. 2001;12:266–71.
Wobbes T, Thomas CM, Segers MF, Nagengast FM. Evaluation of seven tumor markers (CA 50, CA 19–9, CA 19–9 TruQuant, CA 72–4, CA 195, carcinoembryonic antigen, and tissue polypeptide antigen) in the pretreatment sera of patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1992;69:2036–41.
Fernandez-Fernandez L, Tejero E, Tieso A, Rabadan L, Munoz M, Santos I. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis of the tumor markers CEA, CA 19–9 and CA 72–4 in gastric cancer. Int Surg. 1996;81:400–2.
Kochi M, Fujii M, Kanamori N, Kaiga T, Kawakami T, Aizaki K, et al. Evaluation of serum CEA and CA19–9 levels as prognostic factors in patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2000;3:177–86.
Wulfkuhle JD, Liotta LA, Petricoin EF. Proteomic applications for the early detection of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:267–75.
Petricoin EF, Belluco C, Araujo RP, Liotta LA. The blood peptidome: a higher dimension of information content for cancer biomarker discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:961–7.
Hortin GL. The MALDI-TOF mass spectrometric view of the plasma proteome and peptidome. Clin Chem. 2006;52:1223–37.
Davies HA. The ProteinChip System from Ciphergen: a new technique for rapid, micro-scale protein biology. J Mol Med. 2000;78:B29.
Kanmura S, Uto H, Sato Y, Kumagai K, Sasaki F, Moriuchi A, et al. The complement component C3a fragment is a potential biomarker for hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:459–67.
Nomura F, Tomonaga T, Sogawa K, Ohashi T, Nezu M, Sunaga M, et al. Identification of novel and downregulated biomarkers for alcoholism by surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry. Proteomics. 2004;4:1187–94.
Takano S, Yoshitomi H, Togawa A, Sogawa K, Shida T, Kimura F, et al. Apolipoprotein C-1 maintains cell survival by preventing from apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene. 2008;27:2810–22.
Zhang X, Leung SM, Morris CR, Shigenaga MK. Evaluation of a novel, integrated approach using functionalized magnetic beads, bench-top MALDI-TOF-MS with prestructured sample supports, and pattern recognition software for profiling potential biomarkers in human plasma. J Biomol Tech. 2004;15:167–75.
Sogawa K, Satoh M, Kodera Y, Tomonaga T, Iyo M, Nomura F. A search for novel markers of alcohol abuse using magnetic beads and MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2009;3:821–8.
Kulasingam V, Diamandis EP. Strategies for discovering novel cancer biomarkers through utilization of emerging technologies. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008;5:588–99.
Umemura H, Nezu M, Kodera Y, Satoh M, Kimura A, Tomonaga T, et al. Effects of the time intervals between venipuncture and serum preparation for serum peptidome analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 2009;406:179–80.
Umemura H, Kodera Y, Nomura F. Effects of humidity on the dried-droplet sample preparation for MALDI-TOF MS peptide profiling. Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411:2109–11.
Ebert MP, Meuer J, Wiemer JC, Schulz HU, Reymond MA, Traugott U, et al. Identification of gastric cancer patients by serum protein profiling. J Proteome Res. 2004;3:1261–6.
Ebert MP, Lamer S, Meuer J, Malfertheiner P, Reymond M, Buschmann T, et al. Identification of the thrombin light chain a as the single best mass for differentiation of gastric cancer patients from individuals with dyspepsia by proteome analysis. J Proteome Res. 2005;4:586–90.
Ebert MP, Niemeyer D, Deininger SO, Wex T, Knippig C, Hoffmann J, et al. Identification and confirmation of increased fibrinopeptide a serum protein levels in gastric cancer sera by magnet bead assisted MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 2006;5:2152–8.
Su Y, Shen J, Qian H, Ma H, Ji J, Ma H, et al. Diagnosis of gastric cancer using decision tree classification of mass spectral data. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:37–43.
Inoue M, Tsugane S. Epidemiology of gastric cancer in Japan. Postgrad Med J. 2005;81:419–24.
Hatakeyama M. Helicobacter pylori and gastric carcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:239–48.
Ohata H, Kitauchi S, Yoshimura N, Mugitani K, Iwane M, Nakamura H, et al. Progression of chronic atrophic gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori infection increases risk of gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2004;109:138–43.
Mukoubayashi C, Yanaoka K, Ohata H, Arii K, Tamai H, Oka M, et al. Serum pepsinogen and gastric cancer screening. Intern Med. 2007;46:261–6.
Villanueva J, Shaffer DR, Philip J, Chaparro CA, Erdjument-Bromage H, Olshen AB, et al. Differential exoprotease activities confer tumor-specific serum peptidome patterns. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:271–84.
Schaub NP, Jones KJ, Nyalwidhe JO, Cazares LH, Karbassi ID, Semmes OJ, et al. Serum proteomic biomarker discovery reflective of stage and obesity in breast cancer patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2009;208:970–8.
Roeise O, Sivertsen S, Ruud TE, Bouma BN, Stadaas JO, Aasen AO. Studies on components of the contact phase system in patients with advanced gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer. 1990;65:1355–9.
Colman RW, Jameson BA, Lin Y, Johnson D, Mousa SA. Domain 5 of high molecular weight kininogen (kininostatin) down-regulates endothelial cell proliferation and migration and inhibits angiogenesis. Blood. 2000;95:543–50.
Zhang JC, Donate F, Qi X, Ziats NP, Juarez JC, Mazar AP, et al. The antiangiogenic activity of cleaved high molecular weight kininogen is mediated through binding to endothelial cell tropomyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:12224–9.
Asakura S, Hurley RW, Skorstengaard K, Ohkubo I, Mosher DF. Inhibition of cell adhesion by high molecular weight kininogen. J Cell Biol. 1992;116:465–76.
Kawasaki M, Maeda T, Hanasawa K, Ohkubo I, Tani T. Effect of His-Gly-Lys motif derived from domain 5 of high molecular weight kininogen on suppression of cancer metastasis both in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:49301–7.
Liu Y, Pixley R, Fusaro M, Godoy G, Kim E, Bromberg ME, et al. Cleaved high-molecular-weight kininogen and its domain 5 inhibit migration and invasion of human prostate cancer cells through the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Oncogene. 2009;28:2756–65.
Fortin T, Salvador A, Charrier JP, Lenz C, Bettsworth F, Lacoux X, et al. Multiple reaction monitoring cubed for protein quantification at the low nanogram/milliliter level in nondepleted human serum. Anal Chem. 2009;81:9343–52.
Baechle D, Sparbier K, Dihazi H, Blaschke S, Mueller GA, et al. Towards stable diagnostic setups in clinical proteomics: absolute quantitation of peptide biomarkers using MALDI-TOF-MS. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2007;1:1280–4.
Acknowledgments
We thank Masumi Ishibashi and Satomi Tojo Nishimura for their technical assistance. We also thank members of the clinical laboratory staff of Kimitsu Chuo Hospital and PortSquare Kashiwado Clinic for collecting serum samples. This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (Nos. 19390154 and 20790411).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umemura, H., Togawa, A., Sogawa, K. et al. Identification of a high molecular weight kininogen fragment as a marker for early gastric cancer by serum proteome analysis. J Gastroenterol 46, 577–585 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0369-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0369-3