Abstract
Background
Endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) is a standard procedure for the removal of bile duct stones. However, additional EST may increase the risk of bleeding and perforation in patients with prior EST. Endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation (EPLBD) can be an alternative method for removing recurrent common bile duct stones with lower risk of bleeding and perforation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic outcomes and complications of EPLBD in patients with recurrent common duct stones who underwent EST previously.
Methods
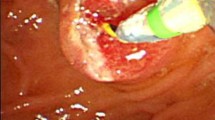
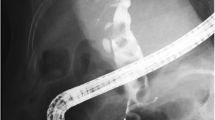
Between January 2006 and August 2009, 70 patients with recurrent bile duct stones who had a history of EST were studied retrospectively. All patients underwent EPLBD without additional EST to enlarge the ampullary orifice. The size of the balloon for EPLBD was 12–18 mm and the duration of the balloon dilatation was 30–60 s.
Results
Of the 70 patients, there were 24 patients (34.3%) with periampullary diverticula, 18 patients (25.7%) with hypertension, 4 patients (5.7%) with ischemic heart diseases, 2 patients (2.9%) with liver cirrhosis, and 1 patient (1.4%) with chronic kidney disease. Mean diameter of the stones was 12.5 ± 5.5 mm. Complete clearance of the duct was achieved in all patients and mechanical lithotripsy was needed in 1 patient (1.4%). Sixty-eight cases (97.1%) required only 1 session of ERCP to achieve complete ductal clearance. Mild pancreatitis occurred in 1 patient (2.3%), but there was no bleeding or perforation.
Conclusion
EPLBD is an effective and safe method for the treatment of recurrent common duct stones in patients with prior EST.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Classen ML, Demling L. Endoscopic sphincterotomy of the papilla of the vater and extraction of stones from the choledochal duct. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1974;99:496–7.
Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J, Geenen JE, Russel RC, Meyers WC, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: an attempt at consensus. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991;37:383–93.
Ikeda S, Tnanka M, Matsumoto S, Yoshimoto H, Itoh H. Endoscopic sphincterotomy: long-term results in 408 patients with complete follow–up. Endoscopy. 1988;20:13–7.
Bergmann JJ, van der Mey S, Rauws EA, Tijssen JG, Gouma DJ, Tytpat GN, et al. Long-term follow-up after endoscopic sphincteritomy for bile duct stones in patients younger than 60 years of age. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996;44:643–9.
Prat F, Malak NA, Pelletiet G, Buffet C, Fritsch J, Choury AD, et al. Biliary symptoms and complications more than 8 years after endoscopic sphincterotomy for choledocholithiasis. Gastroenterology. 1996;110:894–9.
Tanaka M, Takahata S, Konomi H, Matsunaga H, Yokohata K, Takeda T, et al. Long-term consequence of endoscopic sphincterotomy for bile duct stones. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998;48:465–9.
Leung JWC, Chan FKL, Sung JJY, Chung SCS. Endoscopic sphincterotomy-induced hemorrhage: a study of risk factors and the role of epinephrine injection. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995;42:550–4.
Geenen J, Vennes JA, Silvis SE. Resume of a seminar on endoscopic retrograde sphincterotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1981;27:31–8.
Staritz M, Ewe K, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH. Endoscopic papillary dilatation (EPD) for the treatment of common bile duct stones and papillary stenosis. Endoscopy. 1983;15:197–8.
Sato H, Kodama T, Takaaki J, Tatsumi Y, Maeda T, Fujita S, et al. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation may preserve sphincter of Oddi function after common bile duct stone management: evaluation from the viewpoint of endoscopic manometry. Gut. 1997;41:541–4.
Komatsu Y, Kawabe T, Toda N, Ohashi M, Isayama M, Tateishi K, et al. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation for the management of common bile duct stones: experience of 226 cases. Endoscopy. 1998;30:12–7.
Ersoz G, Tekesin O, Ozutemiz AO, Gunsar F. Biliary sphincterotomy plus dilatation with a large balloon for bile duct stones that are difficult to extract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57:156–9.
Meydeo A, Bhandari S. Balloon sphincteropalsty for removing difficult bile duct stones. Endoscopy. 2007;39:958–61.
Minami A, Hirose S, Nomoto T, Hayakawa S. Small sphincterotomy combined with papillary dilation with large balloon permits retrieval of large stones without mechanical lithotripsy. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:2179–82.
Kim GH, Kang DH, Song GA, Heo J, Park CH, Ha TI, et al. Endoscopic removal of bile-duct stones by using a rotatable papillotome and a large-balloon dilator. Gastrointest Endosoc. 2008;67:1134–8.
Espinel J, Pinedo E, Olcoz JL. Large hydrostatic balloon for choledocholithiasis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2007;99:33–8.
Freeman ML, Nelson DB, Sherman S, Haber GB, Herman ME, Darsher PJ, et al. Complications of endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:909–18.
Minami A, Nakatsu T, Uchida N, et al. Papillary dilatation vs sphincterotomy in endoscopic removal of bile duct stonesa randomized trial with manometric function. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:2550–4.
Disario JA, Freeman ML, Bjorkman DJ. Endoscopic balloon dilatation comparedwith sphincterotomy for extraction of bile duct stones. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1291–9.
Rösch W, Rienmann JF, Lux G, Linder HG. Long-term follow-up after endoscopic sphincterotomy. Endoscopy. 1981;13:152–3.
Riemann JF, Lux G, Förster P, Altendorf A. Long-term results after endoscopic papillotomy. Endoscopy. 1983;15:165–8.
Escourrou J, Cordova JA, Lazorthes F, Frexinos J, Ribet A. Early and late complications after endoscopic sphincterotomy for biliary lithiasis with and without the gall bladder “in situ”. Gut. 1984;25:598–602.
Jacobsen O, Matzen P. Long-term follow-up study of patients after endoscopic sphincterotomy for choledocholithiasis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987;22:903–6.
Seifert E. Long-term follow-up after endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST). Endoscopy. 1988;20:232–5.
Ingoldby CJ, El-Saadi J, Hall RI, Denyer ME. Late results of endoscopic sphincterotomy for bile duct stones in elderly patients with gall bladders in situ. Gut. 1989;30:1129–31.
Hawes RH, Cotton PB, Vallon AG. Follow-up 6 to 11 years after duodenoscopic sphincterotomy for stones in patients with prior cholecystectomy. Gastroenterology. 1990;98:1008–12.
Pereira-Lima JC, Jakobs R, Winter UH, Benz C, Martin WR, Admek HE, et al. Long-term results (7 to 10 years) of endoscopic papillotomy for choledocholithiasis. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors for the recurrence of biliary symptoms. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998;48:457–64.
Kim DI, Kim MH, Lee SK, Seo DW, Choi WB, Park HJ, et al. Risk factors for recurrence of primary bile duct stones after endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;54:42–8.
Gregg JA, De Girolami P, Carr-Locke DL. Effects of sphincteroplasty and endoscopic sphincterotomy on the bacteriologic characteristics of the common bile duct. Am J Surg. 1985;149:668–71.
Sugiyama M, Atomi Y. Risk factors predictive of late complications after endoscopic sphincterotomy for bile duct stones: long-term (more than 10 years) follow-up study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:2763–7.
Mavrogiannis C, Liatsos C, Papanikolaou IS, Psilopoulous DI, Goulas SS, Romanos A, et al. Safety of extension of a previous endoscopic sphincterotomy: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:72–6.
Mathuna PM, White P, Clarke E, Merriman R, Lenon JR, Growe J. Endoscopic balloon sphincteriplasty (papillary dilatation) for bile duct stones: efficact, sagety, and follow-up in 100 patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995;42:468–74.
Bergman JJ, Rauws EA, Fockens P, van Berkel AM, Bossuyt PM, Tijssen JG, et al. Randomized trials of endoscopic balloon dislatation versus endoscopic sphincterotomy for removal of bileduct stones. Lancet. 1997;349:1124–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K.O., Kim, T.N. & Lee, S.H. Endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation for the treatment of recurrent bile duct stones in patients with prior sphincterotomy. J Gastroenterol 45, 1283–1288 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0284-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0284-7