Abstract
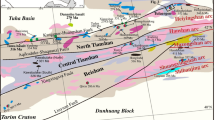
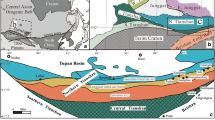
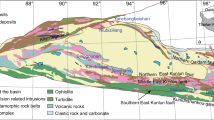
The large to middle-sized magmatic Ni–Cu sulfide deposits are spatially situated in the eastern portion of Eastern Tianshan, whereas those in the western portion have been poorly understood due to their quantity and scale. The Haibaotan Ni–Cu sulfide occurrence is newly discovered in the western portion of Eastern Tianshan, which provides an opportunity for understanding how its magmatic conduit system was generated and evolved. The Haibaotan mafic–ultramafic intrusion is dominated by peridotite, pyroxenite, olivine gabbro, and gabbro, and sulfide orebodies occur mainly within gabbro. Gabbro from the Haibaotan intrusion is dated at 315.5 ± 1.9 Ma, which suggests that the Haibaotan intrusion is generated in a subduction evironment. The age is much earlier than the emplacement of other mineralized mafic–ultramafic intrusions (~ 280 Ma) in Eastern Tianshan. High zircon εHf(t) values (+ 7.09 to + 18.44) indicate that the parental magmas of the Haibaotan intrusion have been derived from a metasomatized mantle source. Additionally, mafic–ultramafic rocks in the Haibaotan intrusion exhibit enrichment of large ion lithophile elements (LILE) and light rare earth elements (LREE), together with a depletion of Zr, Ti, and Nb, which is indicative of a subduction-modified mantle source. Core–rim variations of olivine forsterite (Fo) and Ni contents imply that the Haibaotan intrusion resulted from successive magma pulses, and the variable PGE tenors reflect that the sulfide droplets scavenged metals from multiple magma pulses. The low Se/S ratios of sulfide mineralization suggest that the addition of crustal sulfur triggered sulfide segregation in the shallow magma conduit system. The evolution history of the Haibaotan magma conduit system meets the requirements for generating a magmatic Ni–Cu deposit. This study highlights that the subduction environments are favorable for the formation of magmatic sulfide deposits in Eastern Tianshan.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen T (2002) Correction of common lead in U–Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem Geol 192(1):59–79
Arndt NT, Lesher CM (1992) Fractionation of REE’s by olivine and the origin of Kambalda komatiites, Western Australia. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:4191–4204
Arndt N, Chauvel C, Fedorenko V, Czamanske G (1998) Two mantle sources, two plumbing systems: tholeiitic and alkaline magmatism of the Maymecha River basin, Siberian flood volcanic province. Contrib Mineral Petrol 133:297–313
Arndt N, Lesher CM, Czamanske GK (2005) Mantle-derived magmas and magmatic Ni–Cu-(PGE) deposits. Econ Geol 100:5–24
Asif M, Parry SJ (1991) Study of the digestion of chromite during nickel sulphide fire assay for the platinum group elements and gold. Analyst 116:1071–1073
Barnes SJ (1986) The effect of trapped liquid crystallization on cumulus mineral compositionsin layered intrusions. Contrib Mineral Petrol 93:524–531
Barnes SJ, Lightfoot PC (2005) Formation of magmatic nickel sulphide ore deposits and processes affecting their copper and platinum group element contents. In: Hedenquist JW, Thompson JFH, Goldfarb RJ, Richards JP (Eds) Economic geology 100th anniversary, vol 190, pp 179–213
Barnes SJ, Maier WD (1999) The fractionation of Ni, Cu, and the noble metals in silicate and sulfide liquids. In: Keays RR, Lesher CM, Lightfoot PC, Farrow CEG (eds) Short course notes, vol 13. Geological Association of Canada, Canada, pp 69–106
Barnes SJ, Couture JF, Sawyer EW, Bouchaib C (1993) Nickel–copper occurrences in the Belleterre-Angliers belt of the Pontiac Subprovince and the use of Cu–Pd ratios in interpreting platinumgroup element distributions. Econ Geol 88:1402–1414
Barnes SJ, Osborne GA, Cook D, Barnes L, Maier WD, Godel B (2011) The Santa Rita nickel sulfide deposit in the Fazenda Mirabela intrusion, Bahia, Brazil: geology, sulfide geochemistry, and genesis. Econ Geol 106:1083–1110
Barnes SJ, Godel B, Gürer D, Brenan JM, Robertson J, Paterson D (2013) Sulfide-olivine Fe–Ni exchange and the origin of anomalously Ni rich magmatic sulfides. Econ Geol 108:1971–1982
BGMRXUAR (Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region) (1993) Regional geology of Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region (in Chinese)
Bulle F, Layne Gd (2016) Multi-element variations in olivine as geochemical signatures of Ni–Cu sulfide mineralization in mafic magma systems—examples from Voisey’s Bay and Pants Lake intrusions, Labrador, Canada. Miner Deposita 51:49–56
Campbell IH, Naldrett AJ (1979) The influence of silicate: sulfide ratios on the geochemistry of magmatic sulfides. Econ Geol 74:1503–1506
Deng YF, Song XY, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Chen LM, Zheng WQ (2012) Correlations between Fo number and Ni content of olivine of the Huangshandong Intrusion, eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang, and the genetic significances. Acta Petrol Sin 28:2224–2234 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng YF, Song XY, Chen LM, Zhou TF, Pirajno F, Yuan F, Xie W, Zhang DY (2014) Geochemistry of the Huangshandong Ni–Cu deposit in northwestern China: implications for the formation of magmatic sulfide mineralization in orogenic belts. Ore Geol Rev 56:181–198
Deng YF, Song XY, Hollings P, Chen LM, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Xie W, Zhang D, Zhao BB (2017) Lithological and geochemical constraints on the magma conduit systems of the Huangshan Ni–Cu sulfide deposit, NW China. Miner Deposita 52:845–862
Deng YF, Yuan F, Hollings P, Song XY, Zhou TF, Fu B, Denyszyn S, Zhao BB (2020) Magma generation and sulfide saturation of Permian mafic-ultramafic intrusions from the western part of the Northern Tianshan in NW China: implications for Ni–Cu mineralization. Miner Deposita 55:515–534
Djafer SA, Ouzegane K, Liegeois JP, Kienast JR (2003) An example of post-collisional mafic magmatism: the gabbro-anorthosite layered complex from the Tin Zebanearea (western Hoggar, Algeria). J Afr Earth Sc 37:313–330
Eckstrand OR, Grinenko LN, Krouse HR, Paktunc AD, Schwann PL, Scoates RFJ (1989) Preliminary data on sulphur isotopes and Se/S ratios, and the source of sulfur in magmatic sulphides from the Fox River sill, Molson dykes, and Thompson nickel deposits, northern Manitoba. Geol Surv Can Pap 89:235–242
Feng YQ, Qian ZZ, Duan J, Gang Xu, Ren M, Jiang C (2018) Geochronological and geochemical study of the Baixintan magmatic Ni–Cu sulphide deposit: new implications for the exploration potential in the western part of the East Tianshan nickel belt (NW China). Ore Geol Rev 95:366–381
Gao JF, Zhou MF (2013) Generation and evolution of siliceous high-magnesium basaltic magmas in the formation of the Permian Huangshandong intrusion (Xinjiang, NW China). Lithos 162:128–139
Gao JF, Zhou MF, Lightfoot PC, Wang CY, Qi L (2012) Origin of PGE-poor and Cu-rich magmatic sulfides from the Kalatongke deposit, Xinjiang, Northwest China. Econ Geol 107:481–506
Han CM, Xiao WJ, Zhao GC, Ao SJ, Zhang JE, Qu WJ, Du AD (2010) In-situ U–Pb, Hf and Re–Os isotopic analyses of the Xiangshan Ni–Cu–Co deposit in Eastern Tianshan (Xinjiang), Central Asia Orogenic Belt Constraints on the timing and genesis of the mineralization. Lithos 120:547–562
Han CM, Xiao WJ, Zhao GZ, Su BX, Sakyi PA, Ao SJ, Zhang JE, Zhang ZY (2013) SIMS U–Pb zircon dating and Re–Os isotopic analysis of the Hulu Cu–Ni deposit, eastern Tianshan, Central Asian Orogenic Belt, and its geological significance. J Geosci 58:251–270
Hawkesworth C, Turner S, Peate D, McDermott F, Calsteren P (1997) Elemental U and Th variations in island arc rocks: implications for U-series isotopes. Chem Geol 139:207–221
Herzberg C, O’Hara MJ (2002) Plume-associated ultramafic magmas of phanerozoic age. J Petrol 43:1857–1883
Hoskin PW, Schaltegger U (2003) The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev Mineral Geochem 53:27–62
Hou KJ, Li YH, Zou TR, Qu XM, Shi YR, Xie GQ (2007) Laser ablation-MCICP-MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications. Acta Petrol Sin 23:2595–2604 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hu AQ, Jahn B, Zhang GX, Chen YB, Zhang QF (2000) Crustal evolution and Phanerozoic crustal growth in northern Xinjiang: Nd isotopic evidence. Part I Isotopic characterizationof basement rocks. Tectonophysics 328:15–51
Huang ZB, Jin X (2006) Geochemistry features and tectonic setting of the Hongshishan ophiolite in Gansu Province. Chin J Geol 41:601–611 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jackson SE, Pearson NJ, Griffin WL (2004) The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U–Pb zircon geochronology. Chem Geol 211(1):47–69
Jahn BM, Wu FY, Chen B (2000) Massive granitoid generation in Central Asia: Nd isotope evidence and implication for continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Episodes 23:82–92
Jahn BM, Windley B, Natal’in B, Dobretsov N (2004) Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asia. J Asian Earth Sci 23:599–603
Jiao JG, Zheng PP, Liu RP, Duan J, Jiang C (2013) SHRIMP zircon U–Pb age of the No 3 intrusion in the Tularergen Cu–Ni mining area ‘East Tianshan Mountains’ Xinjiang and its geological significance. Geol Explor 49:0393–0404 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Johnson MC, Plank T (1999) Dehydration and melting experiments constrain the fate of subducted sediments. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 1:1–26
Jugo P, Luth R, Richards J (2005) Experimental data on the speciation of sulfur as a function of oxygen fugacity in basaltic melts. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69(2):497–503
Keays RR, Lightfoot PC (2010) Crustal sulfur is required to form magmatic Ni–Cu sulfide deposits: evidence from chalcophile element signatures of Siberian and Deccan Trap basalts. Miner Deposita 45:241–257
Kelemen PB, Hanghøj K, Greene AR (2004) One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust. Treatise Geochem 3:593–659
Kinny PD, Mass R (2003) Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon. In: Hanchar JM, Hoskin PWO (eds) Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry, vol 53 (1), pp 327–341
Krivolutskaya NA, Latyshev AV, Dolgal AS, Gongalsky BI, Makarieva EM, Makariev AA, Svirskaya NM, Bychkova YV, Yakushev AI, Asavin AM (2019) Unique PGE–Cu–Ni Noril’sk deposits, Siberian trap province: magmatic and tectonic factors in their origin. Minerals 9(1):66–111
Lambert DD, Frick LR, Foster JG, Li C, Naldrett AJ (2000) Re–Os isotopic systematics of the Voisey’s Bay Ni–Cu–Co magmatic sulfide system. Canada: II. Implications for parental magma chemistry, ore genesis, and metal redistribution. Econ Geol 95:867–888
Lesher CM, Burnham OM (2001) Multicomponent elemental and isotopic mixing in Ni–Cu–(PGE) ores at Kambalda, Western Australia. Can Mineral 39:421–446
Li CS, Ripley EM (2003) Compositional variations of olivine and sulfur isotopes in the Noril’sk and Talnakh intrusions, Siberia: implications for ore-forming processes in dynamic magma conduits. Econ Geol 98:69–86
Li CS, Ripley EM (2005) Empirical equations to predict the sulphur content of mafic magmas at sulfide saturation and applications to magmatic sulfide deposits. Miner Deposita 40:218–230
Li C, Naldrett AJ, Ripley EM (2001) Critical factors for the formation of a nickel-copper deposit in an evolved magma system: lessons from a composition of the Pants Lake and Voisey’s Bay sulfide occurences in Labrador, Canada. Miner Deposita 36:85–92
Li C, Ripley EM, Naldrett AJ (2003) Compositional variations of olivine and sulphur isotopes in the Noril’sk and Talnakh intrusions, Siberia: implications for ore-forming processes in dynamic magma conduits. Econ Geol 98:69–86
Li CS, Naldrett AJ, Ripley EM (2007) Controls on the Fo and Ni contents of olivine in sulfide-bearing mafic/ultramafic intrusions: principles, modeling, and examples from Voisey’s Bay. Earth Sci Front 14:177–185
Li HK, Zhu SX, Xiang ZQ, Su WB, Lu SN, Zhou HY, Yang FJ (2010) Zircon U–Pb dating on tuff bed from Gaoyuzhuang Formation in Yanqing, Beijing: Further constraints on the new subdivision of the mesoproterozoic stratigraphy in the northern North China Craton. Acta Petrol Sin 26(7):2131–2140
Lorand JP, Alard O, Luguet A, Keays RR (2003) Sulphur and selenium systematics of the subcontinental lithosperic mantle: Inferences from the Massif Central xenolith suite (France). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:4137–4151
Ludwig KR (2003) Isoplot 3.00: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Berkeley, CA
Maier WD, Barnes SJ, Chinyepi G, Barton JJ, Eglington B, Setshedi T (2008) The composition of magmatic Ni–Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposits in the Tati and Selebi-Phikwe belts of eastern Botswana. Miner Deposita 43:37–60
Mao JW, Pirajno F, Zhang ZH, Chai FM, Wu H, Chen SP, Cheng SL, Yang JM, Zhang CQ (2008) A review of the Cu–Ni sulfide deposits in the ChineseTianshan and Altay orogens (Xinjiang Autonomous Region, NW China): principal characteristics and ore-forming processes. J Asian Earth Sci 32:184–203
Mao YJ, Qin KZ, Li C, Xue SC, Ripley EM (2014) Petrogenesis and ore genesis of the Permian Huangshanxi sulfide ore-bearing mafic-ultramafic intrusion in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, western China. Lithos 200–201:111–125
Mao YJ, Qin KZ, Li C, Tang DM (2015) A modified genetic model for the Huangshandong magmatic sulfide deposit in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Xin-jiang, western China. Miner Deposita 50:65–82
Mao YJ, Tang DM, Qin KZ, Valentina T (2016) Geochemistry of the ~326 Ma Xinyuan mafic intrusion in the Eastern Junggar Terrane, Northwest China: implications for tectonic setting and magmatic Ni–Cu mineralization potential. Int Geol Rev 59(10):1276–1291
Mao YJ, Qin KZ, Barnes SJ, Tang DM, Xue SC, Vaillant ML (2017) Genesis of the Huangshannan high-Ni tenor magmatic sulfide deposit in the Eastern Tianshan, northwest China: constraints from PGE geochemistry and Os–S isotopes. Ore Geol Rev 90:591–606
McDonough WF, Sun SS (1995) The composition of the Earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253
Mungall JE, Hanley JJ, Arndt NT, Debecdelievre A (2006) Evidence from meimechites and other low-degree mantle melts for redox controls on mantle-crust fractionation of platinum-group elements. PNAS 103(34):12695–12700
Naldrett AJ (2004) Magmatic sulfide deposits: geology, geochemistry and exploration. Springer, Berlin, p 728
Naldrett AJ (2010a) From The mantle to the bank: The life of a Ni–Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposit. S Afr J Geol 113(1):1–32
Naldrett AJ (2010b) Secular variation of magmatic sulfide deposits and their source magmas. Econ Geol 105:669–688
Pang BC, Li QG, Chen XL, Liu SW, Wang ZQ, Chen YJ, Xiao B (2020) Paleozoic intrusive magmatic activity and basement properties of the Dananhu-Tousuquan island arc in the Eastern Tianshan mountains. Northwest Geol 53:1–26 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Pearce JA, Thirlwall MF, Ingram G, Murton BJ, Arculus RJ, Vanderlaan SR (1992) Isotopic evidence for the origin of boninites and related rocks drilled in the Izu-Bonin (Ogasawara) forearc. Proc ODP Sci Results 125:237–261
Qin KZ, Fang TH, Wang SL, Zhu BQ, Feng YM, Yu HF, Xiu QY (2002) Plate tectonics division, evolution and metallogenic settings in eastern Tianshan mountains, NW-China. Xinjiang Geol 20:302–308 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qin KZ, Sun BX, Sakyi PA, Tang DM, Li XH, Sun H, Xiao QH, Liu PP (2011) SIMS zircon U–Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd isotopes of Ni–Cu-bearing mafic-ultramafic intrusions in Eastern Tianshan and Beishan in correlation with flood basalts in Tarim basin (NW China): constraints on a ca. 280 Ma mantle plume. Am J Sci 311:237–260
Ren MH, Wang CY, Ni K, Sun YL (2013) Differentiation of magmas in the formation of Permian mafic-ultramafic intrusions in the Dacaotan area, Eastern Tianshan: implications for Ni–Cu-(PGE) sulfide mineralization potentials. Acta Petrol Sin 29(10):3473–3486 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ripley EM, Li C (2003) Sulphur isotope exchange and metal enrichment in the formation of magmatic Cu-Ni-(PGE) deposits. Econ Geol 98:635–641
Ripley EM, Li C, Shin D (2002) Paragneiss assimilation in the genesis of magmatic Ni–Cu–Co sulfide mineralization at Voisey’s Bay, Labrador: δ34S, δ13C, and Se/S evidence. Econ Geol 97:1307–1318
Saleeby JB (1992) Age and tectonic setting of the Duke Island ultramafic intrusion, southeast Alaska. Can J Earth Sci 29:506–522
San JZ, Hui WD, Qin KZ, Sun H, Xu XW (2007) Geological characteristics of the Tulargen magmatic Cu–Ni–Co deposit in eastern Xinjiang and its exploration direction. Mineral Deposits 26:307–316 (in Chinese with English abstract)
San JZ, Qin KZ, Tang DM, Su BX, Sun H, Xiao QH, Liu PP, Cao MJ (2010) Precise zircon U–Pb ages of the large Tulargen Cu–Ni ore-bearing mafic–ultramafic complex and their geological implications. Acta Petrol Sin 26:3027–3035 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sengör AMC, Natal’in BA, Burtman VS (1993) Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Paleozoic crustal growth in Asia. Nature 364:299–307
Song XY, Li XR (2009) Geochemistry of the Kalatongke Ni–Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposit, NW China: Implications for the formation of magmatic sulfide mineralization in a postcollisional environment. Miner Deposita 44:303–327
Song XY, Hu RZ, Chen LM (2009) Geochemical natures of copper, nickel and PGE and their significance for the study of origin and evolution of mantle-derived magmas and magmatic sulfide deposits. Earth Sci Front 16(4):287–305 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Song XY, Wang YS, Chen LM (2011a) Magmatic Ni–Cu-(PGE) deposits in magma plumbing systems: features, formation and exploration. Geosci Front 2:375–384
Song XY, Xie W, Deng YF, Crawford AJ, Zheng WQ, Zhou GF, Deng G, Cheng SL, Li J (2011b) Slab break-off and the formation of Permianmafic-ultramafic intrusions in southern margin of Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Xinjiang, NW China. Lithos 127:128–143
Song XY, Chen LM, Deng YF, Xie W (2013) Syn-collisional tholeiitic magmatism induced by slab detachment at the southern margin of the Central Asian orogenic belt. J Geol Soc 170:941–950
Su BX, Qin KZ, Sun H, Tang DM, Sakyi PA, Chu ZY, Liu PP, Xiao QH (2012) Subduction-induced mantle heterogeneity beneath Eastern Tianshan and Beishan: insights from Nd-Sr-Hf-O isotopic mapping of Late Paleozoic mafic-ultramafic complexes. Lithos 134:41–51
Sun H (2009a) Ore-forming mechanism in conduit system and ore-bearing propertyevaluation for mafic–ultramafic complex in Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang. Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Ph. D thesis in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun H (2009b) Ore-forming mechanism in conduit system and ore-bearing property evaluation for mafic–ultramafic complex in Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang. Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Ph. D thesis in Chinese withEnglish abstract)
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics in ocean basalt: implication for mantle composition and processes. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 42(1):313–345
Sun H, Tang DM, Qing KZ, Fan X, Xiao QH, Su BX (2009) Advances of geochemical behavior of chalcophile elements and applications in metallogeny of magmatic Cu–Ni-PGE sulfide deposits. Geol Rev 55(6):840–850 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun T, Qian ZZ, Deng YF, Li CS, Song XY, Tang QY (2013) PGE and isotope (Hf-Sr-Nd-Pb) constraints on the origin of the Huangshandong magmatic Ni–Cu sulfide deposit in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Northwestern China. Econ Geol 108:1849–1864
Takazawa E, Frey FA, Shimizu N, Obtata M (2000) Whole rock compositional variations in an upper mantle peridotite (Horoman, Hokkaido, Japan): are they consistent with a partial melting process? Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:695–716
Tang ZL, Bai YL, Li ZL (2002) Geotectonic setting of large and super large mineral deposits on the southwestern margin of the north China Plate. Acta Petrol Sin 76:367–377 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tang DM, Qin KZ, Sun H, Su BX, Xiao QH (2012) the role of Ni–Cu sulfide deposits in Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang, Northwest China: Evidence from trace element geochemistry, Re-Os, Sr-Nd, zircon Hf-O, and sulfur isotopes. J Asian Earth Sci 49:145–160
Tang DM, Qin KZ, Su BX, Sakyi PA, Mao YJ, Xue SC (2014) Petrogenesis and mineralization of the Hulu Ni–Cu sulfide deposit in Xinjiang, NW China: constraints from Sr-Nd isotopic and PGE compositions. Int Geol Rev 56:711–733
Thakurta J, Ripley EM, Li CS (2008) Geochemical constraints on the origin of sulfide mineralization in the Duke Island Complex, southeastern Alaska. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 9:1–34
Wang MF, Xia QL, Xiao F, Wang QX, Yang WS, Jiang CL (2012) Rock geochemistry and platinum group elements characteristics of Tudun Cu-Ni sulfide deposit in East Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang and their metallogenic implications. Miner Deposits 31(6):1195–1210 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang MX, Wang CY, Sun YL (2013) Mantle source, magma differentiation and sulfide saturation of the∼637 Ma Zhouan mafic–ultramafic intrusion in the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, Central China. Precambr Res 228:206–222
Wang YH, Xue CJ, Liu JJ, Zhang FF (2016a) Geological, geochronological, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-O-Hf isotopic constraints on origins of intrusions associated with the Baishan porphyry Mo deposit in eastern Tianshan, NW China. Miner Deposita 51:953–969
Wang YH, Zhang FF, Liu JJ, Que CY (2016b) Carboniferous magmatism and mineralization in the area of the fuxing Cu deposit, Eastern Tianshan, China: evidence from zircon U–Pb ages, petrogeochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Hf-O isotopic compositions. Gondwana Research 34:109–128
Windley BF, Alexeiev D, Xiao WJ, Kröner A, Badarch G (2007) Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. J Geol Soc 164:31–47
Woodhead J, Hergt J, Shelley M, Eggins S, Kemp R (2004) Zircon Hf-isotope analysis with an excimer laser, depth profiling, ablation of complex geometries and comcomitant age estimation. Chem Geol 209:121–135
Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF, Gao S (2007) Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrol Sin 23(2):185–220 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiao WJ, Zhang LC, Qin KZ, Sun S, Li JL (2004) Paleozoic accretionary collisional tectonics of the eastern Tianshan (China): implications for the continental growth of central Asia. Am J Sci 304:370–395
Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Yuan C, Sun M, Han CM, Lin SF, Chen HL, Yan QR, Liu DY, Qin KZ, Li JL, Sun S (2009) Paleozoic multiple subduction-accretion processes of the southern Altaids. Am J Sci 309:221–270
Xiao WJ, Mao QG, Windley BF, Han CM, Qu JF, Zhang JE, Ao SJ, Guo QQ, Cleven NR, Lin SF, Shan YH, Li JL (2010) Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional processes of the Beishan orogenic collage. Am J Sci 310:1553–1594
Xie W, Song XY, Chen LM, Deng YF, Zheng WQ, Wang YS, Ba DH, Yin MH, Luan Y (2014) Geochemistry insights on the genesis of the subduction-related Heishan magmatic Ni–Cu-(PGE) deposit in Gansu, NW China, at the southern margin of the central Asian Orogenic Belt. Econ Geol 109:1563–1583
Xue SC, Qin KZ, Tang DM, Mao YJ, Yao ZS (2015) Compositional characteristics of pyroxenes from Permian mafic-ultramafic complexes in Eastern Xinjiang, and their implications for petrogenesis and Ni–Cu mineralization. Acta Petrol Sin 31:2175–2192 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang MJ, Li CS, Fu PE, Hu PQ, Ripley EM (2011) The Permian Huangshanxi Cu-Ni deposit in western China: intrusive-extrusive association, ore genesis, and exploration implications. Miner Deposita 46:153–170
Zhao Y, Xue CJ, Zhao XB, Yang YQ, Ke JJ (2015) Magmatic Cu–Ni sulfide mineralization of the Huangshannan mafic–untramafic intrusion, Eastern Tianshan, China. J Asian Earth Sci 105:155–172
Zhao Y, Xue CJ, Zhao XB, Yang YQ, Ke JJ, Zu B (2016a) Variable mineralization processes during the formation of the Permian Hulu Ni–Cu sulfide deposit, Xinjiang, Northwestern China. J Asian Earth Sci 126:1–13
Zhao Y, Xue CJ, Zhao XB, Yang YQ, Ke JJ, Zu B, Zhang GZ (2016b) Origin of anomalously Ni-rich parental magmas and genesis of the Huangshannan Ni–Cu sulfide deposit, Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Northwestern China Ore Geol Rev 77:57–71
Zhao Y, Xue CJ, Symons DTA, Zhao XB, Zhang GZ, Yang YQ, Zu B (2018) Temporal variations in the mantle source beneath the Eastern Tianshan nickel belt and implications for Ni–Cu mineralization potential. Lithos 314:597–616
Zhao Y, Xue CJ, Liu SA, Mathur R, Zhao XB, Yang YQ, Dai JF, Man RH, Liu XM (2019) Redox reactions control Cu and Fe isotope fractionation in a magmatic Ni–Cu mineralization system. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 249:42–58
Zhou MF, Lesher CM, Yang ZX, Li JW, Sun M (2004) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of 270 Ma Ni–Cu-(PGE) sulfide-bearing mafic intrusions in the Huangshan district, eastern Xinjiang, northwest China: implications for the tectonic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Chem Geol 209:233–257
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Key R & D Program of China (2017YFC0601202); the Research Startup Project of Yunnan University (YJRC4201804); Open Funds from the Key Laboratory of Deep Earth Dynamics of Ministry of Natural Resource (J1901-16); the State Key Laboratory for Mineral Deposits Research (2021-LAMD-K10); Open Research Project from the State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources (GPMR202107, GPMR202118); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41803013, 41973037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, M., Zhao, Y., Xue, C. et al. The genesis of the Ni–Cu sulfide mineralization of the carboniferous Haibaotan intrusion, Eastern Tianshan, Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 112, 51–76 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-022-02238-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-022-02238-6