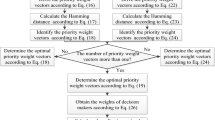
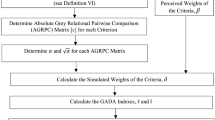
Abstract
Multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) has attracted wide interest due to its extensive applications in practice. In our previous study, a method called D-AHP (AHP method extended by D numbers preference relation) was proposed to study the MCDM problems based on a D numbers extended fuzzy preference relation, and a solution for the D-AHP method has been given to obtain the weights and ranking of alternatives from the decision data, in which the results obtained by using the D-AHP method are influenced by the credibility of information. However, in previous study the impact of information’s credibility on the results is not sufficiently investigated, which becomes an unsolved issue in the D-AHP. In this paper, we focus on the credibility of information within the D-AHP method and study its impact on the results of a MCDM problem. Information with different credibilities including high, medium and low, respectively, is taken into consideration. The results show that the credibility of information in the D-AHP method slightly impacts the ranking of alternatives, but the priority weights of alternatives are influenced in a relatively obvious extent.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoine V, Quost B, Masson MH, Denoeux T (2014) CEVCLUS: evidential clustering with instance-level constraints for relational data. Soft Comput 18(7):1321–1335
Aplak HS, Sogut MZ (2013) Game theory approach in decisional process of energy management for industrial sector. Energy Convers Manag 74:70–80
Aplak HS, Türkbey O (2013) Fuzzy logic based game theory applications in multi-criteria decision making process. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 25(2):359–371
Chen YH, Chao RJ (2012) Supplier selection using consistent fuzzy preference relations. Expert Syst Appl 39(3):3233–3240
Chen SJJ, Hwang CL, Beckmann MJ, Krelle W (1992) Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making: methods and applications. Springer, New York
Dempster AP (1967) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann Math Stat 38(2):325–339
Deng Y (2012) D numbers: theory and applications. J Inf Comput Sci 9(9):2421–2428
Deng X, Jiang W (2018) An evidential axiomatic design approach for decision making using the evaluation of belief structure satisfaction to uncertain target values. Int J Intell Syst 33(1):15–32
Deng X, Hu Y, Deng Y, Mahadevan S (2014a) Environmental impact assessment based on D numbers. Expert Syst Appl 41(2):635–643
Deng X, Hu Y, Deng Y, Mahadevan S (2014b) Supplier selection using AHP methodology extended by D numbers. Expert Syst Appl 41(1):156–167
Deng X, Han D, Dezert J, Deng Y, Shyr Y (2016) Evidence combination from an evolutionary game theory perspective. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(9):2070–2082
Deng X, Xiao F, Deng Y (2017) An improved distance-based total uncertainty measure in belief function theory. Appl Intell 46(4):898–915
Denoeux T (2013) Maximum likelihood estimation from uncertain data in the belief function framework. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(1):119–130
Fei L, Wang H, Chen L, Deng Y (2017) A new vector valued similarity measure for intuitionistic fuzzy sets based on OWA operators. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 15(5):31–49
García-Cascales MS, Lamata MT (2012) On rank reversal and TOPSIS method. Math Comput Model 56(5):123–132
Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F, Chiclana F, Luque M (2004) Some issues on consistency of fuzzy preference relations. Eur J Oper Res 154(1):98–109
Herrera-Viedma E, Alonso S, Chiclana F, Herrera F (2007) A consensus model for group decision making with incomplete fuzzy preference relations. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15(5):863–877
Jiang W, Wang S (2017) An uncertainty measure for interval-valued evidences. Int J Comput Commun Control 12(5):631–644
Jiang W, Zhan J (2017) A modified combination rule in generalized evidence theory. Appl Intell 46(3):630–640
Jiang W, Wei B, Tang Y, Zhou D (2017a) Ordered visibility graph average aggregation operator: an application in produced water management. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 27(2):023117
Jiang W, Xie C, Zhuang M, Tang Y (2017b) Failure mode and effects analysis based on a novel fuzzy evidential method. Appl Soft Comput 57:672–683
Jiang W, Wei B, Liu X, Li X, Zheng H (2018) Intuitionistic fuzzy power aggregation operator based on entropy and its application in decision making. Int J Intell Syst 33(1):49–67
Kang B, Chhipi-Shrestha G, Deng Y, Hewage K, Sadiq R (2017) Stable strategies analysis based on the utility of Z-number in the evolutionary games. Appl Math Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2017.12.006
Liu HC, You JX, Fan XJ, Lin QL (2014) Failure mode and effects analysis using D numbers and grey relational projection method. Expert Syst Appl 41(10):4670–4679
Liu T, Deng Y, Chan F (2017) Evidential supplier selection based on DEMATEL and game theory. Int J Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40,815-017-0400-4
Liu, B., Hu, Y., Deng, Y.: New failure mode and effects analysis based on D numbers downscaling method. Int J Comput Commun Control 13(2) (2018, in press)
Nie S, Hu B, Li Y, Hu Z, Huang GH (2011) Identification of filter management strategy in fluid power systems under uncertainty: an interval-fuzzy parameter integer nonlinear programming method. Int J Syst Sci 42(3):429–448
Opricovic S, Tzeng GH (2004) Compromise solution by MCDM methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur J Oper Res 156(2):445–455
Opricovic S, Tzeng GH (2007) Extended VIKOR method in comparison with outranking methods. Eur J Oper Res 178(2):514–529
Peldschus F, Zavadskas EK (2005) Fuzzy matrix games multi-criteria model for decision-making in engineering. Informatica 16(1):107–120
Ribeiro RA (1996) Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making: a review and new preference elicitation techniques. Fuzzy Sets Syst 78(2):155–181
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resources allocation. McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York
Sayadi MK, Heydari M, Shahanaghi K (2009) Extension of VIKOR method for decision making problem with interval numbers. Appl Math Model 33(5):2257–2262
Shafer G (1976) A mathematical theory of evidence. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Tanino T (1984) Fuzzy preference orderings in group decision making. Fuzzy Sets Syst 12(12):117–131
Tsaur RC (2011) Decision risk analysis for an interval TOPSIS method. Appl Math Comput 218(8):4295–4304
Wang Z, Bauch CT, Bhattacharyya S, d’Onofrio A, Manfredi P, Perc M, Perra N, Salathé M, Zhao D (2016) Statistical physics of vaccination. Phys Rep 664:1–113
Wang Z, Jusup M, Wang RW, Shi L, Iwasa Y, Moreno Y, Kurths J (2017) Onymity promotes cooperation in social dilemma experiments. Sci Adv 3(3):e1601444
Wei GW (2008) Maximizing deviation method for multiple attribute decision making in intuitionistic fuzzy setting. Knowl Based Syst 21(8):833–836
Xu Z (2007) A survey of preference relations. Int J Gen Syst 36(2):179–203
Xu H, Deng Y (2018) Dependent evidence combination based on Shearman coefficient and Pearson coefficient. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2783320
Xu Z, Yager RR (2008) Dynamic intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making. Int J Approx Reason 48(1):246–262
Xu S, Jiang W, Deng X, Shou Y (2018) A modified Physarum-inspired model for the user equilibrium traffic assignment problem. Appl Math Model 55:340–353
Yager RR (1992) Decision making under Dempster–Shafer uncertainties. Int J Gen Syst 20(3):233–245
Yager RR (2014) An intuitionistic view of the Dempster–Shafer belief structure. Soft Comput 18(11):2091–2099
Yager RR, Liu L et al (2008) Classic works of the Dempster–Shafer theory of belief functions, vol 219. Springer, Berlin
Yang JB, Xu DL (2013) Evidential reasoning rule for evidence combination. Artif Intell 205:1–29
Yang M, Khan FI, Sadiq R, Amyotte P (2013) A rough set-based game theoretical approach for environmental decision-making: a case of offshore oil and gas operations. Process Saf Environ Prot 91(3):172–182
Zhang R, Ashuri B, Deng Y (2017) A novel method for forecasting time series based on fuzzy logic and visibility graph. Adv Data Anal Classif 11(4):759–783
Zhang Q, Li M, Deng Y (2018) Measure the structure similarity of nodes in complex networks based on relative entropy. Phys A Stat Mech Its Appl 491:749–763
Zheng H, Deng Y (2018a) Evaluation method based on fuzzy relations between Dempster-Shafer belief structure. Int J Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.21956
Zheng X, Deng Y (2018b) Dependence assessment in human reliability analysis based on evidence credibility decay model and IOWA operator. Ann Nucl Energy 112:673–684
Zheng H, Deng Y, Hu Y (2017) Fuzzy evidential influence diagram and its evaluation algorithm. Knowl Based Syst 131:28–45
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to anonymous reviewers for their useful comments and suggestions on improving this paper. The work was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61573290, 61503237).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, X., Deng, Y. D-AHP method with different credibility of information. Soft Comput 23, 683–691 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2993-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2993-9