Abstract
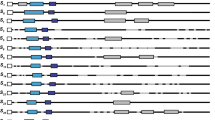
The gene SFB encodes an F-box protein that has appropriate S-haplotype-specific variation to be the pollen determinant in the S-RNase-based gametophytic self-incompatibility (GSI) reaction in Prunus (Rosaceae). To further characterize Prunus SFB, we cloned and sequenced four additional alleles from sweet cherry (P. avium), SFB 1, SFB 2, SFB 4, and SFB 5. These four alleles showed haplotype-specific sequence diversity similar to the other nine SFB alleles that have been cloned. In an amino acid alignment of Prunus SFBs, including the four newly cloned alleles, 121 out of the 384 sites were conserved and an additional 65 sites had only conservative replacements. Amino acid identity among the SFBs ranged from 66.0% to 82.5%. Based on normed variability indices (NVI), 34 of the non-conserved sites were considered to be highly variable. Most of the variable sites were located at the C-terminal region. A window-averaged plot of NVI indicated that there were two variable and two hypervariable regions. These variable and hypervariable regions appeared to be hydrophilic or at least not strongly hydrophobic, which suggests that these regions may be exposed on the surface and function in the allele specificity of the GSI reaction. Evidence of positive selection was detected using maximum likelihood methods with sites under positive selection concentrated in the variable and hypervariable regions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MA, Cornish EC, Mau S-L, Williams EG, Hoggart R, Atkinson A, Bonig I, Grego B, Simpson R, Roche P, Haley JD, Penschow J, Niall HD, Tregear GW, Coghlan JP, Crawford RJ, Clarke AE (1986) Cloning of cDNA for a stylar glycoprotein associated with expression of self-incompatibility in Nicotiana alata. Nature 321:38–44
Clark AG, Kao T-H (1991) Excess nonsynonymous substitution at shared polymorphic sites among self-incompatibility alleles of Solanaceae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9823–9827
Craig KL, Tyers M (1999) The F-box: a new motif for ubiquitin dependent proteolysis in cell cycle regulation and signal transduction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 72:299–328
Davis M, Hatzubai A, Andersen JS, Ben-Shusham E, Fisher Z, Yaron A, Bauskin A, Mercurio F, Mann M, Ben-Neriah Y (2002) Pseudosubstrate regulation of the SCFβ-TrCP ubiquitin ligase by hnRNP-U. Genes Dev 16:439–451
Dayhoff MO, Schwartz RM, Orcutt BC (1979) A model for evolutionary change in proteins. In: Dayhoff MO (ed) Atlas of protein sequence and structure, vol 5, Suppl 3. National Biomedical Research Foundation, Washington D.C., pp 345–352
Deshaies RJ (1999) SCF and Cullin/Ring H2-based ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:435–467
Entani T, Iwano M, Shiba H, Che F-S, Isogai A, Takayama S (2003) Comparative analysis of the self-incompatibility (S-) locus region of Prunus mume: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with allelic diversity. Genes Cells 8:203–213
Gagne JM, Downes BP, Shiu S-H, Durski AM, Vierstra RD (2002) The F-box subunit of the SCF E3 complex is encoded by a diverse superfamily of genes in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11519–11524
Golz JF, Oh H-Y, Su V, Kusaba M, Newbigin E (2001) Genetic analysis of Nicotiana pollen-part mutants is consistent with the presence of an S-ribonuclease inhibitor at the S locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:15372–15376
Ioerger TR, Gohike JR, Xu B, Kao T-H (1991) Primary structural features of the self-incompatibility protein in Solanaceae. Sex Plant Reprod 4:81–87
Ishimizu T, Endo T, Yamaguchi-Kabata Y, Nakamura KT, Sakiyama F, Norioka S (1998) Identification of regions in which positive selection may operate in S-RNase of Rosaceae: implication for S-allele-specific recognition sites in S-RNase. FEBS Lett 440:337–342
Kheyr-Pour A, Bintrim SB, Ioerger TR, Remy R, Hammond SA, Kao T-H (1990) Sequence diversity of pistil S-proteins associated with gametophytic self-incompatibility in Nicotiana alata. Sex Plant Reprod 3:88–97
Kuroda H, Takahashi N, Shimada H, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Matsui M (2002) Classification and expression analysis of Arabidopsis F-box-containing protein genes. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1073–1085
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Lai Z, Ma W, Han B, Liang L, Zhang Y, Hong G, Xue Y (2002) An F-box gene linked to the self-incompatibility (S) locus of Antirrhinum is expressed specifically in pollen and tapetum. Plant Mol Biol 50:29–42
Luu D, Quin X, Morse D, Cappadocia M (2000) S-RNase uptake by compatible pollen tubes in gametophytic self-incompatibility. Nature 407:649–651
Matsuura T, Sakai H, Unno M, Ida K, Sato M, Sakiyama F, Norioka S (2001) Crystal structure at 1.5-angstrom resolution of Pyrus pyrifolia pistil ribonuclease responsible for gametophytic self-incompatibility. J Biol Chem 276:45261–45269
McClure BA, Haring V, Ebert PR, Anderson MA, Simpson RJ, Sakiyama F, Clarke AE (1989) Style self-incompatibility gene products of Nicotiana alata are ribonucleases. Nature 342:757–760
McCubbin AG, Kao T-H (2000) Molecular recognition and response in pollen and pistil interactions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:333–364
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3:418–426
Nettancourt D de (2001) Incompatibility and incongruity in wild and cultivated plants. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Nielsen R, Yang Z (1998) Likelihood models for detecting positively selected amino acid sites and applications to the HIV-1 envelope gene. Genetics 148:929–936
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Sassa H, Hirano H, Ikehashi H (1992) Self-incompatibility-related RNases in styles of Japanese pear (Pyrus serotina Rehd.). Plant Cell Physiol 33:811–814
Swofford DL (2001) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods), version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Mass.
Tao R, Yamane H, Sugiura A, Murayama H, Sassa H, Mori H (1999) Molecular typing of S-alleles through identification, characterization and cDNA cloning for S-RNases in sweet cherry. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 124:224–233
Tao R, Namba A, Yamane H, Fuyuhiro Y, Watanabe T, Habu T, Sugiura A (2003) Development of the S f-RNase gene-specific PCR primer set for Japanese apricot (Prunus mume Sieb. et zucc.). Hortic Res (Japan) 2:237–240
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Thompson RD, Kirch HH (1992) The S locus of flowering plants: when self-rejection is self-interest. Trends Genet 8:381–387
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R, Yamane H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Hirano H (1998) Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding S-RNases from almond (Prunus dulcis): primary structural features and sequence diversity of the S-RNases in Rosaceae. Mol Gen Genet 260:261–268
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tamura M, Kusaba M, Tao R, Gradziel TM, Dandekar AM, Hirano H (2001) Characterization of the S-locus region of almond (Prunus dulcis): analysis of a somaclonal mutant and a cosmid contig for an S haplotype. Genetics 158:379–386
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Tao R, Hirano H (2003) Structural and transcriptional analysis of the self-incompatibility locus of almond: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with haplotype-specific polymorphism. Plant Cell 15:771–781
Wang Y, Wang X, Skirpan AL, Kao T-H (2003) S-RNase-mediated self-incompatibility. J Exp Bot 54:115–122
Xue Y, Carpenter R, Dickinson HG, Coen ES (1996) Origin of allelic diversity in Antirrhinum S locus RNases. Plant Cell 8:805–814
Yamane H, Ikeda K, Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R (2003a) A pollen-expressed gene for a novel protein with an F-box motif that is very tightly linked to a gene for S-RNase in two species of cherry, Prunus cerasus and P. avium. Plant Cell Physiol 44:764–769
Yamane H, Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R (2003b) The use of S haplotype-specific F-box protein gene, SFB, as a molecular marker for S-haplotype and self-compatibility in Japanese apricot (Prunus mume). Theor Appl Genet 107:1357-1361
Yang Z (1997) PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci 13:555–556
Yang Z (1998) Likelihood ratio tests for detecting positive selection and application to primate lysozyme evolution. Mol Biol Evol 15:568–573
Yang Z, Bielawski JP (2000) Statistical methods for detecting molecular adaptation. Trends Ecol Evol 15:496–503
Yang Z, Swanson WJ (2002) Codon substitution models to detect adaptive evolution that account for heterogeneous selective pressures among site classes. Mol Biol Evol 19:49-57
Zhou J, Wang F, Ma W, Zhang Y, Han B, Xue Y (2003) Structural and transcriptional analysis of S-locus F-box genes in Antirrhinum. Sex Plant Reprod 16:165–177
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the gifts of plant material from the National Institute of Fruit Tree Science (Morioka, Japan). This work was supported by the Japan-US Cooperative Science Program, a Grant-in-Aid (no. 13460014) for Scientific Research (B) to R.T., and a Grant-in-Aid (no. 15004783) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Research Fellows to K.U., who is a Research Fellow of JSPS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K. Ikeda and B. Igic contributed equally to this paper
Nucleotide sequence data reported will appear in the EMBL, GenBank and DDBJ nucleotide sequence databases under the accession numbers AB111518, AB111519, AB111520, and AB111521, for SFB 1, SFB 2, SFB 5, and SFB 4, respectively
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, K., Igic, B., Ushijima, K. et al. Primary structural features of the S haplotype-specific F-box protein, SFB, in Prunus . Sex Plant Reprod 16, 235–243 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-003-0200-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-003-0200-x