Abstract
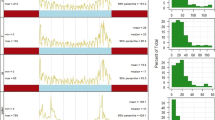
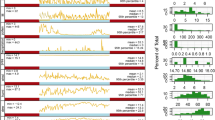
To investigate the influence and lag effect of atmospheric pollen concentration on daily visits of patients with allergic rhinitis (AR), we collected the AR data during the pollen seasons from 2018 to 2019 from the outpatient and emergency department of Beijing Shijitan Hospital. The distributed lag non-linear model (DLNM) was used to analyze the correlation and the lag effect between pollen concentration and the incidence of AR. R4.1.2 was used to generate the Spearman correlation coefficients and plot the lag response curves of relative risk specific and incremental cumulative effects. In 2018 and 2019, the number of AR visits was moderately positively correlated with pollen concentration. The peak value of the overall specific cumulative effect for every 10 grains/1000 mm2 increase in atmospheric pollen concentration occurred on day 0 (2018, 2019), and the lag disappearance time was day 6 (2018) and day 7 (2019), and the specific cumulative effect duration was respectively 6 days (2018) and 7 days (2019), with the curve showing a downward trend with time increase. In 2018, the peak value of the overall incremental cumulative effect was on day 7, the lag disappearance time was day 13, and the duration of the incremental cumulative effect was 13 days, forming a curve pattern of rising first and then falling. In 2019, the peak value time of the overall incremental cumulative effect was on day 8, and the curve went down afterwards until it showed the trend of ascending again after day26.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bernstein DI, Schwartz G, Bernstein JA (2016) Allergic rhinitis: mechanisms and treatment. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 36:261–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iac.2015.12.004
Blando J, Allen M, Galadima H, Tolson T, Akpinar-Elci M, Szklo-Coxe M (2022) Observations of delayed changes in respiratory function among allergy clinic patients exposed to wild fire smoke. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031241
Dondi A, Tripodi S, Panetta V, Asero R, Businco ADR, Bianchi A, Carlucci A, Ricci G, Bellini F, Maiello N, Giudice MM, Frediani T, Sodano S, Iacono ID, Macrì F, Massaccesi V, Caffarelli C, Rinaldi L, Patria MF et al (2013) Pollen-induced allergic rhinitis in 1360 Italian children: comorbidities and determinants of severity. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 24:742–751. https://doi.org/10.1111/pai.12136
Eifan AO, Durham SR (2016) Pathogenesis of rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy 46:1139–1151. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.12780
Gasparrini A (2011) Distributed lag linear and non-linear models in R: the package dlnm. J Stat Softw 43:1–20
Gasparrini A (2014) Modeling exposure-lag-response associations with distributed lag non-linear models. Stat Med 33:881–899. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.5963
Gasparrini A (2016) Modelling lagged associations in environmental time series data: a simulation study. Epidemiology 27:835–842. https://doi.org/10.1097/ede.0000000000000533
Gasparrini A, Armstrong B (2013) Reducing and meta-analyzing estimates from distributed lag non-linear models. BMC Med Res Methodol 13:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-13-1
Gasparrini A, Armstrong B, Kenward MG (2010) Distributed lag non-linear models. Stat Med 29:2224–2234. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3940
Gasparrini A, Scheipl F, Armstrong B, Kenward MG (2017) A penalized framework for distributed lag non-linear models. Biometrics 73:938–948. https://doi.org/10.1111/biom.12645
He HJ, Zhang DS, Qiao BS (2001) Preliminary approach of the relationship between airborne pollen amount and meteorological factors in Beijing urban area. Chin J Microbiol Immunol 21:31–33
Hwang Y, Motomura C, Fukuda H, Kishikawa R, Watanabe N, Yoshihara S (2022) Relationship among airborne pollen, sensitization, and pollen food allergy syndrome in Asian allergic children. PeerJ 10:e14243. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.14243
Liu Y, Sun L, Lu YH, Zhou PM, Bian CY, Jiang CH, Wu B, Liu L (2014) Correlation between airborne pollen dispersal and weather elements in urban district of Chengdu. Pract J Clin Med 11:235–238. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2014.04.083
Ma P, Li RL, Zhao XY, Ning GC, Zhang Y, Wang SG (2017) The lag effect of AQI on the number of emergency room visits for respiratory diseases and its relationship with meteorological conditions in Beijing City. J Lanzhou Univ Nat Sci 53:388–393. https://doi.org/10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2017.03.015
Ma TT, Wang HT, Chen YL, Zhuang Y, Shi HY, Yu RL, Guo MY, Ji Y, Wang XY (2021) Sensitization spectrum of inhaled allergens in outpatients in Beijing area. Chin J Allergy Clin Immunol 15:136–143. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-8705.2021.02.002
Ma WG, Chen RJ, Kan HD (2014) Temperature-related mortality in 17 large Chinese cities: how heat and cold affect mortality in China. Environ Res 134:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.07.007
Meng L, Wang XK, Ouyang ZY, Ren YF, Wang QH (2016) Seasonal dynamics of airborne pollens and its relationship with meteorological factors in Beijing urban area. Environ Sci 37:452–458. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.02.007
Meng YF, Wang CS, Zhang L (2020) Advances and novel developments in allergic rhinitis. Allergy 75:3069–3076. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.14586
Okubo K, Kurono Y, Ichimura K, Enomoto T, Okamoto Y, Kawauchi H, Suzaki H, Fujieda S, Masuyama K (2020) Japanese guidelines for allergic rhinitis 2020. Allergol Int 69:331–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2020.04.001
Schuler CF IV, Montejo JM (2019) Allergic rhinitis in children and adolescents. Pediatr Clin N Am 66:981–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2019.06.004
Wallace DV, Dykewicz MS (2017) Seasonal allergic rhinitis: a focused systematic review and practice parameter update. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 17:286–294. https://doi.org/10.1097/aci.0000000000000375
Yamada T, Saito H, Fujieda S (2014) Present state of Japanese cedar pollinosis: the national affliction. J Allergy Clin Immunol 133:632–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.11.002
Yang J, Ou CQ, Ding Y, Chen PY (2012) Distributed lag linear models. Chin J Health Stat 29:772–777
Zhang B, Wang JX (2019) Time-series study on relationship between air pollutants and outpatient visits in Chongming District of Shanghai. J Environ Occup Med 36:376–380. https://doi.org/10.13213/j.cnki.jeom.2019.18536
Zhang Y, Xin JY, Zhang XL, Ni CJ, Ma P, Wang SG, Feng XY, Hu WD, Zheng CJ (2020) Interaction effects between ambient temperature and black carbon and PM2.5 on mortality in Beijing. China Environ Sci 40:3179–3187. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2020.0356
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful for the help of the Information Center of Beijing Shijitan Hospital. I would like to thank professor Yin Jinshu for her guidance in the writing of this paper and every author’s contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Yin Jinshu proposed the research idea, and Tang Xianshi further refined the scientific methodology and participated in the English writing and proofreading of the manuscript. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Liu Aizhu, and the R code part was written by Sheng Weixuan. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Liu Aizhu, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This retrospective clinical study involved a total of 31,623 cases including 17,203 female (54.4%) and 14,420 male patients (35.6%), with 6982 patients (female 3695, male 3287) reported in 2018 and the rest 24,641 patients (female 13,508, male 11,133) in 2019. Clinical data of patients were collected without intervention in their treatment plans, and therefore posing no risks to the patients’ physical conditions. And the information provided by patients as personal privacy would be well protected from being leaked without informed consent.
Consent to participate
In this retrospective study, only the number of patients was collected, no personal privacy was involved, and no informed consent was obtained.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, A., Sheng, W., Tang, X. et al. Effect of atmospheric pollen concentration on daily visits of allergic rhinitis in Beijing: a distributed lag nonlinear model analysis. Int J Biometeorol 67, 1723–1732 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-023-02533-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-023-02533-0