Abstract
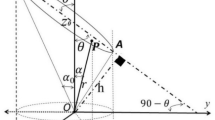
In general, measurements of UV radition are related to horizontal surfaces, as in the case of the internationally standardized and applied UV index, for example. In order to obtain more relevant information on UV exposure of humans the new measuring system ASCARATIS (Angle SCAnning RAdiometer for determination of erythemally weighted irradiance on TIlted Surfaces) was developed and built. Three systems of ASCARATIS have been in operation at different locations in Bavaria for 3 years, providing erythemally weighted UV irradiation data for 27 differently inclined surfaces every 2 min. On the basis of these data virtual three-dimensional models of the human body surface consisting of about 20,000 triangles could be created and each of these triangles coloured according to its UV irradiation. This allowed the UV exposure of the human body to be visualized for any kind of body posture and spatial orientation on the basis of real measuring data. The results of the UV measurements on inclined surfaces have shown that measuring UV radiation on horizontal surfaces, as done routinely worldwide, often underestimates the UV exposure of the human skin. Especially at times of the day or year with low solar elevations the UV exposure of parts of the human skin can be many times higher than that of the horizontal surface. Examples of three-dimensional modelling of the human UV irradiation are shown for different times of the day and year, altitudes above sea level, body postures and genders. In these examples the UV “hotspots” can be detected and, among other things, used to inform and educate the public about UV radiation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum A, Volkenandt M (2002) Skin cancer. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 127:1679–1681
Fisher GJ, Kang S, Varani J, Bata-Csorgo Z, Wan Y, Datta S, Voorhees JJ (2002) Mechanisms of photoaging and chronological skin aging. Arch Dermatol 138:1462–1470
Geller AC, Annas GD (2003) Epidemiology of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer. Semin Oncol Nurs 19:2–11
Mech M, Koepke P (2004) Model for UV irradiance on arbitrarily oriented surfaces. Theor Appl Climatol 77:151–158
Oppenrieder A, Hoeppe P, Koepke P, Reuder J, Schween J, Schreder J (2003) Simplified calibration for broadband solar ultra violet radiation measurements. Photochem Photobiol 78:603–606
Oppenrieder A, Hoeppe P, Koepke P (2004) Routine measurement of erythemally effective UV irradiance on inclined surfaces. J Photochem Photobiol [B] 74:85–94
Ruggaber A, Dlugi R, Nakajima T (1994) Modelling radiation quantities and photolysis frequencies in the troposphere. J Atmos Chem 18:171–210
Schauberger G (1990) Model for the global irradiance of the solar biologically-effective ultraviolet-radiation on inclined surfaces. Photochem Photobiol [B] 52:1029–1032
Schwander H, Koepke P, Ruggaber A, Nakajima T, Oppenrieder A (2000) System for transfer of atmospheric radiation STAR - version 2000. Freely available: http://www.meteo.physik.uni-muenchen.de/strahlung/uvrad/Star/STARinfo.htm
Seefeldner M, Hoeppe P, Koepke P, Oppenrieder A, Rabus D, Schreier M (2004) A 2-axis tracking system with data logger. J Atmos Ocean Technol 21:975–979
Webb A, Weihs P, Blumthaler M (1999) Spectral UV-irradiance on vertical surfaces: a case study. Photochem Photobiol 69:464–470
WMO (1997) TD921 Report of the WMO/WHO meeting of experts on standardization of UV-indices in Les Diableret (Switzerland). WMO. Geneva
Acknowledgements
The project is sponsored by the Bavarian Research Network BayForUV and the Environmental Research Station Schneefernerhaus. More information on the study can be obtained at: http://www.bayforuv.de/englisch/topindex.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoeppe, P., Oppenrieder, A., Erianto, C. et al. Visualization of UV exposure of the human body based on data from a scanning UV-measuring system. Int J Biometeorol 49, 18–25 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-004-0211-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-004-0211-9