Abstract
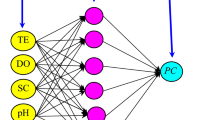
A total dissolved solid (TDS) is an important indicator for water quality assessment. Since the composition of mineral salts and discharge affects the TDS of water, it is important to understand the relationship of mineral salt composition with TDS. In the present study, four artificial intelligence approaches, namely artificial neural networks (ANNs), two different adaptive-neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) including ANFIS with grid partition (ANFIS-GP) and ANFIS with subtractive clustering (ANFIS-SC), and gene expression programming (GEP) were applied to forecast TDS in river water over a period of 18 years at seven different sites. Five different GEP, ANFIS and ANN models comprising various combinations of water quality and flow variables from Zarinehroud basin in northwest of Iran were developed to forecast TDS variations. The correlation coefficient (R), root mean square error and mean absolute error statistics were used for evaluating the accuracy of models. Based on the comparisons, it was found that the GEP, ANFIS-GP, ANFIS-SC and ANN models could be employed successfully in forecasting TDS variations. A comparison was made between these artificial intelligence approaches which emphasized the superiority of GEP over the other intelligent models.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
[APHA] American Public Health Association (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 18th Edition, Washington DC
Abonyi J, Andersen H, Nagy L, Szeifert F (1999) Inverse fuzzy-process-model based direct adaptive control. Math Comput Simul 51:119–132
Abudu S, King JP, Sheng Z (2012) Comparison of the performance of statistical models in forecasting monthly total dissolved solids in the Rio Grande1. JAWRA 48(1):10–23
Altunkaynak A, Şen Z (2007) Fuzzy logic model of lake water level fluctuations in Lake Van Turkey. Theor Appl Climatol 90(3–4):227–233
Aqil M, Kita I, Yano A, Nishiyama S (2007) Analysis and prediction of flow from local source in a river basin using a neuro-fuzzy modeling tool. J Environ Manage 85:215–223
Asadollahfardi G, Taklify A, Ghanbari A (2011) Application of artificial neural network to predict TDS in Talkheh Rud River. J Irrig Drain Eng 138(4):363–370
Aytek A, Alp M (2008) An application of artificial intelligence for rainfall runoff modeling. J Earth Syst Sci 117(2):145–155
Azamathulla HM (2012) Gene expression programming for prediction of scour depth downstream of sills. J Hydrol 460:156–159
Azamathulla HM, Ahmad Z (2012) Gene-expression programming for transverse mixing coefficient. J Hydrol 434:142–148
Azamathulla HM, Ghani AA (2011) Genetic programming for predicting longitudinal dispersion coefficients in streams. Water Resour Manage 25:1537–1544
Bakhtyar R, Ghaheri A, Yeganeh-Bakhtiary A, Baldock TE (2008) Longshore sediment transport estimation using a fuzzy inference system. Appl Ocean Res 30:273–286
Bowers JA, Shedrow CB (2000) Predicting stream water quality using artificial neural networks.WSRC-MS-2000-00112. http://www.osti.gov/bridge/
Chang LC, Chang FJ (2001) Intelligent control for modeling of real-time reservoir operation. Hydrol Process 15:1621–1634
Chiu S (1994) Fuzzy model identification based on cluster estimation. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 2(3):267–278
Chiu S (1997) Extracting fuzzy rules from data for function approximation and pattern classification. In: Dubois D, Prade H, Yager R (eds) Fuzzy information engineering: a guided tour of applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 149–162
Drake JT (2000) Communications phase synchronization using the adaptive network fuzzy inference system. Dissertation, New Mexico State University
Ferreira C (2001) Gene expression programming: a new adaptive algorithm for solving problems. Complex Syst 13(2):87–129
Ferreira C (2006) Gene expression programming: mathematical modeling by an artificial intelligence, 2nd edn. Springer, Germany
Firat M, Güngör M (2010) Monthly total sediment forecasting using adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 24(2):259–270
Giustolisi O (2004) Using genetic programming to determine Chezy resistance coefficient in corrugated channels. J Hydroinform 6:157–173
Hashmi MZ, Shamseldin AY, Melville BW (2011) Statistical downscaling of watershed precipitation using gene expression programming (GEP). Environ Model Softw 26:1639–1646
Haykin S (1998) Neural networks—a comprehensive foundation, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, pp 26–32
Hong YS, Rosen MR (2002) Identification of an urban fractured-rock aquifer dynamics using an evolutionary self-organizing modelling. J Hydrol 259:89–104
Hundecha Y, Bardossy A, Theisen H (2001) Development of a fuzzy logic based rainfall-runoff model. Hydrol Sci J 46(3):363–376
Jang JSR (1993) ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE T Syst Man Cyb 23(3):665–685
Karunanithi N, Grenney WJ, Whitley D, Bovee K (1994) Neural networks for river flow prediction. J Comput Civil Eng ASCE 8(2):201–220
Kashani MH, Dinpashoh Y (2012) Evaluation of efficiency of different estimation methods for missing climatological data. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 26(1):59–71
Kennedy P, Condon M, Dowling J (2003) Torque-ripple minimization in switched reluctant motors using a neuro-fuzzy control strategy. In: Proceeding of the IASTED International Conference on Modeling and Simulation
Keskin ME, Terzi O, Taylan D (2004) Fuzzy logic model approaches to daily pan evaporation estimation in western Turkey. Hydrol Sci J 49(6):1001–1010
Kim S (2011) Nonlinear hydrologic modeling using the stochastic and neural networks approach. Disaster Adv 4(1):53–63
Kisi O (2005) Suspended sediment estimation using neuro-fuzzy and neural network approaches. Hydrol Sci J 50(4):683–696
Kisi O (2006) Daily pan evaporation modeling using a neuro-fuzzy computing technique. J Hydrol 329:636–646
Kisi O (2007) Streamflow forecasting using different artificial neural network algorithms. ASCE J Hydrol Eng 12(5):532–539
Kisi O (2008) River flow forecasting and estimation using different artificial neural network techniques. Hydrol Res 39(1):27–40
Kisi O, Shiri J (2010) A comparison of genetic programming and ANFIS in forecasting daily, monthly and daily stremflows. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on innovations in intelligent systems and applications. 21–24 June, Kayseri and Cappadocia, Turkey, pp. 118–122
Kisi O, Cimen M, Shiri J (2012) Suspended sediment modeling using genetic programming and soft computing techniques. J Hydrol 450:48–58
Kisi O, Shiri J, Tombul M (2013) Modeling rainfall-runoff process using soft computing techniques. Comput Geosci 51:108–117
Krauss G, Kindangen JI, Depecker P (1997) Using artificial neural networks to predict interior velocity coefficients. Build Environ 32:295–303
Kuo J, Hsieh M, Lung W, She N (2007) Using artificial neural network for reservoireutriphication prediction. Ecol Model 200:171–177
Kurtulus B, Razack M (2010) Modeling daily discharge responses of a large karstic aquifer using soft computing methods: artificial neural network and neuro-fuzzy. J Hydrol 381(1):101–111
Kusiak A, Wei X (2011) Prediction of methane production in wastewater treatment facility: a data-mining approach. Ann Oper Res, 1–11
Legates DR, McCabe GJ (1999) Evaluating the use of goodness-of-fit measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour Res 35(1):233–241
Li W, Yang M, Liang Z, Zhu Y, Mao W, Shi J, Chen Y (2013) Assessment for surface water quality in Lake Taihu Tiaoxi River Basin China based on support vector machine. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 27(8):1861–1870
Mamdani EH, Assilian S (1975) An experimental in linguistic synthesis with fuzzy logic controller. Int J Man Machine Stud 7:1–13
Maqsood I, Khan MR, Huang GH, Abdalla R (2005) Application of soft computing models to hourly weather analysis in southern Saskatchewan, Canada. Eng Appl Artif Intell 18:115–125
Mukhopadhyay A (1999) Spatial estimation of transmissivity using artificial neural network. Ground Water 37:458–464
NIST/SEMATECH e-Handbook of Statistical Methods (2006) http://www.itl.nist.ov/div898/handbook
Noori R, Hoshyaripour G, Ashrafi K, Araabi BN (2010) Uncertainty analysis of developed ANN and ANFIS models in prediction of carbon monoxide daily concentration. Atmos Environ 44:476–482
Orouji H, Bozorg Haddad O, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Mariño MA (2013) Modeling of water quality parameters using data-driven models. J Environ Eng 139(7):947–957
Palani S, Liong S, Tkalich P (2008) AnANNapplication forwater quality forecasting. Mar Pollut Bull 56:1586–1597
Raman H, Chandramouli V (1996) Deriving a general operating policy for reservoirs using neural networks. J Water Resour Plan Manage 122:342–347
Rawlings JO (1988) Applied regression analysis: a research tool. Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole Advanced Books & Software, Pacific Grove, California
Rezaeian-Zadeh M, Zand-Parsa S, Abghari H, Zolghadr M, Singh VP (2012) Hourly air temperature driven using multi-layer perceptron and radial basis function networks in arid and semi-arid regions. Theor Appl Climatol 109(3–4):519–528
Russel SO, Campbell PF (1996) Reservoir operating rules with fuzzy programming. J Water Resour Plan Manage 122(3):165–170
Samhouri M, Abu-Ghoush M, Yaseen E, Herald T (2009) Fuzzy clustering-based modeling of surface interactions and emulsions of selected whey protein concentrate combined to ı-carrageenan and gum arabic solutions. J Food Eng 91:10–17
Sanikhani H, Kisi O (2012) River flow estimation and forecasting by using two different adaptive neuro-fuzzy approaches. Water Resour Manage 26:1715–1729
Sanikhani H, Kisi O, Nikpour MR, Dinpashoh Y (2012) Estimation of daily pan evaporation using two different adaptive neuro-fuzzy computing techniques. Water Resour Manage 26:4347–4365
Shu C, Ouarda TBMJ (2008) Regional flood frequency analysis at ungauged sites using the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. J Hydrol 349(1):31–43
Singh KP, Malik A, Basant N, Saxena P (2007) Multi-way partial least squares modeling of water quality data. Anal Chim Acta 584:385–396
Singh KP, Basant A, Malik A, Jain G (2009) Artificial neural network modeling of the river water quality-a case study. Ecol Model 220(6):888–895
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE T Syst Man Cyb 15:116–132
Talebizadeh M, Moridnejad A (2011) Uncertainty analysis for the forecast of lake level fluctuations using ensembles of ANN and ANFIS models. Expert Syst Appl 38:4126–4135
Talei A, Chua LHC, Quek C (2010) A novel application of a neuro-fuzzy computational technique in event-based rainfall–runoff modeling. Expert Syst Appl 37(12):7456–7468
Tayfur G (2002) Artificial neural networks for sheet sediment transport. Hydrol Sci J 47:879–892
Tsukamoto Y (1979) An approach to reasoning method. In: Gupta M, Ragade RK, Yager RR (eds) Advances in fuzzy set theory and applications. Amsterdam, pp 137–149
Tutmez B, Hatipoglu Z, Kaymak U (2006) Modelling electrical conductivity of groundwater using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Comput Geosci 32(4):421–433
Verma A, Wei X, Kusiak A (2013) Predicting the total suspended solids in wastewater: a data-mining approach. Eng Appl Artif Intell 26(4):1366–1372
Wang Y, Guo S, Chen H, Zhou Y (2014) Comparative study of monthly inflow prediction methods for the Three Gorges Reservoir. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28(3):555–570
Wei M, Bai B, Sung AH, Liu Q, Wang J, Cather ME (2007) Predicting injection profiles using ANFIS. Inform Sci 177:4445–4461
Wei X, Kusiak A, Sadat HR (2012) Prediction of influent flow rate: data-mining approach. J Energy Eng 139(2):118–123
Yager RR, Filev DP (1994) Approximate clustering via the mountain method. IEEE T Syst Man Cyb 24(8):1279–1284
Yarar A, Onucyıldız M, Copty NK (2009) Modelling level change in lakes using neuro-fuzzy and artificial neural networks. J Hydrol 365(3):329–334
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaman Zad Ghavidel, S., Montaseri, M. Application of different data-driven methods for the prediction of total dissolved solids in the Zarinehroud basin. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28, 2101–2118 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-014-0899-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-014-0899-y