Abstract
Background
Fetuses exposed to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor antagonists during the second and/or third trimesters of gestation are at high risk of developing severe complications. They consist in fetal hypotension, and anuria/oligohydramnios leading to Potter sequence, frequently associated with hypocalvaria. Most fetuses die during the pre- or postnatal period, whereas others recover normal or subnormal renal function. However, the secondary occurrence of renal failure or hypertension has been reported in children after apparent complete recovery.
Methods
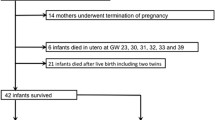
In this context, we analyzed renal lesions in 14 fetus/neonates who died soon after exposure to renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) blockers. Our objective was to determine the causes for the persistence or the secondary occurrence of renal complications reported in some of the survivors.
Results
As previously described, renal tubular dysgenesis is usually observed. Additional lesions, such as thickening of the muscular wall of arterioles and interlobular arteries, glomerular cysts, and interstitial fibrosis, develop early during fetal life.
Conclusion
We suggest that renal lesions that develop before birth may persist after withdrawal of the causative drugs and normalization of blood and renal perfusion pressure. Their persistence could explain the severe long-term outcome of some of these patients. Long-term study of children exposed to RAS blockers during fetal life is strongly recommended.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guignard JP, Gouyon JB, John EG (1991) Vasoactive factors in the immature kidney. Pediatr Nephrol 5:443–446
Duminy PC, Burger PD (1981) Fetal abnormality associated with the use of captopril during pregnancy. S Afr Med J 60:805
Cooper WO, Hernandez-Diaz S, Arbogast PG, Dudley JA, Dyer S, Gideon PS, Hall K, Ray WA (2006) Major congenital malformations after first-trimester exposure to ACE inhibitors. N Engl J Med 354(23):2443–2451
Schaefer C (2003) Angiotensin II-receptor-antagonists: further evidence of fetotoxicity but not teratogenicity. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 67:591–594
Porta M, Hainer JW, Jansson SO, Malm A, Bilous R, Chaturvedi N, Fuller JH, Klein R, Orchard T, Parving HH, Sjølie AK, DIRECT Study Group (2011) Exposure to candesartan during the first trimester of pregnancy in type 1 diabetes: experience from the placebo-controlled DIabetic REtinopathy Candesartan Trials. Diabetologia 54:1298–1303
Karthikeyan VJ, Ferner RE, Baghdadi S, Lane DA, Lip GY, Beevers DG (2011) Are angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers safe in pregnancy: a report of ninety-one pregnancies. J Hypertens 29:396–399
Diav-Citrin O, Shechtman S, Halberstadt Y, Finkel-Pekarsky V, Wajnberg R, Arnon J, Di Gianantonio E, Clementi M, Ornoy A (2011) Pregnancy outcome after in utero exposure to angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers. Reprod Toxicol 31:540–545
Bullo M, Tschumi S, Bucher BS, Bianchetti MG, Simonetti GD (2012) Pregnancy outcome following exposure to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor antagonists: a systematic review. Hypertension 60:444–450
Martinovic J, Benachi A, Laurent N, Daïkha-Dahmane F, Gubler MC (2001) Fetal toxic effects of angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Report of three additional cases. Lancet 358:241–242
Lacoste M, Cai Y, Guicharnaud L, Mounier F, Dumez Y, Bouvier R, Dijoud F, Gonzales M, Chatten J, Delezoide AL, Daniel L, Joubert M, Laurent N, Aziza J, Sellami T, Amar HB, Jarnet C, Frances AM, Daïkha-Dahmane F, Coulomb A, Neuhaus TJ, Foliguet B, Chenal P, Marcorelles P, Gasc JM, Corvol P, Gubler MC (2006) Renal tubular dysgenesis, a not uncommon autosomal recessive disorder leading to oligohydramnios: role of the renin-angiotensin system. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2253–2263
Spaggiari E, Heidet L, Grange G, Guimiot F, Dreux S, Delezoide AL (2012) Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers Study Group, Muller F Prognosis and outcome of pregnancies exposed to renin-angiotensin system blockers. Prenat Diagn 32:1–6
Bos-Thompson MA, Hillaire-Buys D, Muller F, Dechaud H, Mazurier E, Boulot P, Morin D (2005) Fetal toxic effects of angiotensin II receptor antagonists: case report and follow-up after birth. Ann Pharmacother 39:157–161
Guron G, Mölne J, Swerkersson S, Friberg P, Hansson S (2006) A 14-year-old girl with renal abnormalities after brief intrauterine exposure to enalapril during late gestation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:522–525
Laube GF, Kemper MJ, Schubiger G, Neuhaus TJ (2007) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor fetopathy: long-term outcome. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 92:F402–F403
Pryde PG, Seman AB, Nugent CE, Barr M Jr (1993) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor fetopathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 3:1575–1578
Daïkha-Dahmane F, Levy-Beff E, Jugie M, Lenclen R (2006) Foetal kidney maldevelopment in maternal use of angiotensin II type I receptor antagonists. Pediatr Nephrol 21:729–732
Gubler MC (2014) Renal tubular dysgenesis. Pediatr Nephrol 29:51–59
Marcussen N (1991) Atubular glomeruli in renal artery stenosis. Lab Invest 65:558–565
Madsen K, Marcussen N, Pedersen M, Kjærsgaard G, Facemire C, Coffman TM, Jensen BL (2010) Angiotensin II promotes development of the renal microcirculation through AT 1 receptors. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:448–459
Miura K, Sekine T, Iida A, Takahashi K, Igarashi T (2009) Salt-losing nephrogenic diabetes insipidus caused by fetal exposure to angiotensin receptor blocker. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1235–1238
Guron G, Friberg P (2000) An intact renin-angiotensin system is a prerequisite for normal renal development. J Hypertens 18:123–137
Filler G, Wong H, Condello AS, Charbonneau C, Sinclair B, Kovesi T, Hutchison J (2003) Early dialysis in a neonate with intrauterine lisinopril exposure. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 88:F154–F156
Deva M, Kara T (2012) ACE inhibitor fetopathy: a case series and survey of opinion amongst New Zealand paediatricians, obstetricians, neonatologists, and nephrologists. N Z Med J 125:51–61
Schindera C, Huber BM, Nelle M, Utsch B, Tschumi S, Gerull R (2012) Early development of arterial hypertension in an infant with valsartan nephropathy. J Neonatal Biol 1:1–2
Tufro-McReddie A, Romano LM, Harris JM, Ferder L, Gomez RA (1995) Angiotensin II regulates nephrogenesis and renal vascular development. Am J Physiol 269:F110–F115
Hilgers KF, Reddi V, Krege JH, Smithies O, Gomez RA (1997) Aberrant renal vascular morphology and renin expression in mutant mice lacking angiotensin-converting enzyme. Hypertension 29:216–221
Acknowledgments
We thank pathologists, fetopathologists, and pediatricians whose participation made this study possible by providing us clinical information and pathological material : R Bouvier (Service d’Anatomie Pathologique, Hôpital Mère Enfant, Bron), JB Gouyon (Service de Pédiatrie, CHU Dijon), P Déchelotte (Service d’Anatomie Pathologique, Hôtel-Dieu, Clermont-Ferrand), AL Delezoide (Service de Biologie du Développement, Hôpital Robert Debré, Paris), C Fernandez (Service d’Anatomie Pathologique, CHU de la Timone, Marseille), B Foliguet (Laboratoire de Biologie de la Reproduction et du Développement, Maternité Universitaire Régionale, Nancy). M Gonzales (Service de Génétique et d’Embryologie Médicales, Hôpital Armand Trousseau, Paris), M Joubert (Service d’Anatomie Pathologique, CHU, Nantes). N Laurent (Service d’Anatomie Pathologique, CHU Dijon), A L’Hermine Coulomb (Service d’Anatomie Pathologique, Hôpital Armand Trousseau, Paris), J Martinovic (Hôpital Antoine Béclère, Clamart), M Peuchmaur (Service d’Anatomie Pathologique, Hôpital Robert Debré, Paris), MF Santos- Carvalho, Lisbonne, J Tantau (Service d’Histologie Embryologie, Hôpital Cochin-Saint Vincent de Paul, Paris), G Tessier (Service de Réanimation Pédiatrique, Hôpital Nord, Saint Etienne).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plazanet, C., Arrondel, C., Chavant, F. et al. Fetal renin-angiotensin-system blockade syndrome: renal lesions. Pediatr Nephrol 29, 1221–1230 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2749-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2749-4