Abstract
Background
Endothelial cell injury plays a key role in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis (LN) and atherosclerosis. The aim of this study was to identify factors involved in the process of endothelial damage in children and adolescents with LN.
Methods
We evaluated the relationship between plasma vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), its soluble receptors sVEGFR-1 and sVEGFR-2 and markers of endothelial inflammation and injury (angiopoietin-2 and thrombomodulin, respectively) in 23 children and adolescents with LN (active LN, n = 14; inactive LN, n = 9; mean age 15 years) and 20 healthy controls (HC; mean age 12 years).
Results
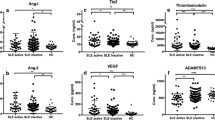
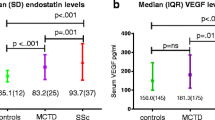
VEGF, sVEGFR-1, angiopoietin-2 and thrombomodulin levels were significantly higher in children and adolescents with active LN than in patients in remission or HC. In active LN, however, VEGF was inversely related to sVEGFR-1 (r = −0.802, p < 0.001), angiopoietin-2 (r = −0.684, p = 0.007) and thrombomodulin (r = −0.697, p = 0.006). There was a significant positive correlation between sVEGFR-1 and thrombomodulin (r = 0.814, p < 0.0001), but sVEGFR-2 did not significantly differ between the patient groups and did not correlate with thrombomodulin (r = 0.046, p = 0.833).
Conclusions
sVEGFR-1 may play an important role in promoting endothelial damage in children and adolescents with active LN and could possibly be used to monitor disease severity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appel GB, Pirani CL, D'Agati V (1994) Renal vascular complications of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1499–1515
Banfi G, Bertani T, Boeri V, Faraggiana T, Mazzucco G, Monga G, Sacchi G (1991) Renal vascular lesions as a marker of poor prognosis in patients with lupus nephritis. Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Nefrite Lupica (GISNEL). Am J Kidney Dis 18:240–248
Rajagopalan S, Somers EC, Brook RD, Kehrer C, Pfenninger D, Lewis E, Chakrabarti A, Richardson BC, Shelden E, McCune WJ, Kaplan MJ (2004) Endothelial cell apoptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: a common pathway for abnormal vascular function and thrombosis propensity. Blood 103:3677–3683
El-Magadmi M, Bodill H, Ahmad Y, Durrington PN, Mackness M, Walker M, Bernstein RM, Bruce IN (2004) Systemic lupus erythematosus: an independent risk factor for endothelial dysfunction in women. Circulation 110:399–404
Lee PY, Li Y, Richards HB, Chan FS, Zhuang H, Narain S, Butfiloski EJ, Sobel ES, Reeves WH, Segal MS (2007) Type I interferon as a novel risk factor for endothelial progenitor cell depletion and endothelial dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 56:3759–3769
Kahlenberg JM, Kaplan MJ (2011) The interplay of inflammation and cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 13:203
Dimmeler S, Hermann C, Zeiher AM (1998) Apoptosis of endothelial cells. Contribution to the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis? Eur Cytokine Netw 9:697–698
Turesson C, Jacobsson LT, Matteson EL (2008) Cardiovascular co-morbidity in rheumatic diseases. Vasc Health Risk Manag 4:605–614
McMahon M, Hahn BH, Skaggs BJ (2011) Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease: prediction and potential for therapeutic intervention. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 7:227–241
Roman MJ, Shanker BA, Davis A, Lockshin MD, Sammaritano L, Simantov R, Crow MK, Schwartz JE, Paget SA, Devereux RB, Salmon JE (2003) Prevalence and correlates of accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 349:2399–2406
de Leeuw K, Smit AJ, de Groot E, van Roon AM, Kallenberg CG, Bijl M (2009) Longitudinal study on premature atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Atherosclerosis 206:546–550
Boros CA, Bradley TJ, Cheung MM, Bargman JM, Russell JL, McCrindle BW, Adeli K, Hamilton J, Silverman ED (2011) Early determinants of atherosclerosis in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29:575–581
Gerber HP, McMurtrey A, Kowalski J, Yan M, Keyt BA, Dixit V, Ferrara N (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. J Biol Chem 273:30336–30343
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Lee S, Chen TT, Barber CL, Jordan MC, Murdock J, Desai S, Ferrara N, Nagy A, Roos KP, Iruela-Arispe ML (2007) Autocrine VEGF signaling is required for vascular homeostasis. Cell 130:691–703
Mor F, Quintana FJ, Cohen IR (2004) Angiogenesis-inflammation cross-talk: vascular endothelial growth factor is secreted by activated T cells and induces Th1 polarization. J Immunol 172:4618–4623
Ferrara N, Davis-Smyth T (1997) The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev 18:4–25
Melter M, Reinders ME, Sho M, Pal S, Geehan C, Denton MD, Mukhopadhyay D, Briscoe DM (2000) Ligation of CD40 induces the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor by endothelial cells and monocytes and promotes angiogenesis in vivo. Blood 96:3801–3808
Robak E, Sysa-Jedrzejewska A, Robak T (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor and its soluble receptors VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mediators Inflamm 12:293–298
Avihingsanon Y, Benjachat T, Tassanarong A, Sodsai P, Kittikovit V, Hirankarn N (2009) Decreased renal expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in lupus nephritis is associated with worse prognosis. Kidney Int 75:1340–1348
Feliers D (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor as a prognostic marker of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 75:1251–1253
Kendall RL, Thomas KA (1993) Inhibition of vascular endothelial cell growth factor activity by an endogenously encoded soluble receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10705–10709
Kendall RL, Wang G, Thomas KA (1996) Identification of a natural soluble form of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, FLT-1, and its heterodimerization with KDR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 226:324–328
Roeckl W, Hecht D, Sztajer H, Waltenberger J, Yayon A, Weich HA (1998) Differential binding characteristics and cellular inhibition by soluble VEGF receptors 1 and 2. Exp Cell Res 241:161–170
Ebos JM, Bocci G, Man S, Thorpe PE, Hicklin DJ, Zhou D, Jia X, Kerbel RS (2004) A naturally occurring soluble form of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 detected in mouse and human plasma. Mol Cancer Res 2:315–326
Barleon B, Reusch P, Totzke F, Herzog C, Keck C, Martiny-Baron G, Marme D (2001) Soluble VEGFR-1 secreted by endothelial cells and monocytes is present in human serum and plasma from healthy donors. Angiogenesis 4:143–154
Hornig C, Barleon B, Ahmad S, Vuorela P, Ahmed A, Weich HA (2000) Release and complex formation of soluble VEGFR-1 from endothelial cells and biological fluids. Lab Invest 80:443–454
Lorquet S, Berndt S, Blacher S, Gengoux E, Peulen O, Maquoi E, Noel A, Foidart JM, Munaut C, Pequeux C (2010) Soluble forms of VEGF receptor-1 and −2 promote vascular maturation via mural cell recruitment. FASEB J 24:3782–3795
Pavlakovic H, Becker J, Albuquerque R, Wilting J, Ambati J (2010) Soluble VEGFR-2: an antilymphangiogenic variant of VEGF receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1207[Suppl 1]:E7–15
Oh H, Takagi H, Suzuma K, Otani A, Matsumura M, Honda Y (1999) Hypoxia and vascular endothelial growth factor selectively up-regulate angiopoietin-2 in bovine microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 274:15732–15739
Fiedler U, Scharpfenecker M, Koidl S, Hegen A, Grunow V, Schmidt JM, Kriz W, Thurston G, Augustin HG (2004) The Tie-2 ligand angiopoietin-2 is stored in and rapidly released upon stimulation from endothelial cell Weibel-Palade bodies. Blood 103:4150–4156
Fiedler U, Reiss Y, Scharpfenecker M, Grunow V, Koidl S, Thurston G, Gale NW, Witzenrath M, Rosseau S, Suttorp N, Sobke A, Herrmann M, Preissner KT, Vajkoczy P, Augustin HG (2006) Angiopoietin-2 sensitizes endothelial cells to TNF-alpha and has a crucial role in the induction of inflammation. Nat Med 12:235–239
Scharpfenecker M, Fiedler U, Reiss Y, Augustin HG (2005) The Tie-2 ligand angiopoietin-2 destabilizes quiescent endothelium through an internal autocrine loop mechanism. J Cell Sci 118:771–780
Boffa MC, Karmochkine M (1998) Thrombomodulin: an overview and potential implications in vascular disorders. Lupus 7[Suppl 2]:S120–125
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Doria A, Vesco P, Zulian F, Gambari PF (1994) The 1982 ARA/ACR criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus in pediatric and adult patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 12:689–690
Weening JJ, D'Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, Balow JE, Bruijn JA, Cook T, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Ginzler EM, Hebert L, Hill G, Hill P, Jennette JC, Kong NC, Lesavre P, Lockshin M, Looi LM, Makino H, Moura LA, Nagata M (2004) The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:241–250
Brunner HI, Feldman BM, Bombardier C, Silverman ED (1999) Sensitivity of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index, British Isles Lupus Assessment Group Index, and Systemic Lupus Activity Measure in the evaluation of clinical change in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 42:1354–1360
Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29:288–291
Narshi CB, Giles IP, Rahman A (2011) The endothelium: an interface between autoimmunity and atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus? Lupus 20:5–13
Cines DB, Lyss AP, Reeber M, Bina M, DeHoratius RJ (1984) Presence of complement-fixing anti-endothelial cell antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 73:611–625
Belmont HM, Abramson SB, Lie JT (1996) Pathology and pathogenesis of vascular injury in systemic lupus erythematosus. Interactions of inflammatory cells and activated endothelium. Arthritis Rheum 39:9–22
Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis–an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340:115–126
Ostendorf T, Kunter U, Eitner F, Loos A, Regele H, Kerjaschki D, Henninger DD, Janjic N, Floege J (1999) VEGF mediates glomerular endothelial repair. J Clin Invest 104:913–923
Eremina V, Sood M, Haigh J, Nagy A, Lajoie G, Ferrara N, Gerber HP, Kikkawa Y, Miner JH, Quaggin SE (2003) Glomerular-specific alterations of VEGF-A expression lead to distinct congenital and acquired renal diseases. J Clin Invest 111:707–716
Caccamo C, Nostro L, Giorgianni G, Mondello S, Crasci E, Frisina N, Buemi M (2007) Behavior of vascular endothelial growth factor and erythropoietin throughout the menstrual cycle in healthy women. J Reprod Med 52:1035–1039
Schiffer L, Bethunaickan R, Ramanujam M, Huang W, Schiffer M, Tao H, Madaio MP, Bottinger EP, Davidson A (2008) Activated renal macrophages are markers of disease onset and disease remission in lupus nephritis. J Immunol 180:1938–1947
Guo Q, Carrero JJ, Yu X, Barany P, Qureshi AR, Eriksson M, Anderstam B, Chmielewski M, Heimburger O, Stenvinkel P, Lindholm B, Axelsson J (2009) Associations of VEGF and its receptors sVEGFR-1 and −2 with cardiovascular disease and survival in prevalent haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:3468–3473
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Bogdanovic E, Alami J, Van Slyke P, Francia G, Xu P, Mutsaers AJ, Dumont DJ, Kerbel RS (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated decrease in plasma soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 levels as a surrogate biomarker for tumor growth. Cancer Res 68:521–529
Davis B, Dei Cas A, Long DA, White KE, Hayward A, Ku CH, Woolf AS, Bilous R, Viberti G, Gnudi L (2007) Podocyte-specific expression of angiopoietin-2 causes proteinuria and apoptosis of glomerular endothelia. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2320–2329
Yuan HT, Tipping PG, Li XZ, Long DA, Woolf AS (2002) Angiopoietin correlates with glomerular capillary loss in anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 61:2078–2089
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the OeNB Jubiläumsfonds, Austria (13334) to ME.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edelbauer, M., Kshirsagar, S., Riedl, M. et al. Soluble VEGF receptor 1 promotes endothelial injury in children and adolescents with lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 27, 793–800 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-2062-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-2062-z