Abstract
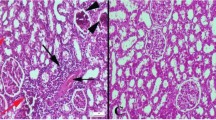
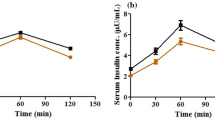
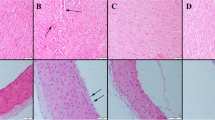
The study determines the effect of soy protein on inflammatory status and expression of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB P65) and receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) in a metabolic syndrome (MS) model. MS was induced in adult male rats by feeding them a high fructose diet (60 g/100 g diet). The rats were randomised into six groups by feeding one of the following semi-synthetic diets for 60 days: corn starch (60%) and casein (20%; CCD), fructose (60%) and casein (20%; FCD), fructose (60%) and soy protein (20%; FSD) or corn starch (60%) and soy protein (20%; CSD). The expression of NF-κB P65, transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and RAGE, histochemical localization of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) assays, collagen deposition and ultrastructural analysis were performed. FCD rats displayed inflammatory changes and increased expression of growth factors and nuclear factors. FSD rats showed reduction in inflammation, fibrogenesis, collagen deposition, NF-κB activation and mitigated the ultrastructural changes. Soy protein prevents inflammation and early nephropathic changes in the MS model secondary to the attenuation of NF-κB activation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elliott SS, Keim NL, Stern JS, Teff K, Havel PJ (2002) Fructose, weight gain, and the insulin resistance syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 76:911–922
Sánchez-Lozada LG, Tapia E, Jiménez A, Bautista P, Cristóbal M, Nepomuceno T, Soto V, Avila-Casado C, Nakagawa T, Johnson RJ, Herrera-Acosta J, Franco M (2007) Fructose-induced metabolic syndrome is associated with glomerular hypertension and renal microvascular damage in rats. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 292:F423–F429
Zhou G, Li C, Cai L (2004) Advanced glycation end-products induce connective tissue growth factor-mediated renal fibrosis predominantly through transforming growth factor beta-independent pathway. Am J Pathol 165:2033–2043
Navarro-González JF, Mora-Fernández C (2008) The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:433–442
Lazar MA (2006) The humoral side of insulin resistance. Nat Med 12:43–54
Dandona P, Aljada A, Bandyopadhyay A (2004) Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol 25:4–7
Tan AL, Forbes JM, Cooper ME (2007) AGE, RAGE, and ROS in diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 27:130–143
Bierhaus A, Humpert PM, Morcos M, Wendt T, Chavakis T, Arnold B, Stern DM, Nawroth PP (2005) Understanding RAGE, the receptor for advanced glycation end products. J Mol Med 83:876–886
Moynagh PN (2005) The NF-κB pathway. J Cell Sci 118:4389–4392
Tan HW, Xing SS, Bi XP, Li L, Gong HP, Zhong M, Zhang Y, Zhang W (2008) Felodipine attenuates vascular inflammation in a fructose-induced rat model of metabolic syndrome via the inhibition of NF-kappa B activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:1051–1059
Azadbakht L, Shakerhosseini R, Atabak S, Jamshidian M, Mehrabi Y, Esmaill-Zadeh A (2003) Beneficiary effect of dietary soy protein on lowering plasma levels of lipid and improving kidney function in type II diabetes with nephropathy. Eur J Clin Nutr 57:1292–1294
Tovar AR, Murguía F, Cruz C, Hernández-Pando R, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Correa-Rotter R, Torres N (2002) A soy protein diet alters hepatic lipid metabolism gene expression and reduces serum lipids and renal fibrogenic cytokines in rats with chronic nephrotic syndrome. J Nutr 132:2562–2569
Lavigne C, Marette A, Jacques H (2000) Cod and soy proteins compared with casein improve glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:491–500
Palanisamy N, Viswanathan P, Ravichandran MK, Anuradha CV (2010) Renoprotective and blood pressure lowering effect of dietary soy protein via protein kinase C-β II inhibition in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 88:28–37
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Woessner JF (1961) The determination of hydroxy proline in tissue and protein samples containing small portions of this amino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys 93:440–447
Paz MA, Lent RW, Faris B, Frazblan C, Blumfeld OO, Gallop PM (1969) Aldehydes in native and denatured calfskin procollagen. Biochem Biophys Res Com 34:221–229
Rao P, Pattabiraman TN (1990) Reevaluation of the phenol sulphuric acid reaction for the estimation of hexoses and pentoses. Anal Biochem 181:18–22
Niehaus WG, Samuelson B (1986) Formation of MDA from phospholipid arachidonate during microsomal lipid peroxidation. Eur J Biochem 6:126–130
Miller EJ, Rhodes RK (1982) Preparation and characterization of different types of collagen. Meth Enzymol 82:33–64
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin’s-Phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Palanisamy N, Viswanathan P, Anuradha CV (2008) Effect of genistein, a soy isoflavone, on whole body insulin sensitivity and renal damage induced by a high-fructose diet. Ren Fail 30:645–654
Levi B, Werman MJ (1998) Long-term fructose consumption accelerates glycation and several age-related variables. J Nutr 128:1442–1449
Vasdev S, Ford CA, Longerich L, Gadag V, Wadhawan S (1998) Role of aldehydes in fructose-induced hypertension. Mol Cell Biochem 181:1–9
Alexandraki K, Piperi C, Kalofoutis C, Singh J, Alaveras A, Kalofoutis A (2006) The inflammatory process in type 2 diabetes. The role of cytokines. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1084:89–117
Chang JW, Kim CS, Kim SB, Park SK, Park JS, Lee SK (2006) Proinflammatory cytokine-induced NF-kappa B activation in human mesangial cells is mediated through intracellular calcium but not ROS: effects of silymarin. Nephron Exp Nephrol 103:156–165
Ortiz A, Bustos C, Alonso J, Alcázar R, López-Armada MJ, Plaza JJ, González E, Egido J (1995) Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the pathogenesis of experimental and human glomerulonephritis. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp 24:53–77
Navarro JF, Milena FJ, Mora C, Leon C, Garcıa J (2006) Renal pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression in diabetic nephropathy: effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and pentoxifylline administration. Am J Nephrol 26:562–570
Dalla Vestra M, Mussap M, Gallina P, Bruseghin M, Cernigoi AM, Saller A, Plebani M, Fioretto P (2005) Acute-phase markers of inflammation and glomerular structure in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:S78–S82
Coleman DL, Ruef C (1992) Interleukin-6: an autocrine regulator of mesangial cell growth. Kidney Int 41:604–606
Prud’homme GJ (2007) Pathobiology of transforming growth factor (beta) in cancer, fibrosis and immunologic disease, and therapeutic considerations. Lab Invest 87:1077–1091
Sharma K, Ziyadeh FN (1995) Hyperglycemia and diabetic kidney disease: the case for transforming growth factor-β1 as a key mediator. Diabetes 4:1139–1146
Wang W, Koka V, Lan HY (2005) Transforming growth factor-(beta) and Smad signalling in kidney diseases. Nephrol 10:48–56
Trujillo J, Cruz C, Tovar A, Vaidya V, Zambrano E, Bonventre JV, Gamba G, Torres N, Bobadilla NA (2008) Renoprotective mechanisms of soy protein intake in the obese Zucker rat. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 295:F1574–F1582
Pat B, Hughson MB, Nicol J, Hoy WE, Gobe GC (2007) A comparison of pathomolecular markers of fibrosis and morphology in kidney from autopsies of African Americans and whites. Virchows Arch 450:41–50
Ng YY, Huang TP, Yang WC, Chen ZP, Yang AH, Mu W (1998) Tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation in progressive tubulointerstitial fibrosis in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Kidney Int 54:864–876
Smoyer WE, Mundel P (1998) Regulation of podocyte structure during the development of nephrotic syndrome. J Mol Med 76:172–183
Zhuo J, Ohishi M, Mendelsohn FA (1999) Roles of AT1 and AT2 receptors in the hypertensive Ren-2 gene transgenic rat kidney. Hypertension 33:347–353
Ijpelaar DH, Schulz A, Koop K, Schlesener M, Bruijn JA, Kerjaschki D, Kreutz R, de Heer E (2008) Glomerular hypertrophy precedes albuminuria and segmental loss of podoplanin in podocytes in Munich-Wistar-Frömter rats. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 294:758–767
Kerjaschki D (2001) Caught flat-footed: podocyte damage and the molecular bases of focal glomerulosclerosis. J Clin Invest 108:1583–1587
Sinha S, Perdomo G, Brown NF, O’Doherty RM (2004) Fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in L6 myotubes is prevented by inhibition of activation and nuclear localization of nuclear factor kappa B. J Biol Chem 279:41294–41301
Boden G, She P, Mozzoli M, Cheung P, Gumireddy K, Reddy P, Xiang X, Luo Z, Ruderman N (2005) Free fatty acids produce insulin resistance and activate the proinflammatory nuclear factor-kappa B pathway in rat liver. Diabetes 54:3458–3465
Barma P, Bhattacharya S, Bhattacharya A, Kundu R, Dasgupta S, Biswas A, Bhattacharya S, Roy SS, Bhattacharya S (2009) Lipid induced over expression of NF-kappa B in skeletal muscle cells is linked to insulin resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:190–200
Chen L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wang B (2008) Improvement of inflammatory responses associated with NF-kB pathway in kidneys from diabetic rat. Inflamm Res 57:199–204
Tomobe K, Philbrick DJ, Ogborn MR, Takahashi H, Holub BJ (1998) Effect of dietary soy protein and genistein on disease progression in mice with polycystic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 31:55–61
Maddox DA, Alavi FK, Silbernick EM, Zawada ET (2002) Protective effects of a soy diet in preventing obesity-linked renal disease. Kidney Int 61:96–104
Gilani GS, Cockell KA, Sepehr E (2005) Effects of antinutritional factors on protein digestibility and amino acid availability in foods. J AOAC Int 88:967–987
Vanden Berghe W, Dijsselbloem N, Vermeulen L, Ndlovu N, Boone E, Haegeman G (2006) Attenuation of mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1-driven nuclear factor-kappa B gene expression by soy isoflavones does not require estrogenic activity. Cancer Res 66:4852–4862
Acknowledgements
The financial support in the form of a Senior Research Fellowship to Mr. N. Palanisamy from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi is gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank Mr. Manickam M, Sakthi Sugars Pvt Ltd, a division of Sakthi Soya Pvt Ltd, Coimbatore, India for providing soy protein. The authors are also thankful to Dr. Ramamurthy, Director, National Centre for Ultrafast Process, Dr. Rama Gopalan, Head, Department of Pathology, University of Madras, Chennai, India for their help in immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article has been retracted. The core data and conclusions were published before in another journal: Eur J Pharmacol. (2011 Sep 30;667:355-64.). There is considerable overlap in the main sections.
The Retraction Note to this article can be found at https://doi.org/dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2398-z.
About this article
Cite this article
Palanisamy, N., Venkataraman Anuradha, C. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Soy protein prevents renal damage in a fructose-induced model of metabolic syndrome via inhibition of NF-kB in male rats. Pediatr Nephrol 26, 1809–1821 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1882-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1882-1