Abstract
Background
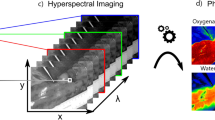
HSI is an optical technology allowing for a real-time, contrast-free snapshot of physiological tissue properties, including oxygenation. Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) has the potential to quantify the gastrointestinal perfusion intraoperatively. This experimental study evaluates the accuracy of HSI, in order to quantify bowel perfusion, and to obtain a superposition of the hyperspectral information onto real-time images.
Methods
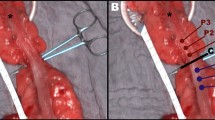
In 6 pigs, 4 ischemic bowel loops were created (A, B, C, D) and imaged at set time points (from 5 to 360 min). A commercially available HSI system provided pseudo-color maps of the perfusion status (StO2, Near-InfraRed perfusion) and the tissue water index. An ad hoc software was developed to superimpose HSI information onto the live video, creating the HYPerspectral-based Enhanced Reality (HYPER). Seven regions of interest (ROIs) were identified in each bowel loop according to StO2 ranges, i.e., vascular (VASC proximal and distal), marginal vascular (MV proximal and distal), marginal ischemic (MI proximal and distal), and ischemic (ISCH). Local capillary lactates (LCL), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and histopathology were measured at the ROIs. A machine-learning-based prediction algorithm of LCL, based on the HSI-StO2%, was trained in the 6 pigs and tested on 5 additional animals.
Results
HSI parameters (StO2 and NIR) were congruent with LCL levels, ROS production, and histopathology damage scores at the ROIs discriminated by HYPER. The global mean error of LCL prediction was 1.18 ± 1.35 mmol/L. For StO2 values > 30%, the mean error was 0.3 ± 0.33.
Conclusions
HYPER imaging could precisely quantify the overtime perfusion changes in this bowel ischemia model.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell C, Reames MK, Robinson M, Symanowski J, Salo JC (2015) Conduit vascular evaluation is associated with reduction in anastomotic leak after esophagectomy. J Gastrointest Surg 19:806–812
Karliczek A, Benaron DA, Baas PC, Zeebregts CJ, Wiggers T, van Dam GM (2010) Intraoperative assessment of microperfusion with visible light spectroscopy for prediction of anastomotic leakage in colorectal anastomoses. Colorectal Dis 12:1018–1025
Urbanavicius L, Pattyn P, de Putte DV, Venskutonis D (2011) How to assess intestinal viability during surgery: a review of techniques. World J Gastrointest Surg 3:59–69
Karliczek A, Harlaar NJ, Zeebregts CJ, Wiggers T, Baas PC, van Dam GM (2009) Surgeons lack predictive accuracy for anastomotic leakage in gastrointestinal surgery. Int J Colorectal Dis 24:569–576
Baiocchi GL, Diana M, Boni L (2018) Indocyanine green-based fluorescence imaging in visceral and hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery: state of the art and future directions. World J Gastroenterol 24:2921–2930
Diana M (2017) Enabling precision digestive surgery with fluorescence imaging. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:97
Diana M (2017) Fluorescence-guided surgery applied to the digestive system: the cybernetic eye to see the invisible. Cir Esp. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ciresp.2017.07.006
Kudszus S, Roesel C, Schachtrupp A, Hoer JJ (2010) Intraoperative laser fluorescence angiography in colorectal surgery: a noninvasive analysis to reduce the rate of anastomotic leakage. Langenbecks Arch Surg 395:1025–1030
Matsui A, Winer JH, Laurence RG, Frangioni JV (2011) Predicting the survival of experimental ischaemic small bowel using intraoperative near-infrared fluorescence angiography. Br J Surg 98:1725–1734
Jafari MD, Wexner SD, Martz JE, McLemore EC, Margolin DA, Sherwinter DA, Lee SW, Senagore AJ, Phelan MJ, Stamos MJ (2015) Perfusion assessment in laparoscopic left-sided/anterior resection (PILLAR II): a multi-institutional study. J Am Coll Surg 220(82–92):e81
Ris F, Liot E, Buchs NC, Kraus R, Ismael G, Belfontali V, Douissard J, Cunningham C, Lindsey I, Guy R, Jones O, George B, Morel P, Mortensen NJ, Hompes R, Cahill RA, Near-Infrared Anastomotic Perfusion Assessment Network V (2018) Multicentre phase II trial of near-infrared imaging in elective colorectal surgery. Br J Surg 105:1359–1367
Blanco-Colino R, Espin-Basany E (2018) Intraoperative use of ICG fluorescence imaging to reduce the risk of anastomotic leakage in colorectal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tech Coloproctol 22:15–23
Karampinis I, Keese M, Jakob J, Stasiunaitis V, Gerken A, Attenberger U, Post S, Kienle P, Nowak K (2018) Indocyanine green tissue angiography can reduce extended bowel resections in acute mesenteric ischemia. J Gastrointest Surg 22:2117–2124
van den Bos J, Al-Taher M, Schols RM, van Kuijk S, Bouvy ND, Stassen LPS (2018) Near-infrared fluorescence imaging for real-time intraoperative guidance in anastomotic colorectal surgery: a systematic review of literature. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 28:157–167
Vallance A, Wexner S, Berho M, Cahill R, Coleman M, Haboubi N, Heald RJ, Kennedy RH, Moran B, Mortensen N, Motson RW, Novell R, O’Connell PR, Ris F, Rockall T, Senapati A, Windsor A, Jayne DG (2017) A collaborative review of the current concepts and challenges of anastomotic leaks in colorectal surgery. Colorectal Dis 19:O1–O12
Diana M, Agnus V, Halvax P, Liu YY, Dallemagne B, Schlagowski AI, Geny B, Diemunsch P, Lindner V, Marescaux J (2015) Intraoperative fluorescence-based enhanced reality laparoscopic real-time imaging to assess bowel perfusion at the anastomotic site in an experimental model. Br J Surg 102:e169–e176
Diana M, Noll E, Diemunsch P, Dallemagne B, Benahmed MA, Agnus V, Soler L, Barry B, Namer IJ, Demartines N, Charles AL, Geny B, Marescaux J (2014) Enhanced-reality video fluorescence: a real-time assessment of intestinal viability. Ann Surg 259:700–707
Wada T, Kawada K, Takahashi R, Yoshitomi M, Hida K, Hasegawa S, Sakai Y (2017) ICG fluorescence imaging for quantitative evaluation of colonic perfusion in laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc 31:4184–4193
Lu G, Fei B (2014) Medical hyperspectral imaging: a review. J Biomed Opt 19:10901
Akbari H, Kosugi Y, Kojima K, Tanaka N (2010) Detection and analysis of the intestinal ischemia using visible and invisible hyperspectral imaging. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57:2011–2017
Holmer A, Marotz J, Wahl P, Dau M, Kammerer PW (2018) Hyperspectral imaging in perfusion and wound diagnostics—methods and algorithms for the determination of tissue parameters. Biomed Tech 63:547–556
Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG, Group NCRRGW (2010) Animal research: reporting in vivo experiments: the ARRIVE guidelines. J Gene Med 12:561–563
Noll E, Diana M, Charles AL, Singh F, Gan TJ, Pottecher J, Moussallieh FM, Namer IJ, Geny B, Diemunsch P (2017) Comparative analysis of resuscitation using human serum albumin and crystalloids or 130/0.4 hydroxyethyl starch and crystalloids on skeletal muscle metabolic profile during experimental haemorrhagic shock in swine: a randomised experimental study. Eur J Anaesthesiol 34:89–97
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ, Gurd FN (1970) Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. I. A morphological, hemodynamic, and metabolic reappraisal. Arch Surg 101:478–483
Diana M, Noll E, Charles AL, Diemunsch P, Geny B, Liu YY, Marchegiani F, Schiraldi L, Agnus V, Lindner V, Swanstrom L, Dallemagne B, Marescaux J (2017) Precision real-time evaluation of bowel perfusion: accuracy of confocal endomicroscopy assessment of stoma in a controlled hemorrhagic shock model. Surg Endosc 31:680–691
Diana M, Noll E, Diemunsch P, Moussallieh FM, Namer IJ, Charles AL, Lindner V, Agnus V, Geny B, Marescaux J (2015) Metabolism-guided bowel resection: potential role and accuracy of instant capillary lactates to identify the optimal resection site. Surg Innov 22:453–461
Diana M, Noll E, Agnus V, Liu YY, Kong SH, Legner A, Diemunsch P, Marescaux J (2017) Reply to letter: “Enhanced reality fluorescence videography to assess bowel perfusion: the cybernetic eye”. Ann Surg 265:e49–e52
Diana M, Dallemagne B, Chung H, Nagao Y, Halvax P, Agnus V, Soler L, Lindner V, Demartines N, Diemunsch P, Geny B, Swanstrom L, Marescaux J (2014) Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy and fluorescence-based enhanced reality for real-time assessment of intestinal microcirculation in a porcine model of sigmoid ischemia. Surg Endosc 28:3224–3233
Quero G, Lapergola A, Barberio M, Seeliger B, Saccomandi P, Guerriero L, Mutter D, Saadi A, Worreth M, Marescaux J, Agnus V, Diana M (2018) Discrimination between arterial and venous bowel ischemia by computer-assisted analysis of the fluorescent signal. Surg Endosc 33:1988–1997
Zuzak KJ, Naik SC, Alexandrakis G, Hawkins D, Behbehani K, Livingston E (2008) Intraoperative bile duct visualization using near-infrared hyperspectral video imaging. Am J Surg 195:491–497
Kohler H, Jansen-Winkeln B, Maktabi M, Barberio M, Takoh J, Holfert N, Moulla Y, Niebisch S, Diana M, Neumuth T, Rabe SM, Chalopin C, Melzer A, Gockel I (2019) Evaluation of hyperspectral imaging (HSI) for the measurement of ischemic conditioning effects of the gastric conduit during esophagectomy. Surg Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06675-4
Jansen-Winkeln B, Maktabi M, Takoh JP, Rabe SM, Barberio M, Kohler H, Neumuth T, Melzer A, Chalopin C, Gockel I (2018) Hyperspectral imaging of gastrointestinal anastomoses. Chirurg 89:717–725
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Guy Temporal and Camille Goustiaux, professionals in medical English proofreading, for their valuable help with revising the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the ARC Foundation through the ELIOS (Endoscopic Luminescent Imaging for precision Oncologic Surgery) Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Jacques Marescaux is the President of both IRCAD and IHU Strasbourg Institutes, which are partly funded by KARL STORZ, Siemens, and Medtronic. Michele Diana is the recipient of the ELIOS grant. Manuel Barberio, Fabio Longo, Claudio Fiorillo, Barbara Seeliger, Pietro Mascagni, Vincent Agnus, Veronique Lindner, Bernard Geny, Anne-Laure Charles, Ines Gockel, Marc Worreth, and Alend Saadi have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barberio, M., Longo, F., Fiorillo, C. et al. HYPerspectral Enhanced Reality (HYPER): a physiology-based surgical guidance tool. Surg Endosc 34, 1736–1744 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06959-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06959-9