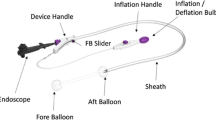
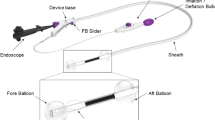
Abstract
Background
Colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is challenging as a result of the limited ability of conventional endoscopic instruments to achieve traction and exposure. The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of colonic ESD in a porcine model using a novel endoscopic surgical platform, the Anubiscope (Karl Storz, Tüttlingen, Germany), equipped with two working channels for surgical instruments with four degrees of freedom offering surgical triangulation.
Methods
Nine ESDs were performed by a surgeon without any ESD experience in three swine, at 25, 15, and 10 cm above the anal verge with the Anubiscope. Sixteen ESDs were performed by an experienced endoscopist in five swine using conventional endoscopic instruments. Major ESD steps included the following for both groups: scoring the area, submucosal injection of glycerol, precut, and submucosal dissection. Outcomes measured were as follows: dissection time and speed, specimen size, en bloc dissection, and complications.
Results
No perforations occurred in the Anubis group, while there were eight perforations (50 %) in the conventional group (p = 0.02). Complete and en bloc dissections were achieved in all cases in the Anubis group. Mean dissection time for completed cases was statistically significantly shorter in the Anubis group (32.3 ± 16.1 vs. 55.87 ± 7.66 min; p = 0.0019). Mean specimen size was higher in the conventional group (1321 ± 230 vs. 927.77 ± 229.96 mm2; p = 0.003), but mean dissection speed was similar (35.95 ± 18.93 vs. 23.98 ± 5.02 mm2/min in the Anubis and conventional groups, respectively; p = 0.1).
Conclusions
Colonic ESDs were feasible in pig models with the Anubiscope. This surgical endoscopic platform is promising for endoluminal surgical procedures such as ESD, as it is user-friendly, effective, and safe.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saito Y, Fukuzawa M, Matsuda T, Fukunaga S, Sakamoto T, Uraoka T, Nakajima T, Ikehara H, Fu KI, Itoi T, Fujii T (2010) Clinical outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal tumors as determined by curative resection. Surg Endosc 24:343–352
Fujishiro M (2008) Perspective on the practical indications of endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastrointestinal neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 14:4289–4295
Parra-Blanco A, Nicolas D, Arnau MR, Gimeno-Garcia AZ, Rodrigo L, Quintero E (2011) Gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection assisted by a new traction method: the clip-band technique. A feasibility study in a porcine model (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 74:1137–1141
Tanaka S, Oka S, Chayama K (2008) Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection: present status and future perspective, including its differentiation from endoscopic mucosal resection. J Gastroenterol 43:641–651
Saito Y, Uraoka T, Matsuda T, Emura F, Ikehara H, Mashimo Y, Kikuchi T, Fu KI, Sano Y, Saito D (2007) Endoscopic treatment of large superficial colorectal tumors: a case series of 200 endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 66:966–973
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Muraki Y, Ono S, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Oka M, Ogura K, Kawabe T, Ichinose M, Omata M (2007) Outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms in 200 consecutive cases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:678–683
Sakamoto N, Osada T, Shibuya T, Beppu K, Matsumoto K, Mori H, Kawabe M, Nagahara A, Otaka M, Ogihara T, Watanabe S (2009) Endoscopic submucosal dissection of large colorectal tumors by using a novel spring-action S-O clip for traction (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 69:1370–1374
Neuhaus H, Costamagna G, Deviere J, Fockens P, Ponchon T, Rosch T (2006) Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) of early neoplastic gastric lesions using a new double-channel endoscope (the “R-scope”). Endoscopy 38:1016–1023
Yonezawa J, Kaise M, Sumiyama K, Goda K, Arakawa H, Tajiri H (2006) A novel double-channel therapeutic endoscope (“R-scope”) facilitates endoscopic submucosal dissection of superficial gastric neoplasms. Endoscopy 38:1011–1015
Dallemagne B, Marescaux J (2010) The ANUBIS™ project. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 19:257–261
Dhumane PW, Diana M, Leroy J, Marescaux J (2011) Minimally invasive single-site surgery for the digestive system: a technological review. J Minim Access Surg 7:40–51
Leroy J, Diana M, Barry B, Mutter D, Melani AG, Wu HS, Marescaux J (2012) Perirectal Oncologic Gateway to Retroperitoneal Endoscopic Single-Site Surgery (PROGRESSS): a feasibility study for a new NOTES approach in a swine model. Surg Innov 19:345–352
Perretta S, Dallemagne B, Barry B, Marescaux J (2013) The ANUBISCOPE® flexible platform ready for prime time: description of the first clinical case. Surg Endosc 27(7):2630
Uraoka T, Saito Y, Matsuda T, Ikehara H, Gotoda T, Saito D, Fujii T (2006) Endoscopic indications for endoscopic mucosal resection of laterally spreading tumours in the colorectum. Gut 55:1592–1597
Shono T, Ishikawa K, Ochiai Y, Nakao M, Togawa O, Nishimura M, Arai S, Nonaka K, Sasaki Y, Kita H (2011) Feasibility of endoscopic submucosal dissection: a new technique for en bloc resection of a large superficial tumor in the colon and rectum. Int J Surg Oncol 2011:948293
Bickenbach K, Strong VE (2012) Comparisons of gastric cancer treatments: East vs. West. J Gastric Cancer 12:55–62
Imaeda H, Iwao Y, Ogata H, Ichikawa H, Mori M, Hosoe N, Masaoka T, Nakashita M, Suzuki H, Inoue N, Aiura K, Nagata H, Kumai K, Hibi T (2006) A new technique for endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer using an external grasping forceps. Endoscopy 38:1007–1010
Rieder E, Makris KI, Martinec DV, Swanstrom LL (2011) The suture-pulley method for endolumenal triangulation in endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy 43(suppl 2 UCTN):E319–E320
Li CH, Chen PJ, Chu HC, Huang TY, Shih YL, Chang WK, Hsieh TY (2011) Endoscopic submucosal dissection with the pulley method for early-stage gastric cancer (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 73:163–167
Acknowledgments
IRCAD-IHU Institutes are recipients of grants from Karl Storz Endoscopes, Tüttlingen, Germany; Covidien, Mansfield, MA, USA; and Siemens AG Healthcare, Munich, Germany. The authors acknowledge the European Funding for Regional Development (FEDER) and the Region of Alsace for supporting the ISIS project. The authors are grateful to Guy Temporal, Camille Fischer, and Christopher Burel for their valuable assistance.
Disclosures
Michele Diana, Hyunsoo Chung, Keng-Hao Liu, Bernard Dallemagne, Nicolas Demartines, Didier Mutter, and Jacques Marescaux have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Michele Diana and Hyunsoo Chung equally contributed to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diana, M., Chung, H., Liu, KH. et al. Endoluminal surgical triangulation: overcoming challenges of colonic endoscopic submucosal dissections using a novel flexible endoscopic surgical platform: feasibility study in a porcine model. Surg Endosc 27, 4130–4135 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3049-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3049-6