Abstract
Background
The aim of this study is to evaluate the utility of image cytometry (ICM)-DNA analysis on cytological brush specimens in improving the sensitivity and diagnostic accuracy for biliary neoplasias.
Methods
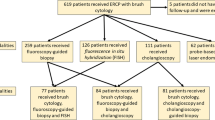
A total of 71 patients with 89 samples of biliary tree brushing from a stenosis were included in this prospective study. Conventional cytology (CC) and DNA ploidy using ICM of the brushing were performed. Benign or malignant findings were confirmed by surgical exploration or a clinical follow-up of at least 12 months.
Results
Diagnosis was confirmed by clinical follow-up in 44 cases and surgical investigation or histology in 41 cases. A definitive diagnosis of the smears resulted in 40 malignant and 49 benign diagnoses. The sensitivity was 0.666 for CC and 0.658 for ICM, and the specificity was 0.920 and 0.937, respectively. The positive predictive value (PPV) was 0.866 for CC and 0.900 for ICM. McNemar’s test did not reveal a significant difference between CC and ICM (P = 0.803). Agreement of the two methods was found in 73 samples, raising specificity to 0.998 but not sensitivity (0.725).
Conclusions
ICM-DNA seems not to improve significantly the PPV and NPV for detecting neoplasias of the biliary tract compared to CC. Nevertheless a clinical advantage can be seen in the agreement of the two methods in diagnosing dysplasia or cancer, since it did not show false positive results.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CC:
-
Conventional cytology
- ICM:
-
DNA-image-cytometry
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- PSC:
-
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- SL:
-
Stem line
References
de Bellis M, Sherman S, Fogel DL, Cramer H, Chappo J, McHenry L Jr, Watkins JL, Lehman GA (2002) Tissue sampling at ERCP in suspected malignant biliary strictures (part 1). Gastroint Endosc 4:552–561
Volmar KE, Vollmer RT, Routbort MJ, Creager AJ (2006) Pancreatic and bile duct brushing cytology in 1, 000 cases. Cancer Cytopathol 108:231–238
Dumonceau JM, Gomez CM, Casco C, Genevay M II, Marcolongo M, Bongiovanni M, Morel P, Majno P, Hadengue A (2008) Grasp or brush for biliary sampling at endoscopic retrograde cholangiography? A blinded randomized controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol 103:333–340
Selvaggi SM (2004) Biliary brushing cytology. Cytopathology 15:74–79
Haroske G, Baak JP, Danielsen H, Giroud F, Gschwendtner A, Oberholzer M, Reith A, Spieler P, Böcking A (2001) Fourth updated ESACP consensus report on diagnostic DNA image cytometry. Anal Cell Pathol 23:89–95
Fogel EL, de Bellis M, McHenry L, Watkins JL, Chappo J, Cramer H, Schmidt S, Lazzell-Pannell S, Sherman S, Lehman GA (2006) Effectiveness of a new long cytology brush in the evaluation of malignant biliary obstruction: a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc 63:71–77
Wakabayashi H, Akamoto S, Yachida S, Okano K, Izuishi K, Nishiyama Y, Maeta H (2005) Significance of fluorodeoxyglucose PET imaging in the diagnosis of malignancies in patients with biliary stricture. Eur J Surg Oncol 31:1175–1179
Prytz H, Keiding S, Bjornsson E, Broome U, Almer S, Castedal M, Munk OL (2006) Dynamic FDG-PET is useful for detection of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with PSC listed for liver transplantation. Swedish Internal Medicine Liver Club. Hepatology 44:1572–1580
Osterheld MC, Andrejevic Blant S, Caron L, Braunschweig R, Dorta G, Bouzourene H, Mihaescu A (2005) Digital image DNA cytometry: a useful tool for the evaluation of malignancy in biliary strictures. Cell Oncol 27:255–260
Rumalla A, Baron Th, Leontovich O, Burgart LJ, Yacavone RF, Therneau TM, De Groen PC, Sebo TJ (2001) Improved diagnostic yield of endoscopic biliary brush cytology by digital image analysis. Mayo Clin Proc 76:29–33
Baron TH, Harewood GC, Rumalla A, Pochron NL, Stadheim LM, Gores GJ, Therneau TM, De Groen PC, Sebo TJ, Salomao DR, Dipp BR (2004) A prospective comparison of digital image analysis and routine cytology for the identification of malignancy in biliary tract strictures. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:214–219
Lindberg B, Enochsson L, Tribukait B, Arnelo U, Bergquist A (2006) Diagnostic and prognostic implications of DNA ploidy and S-phase evaluation in the assessment of malignancy in biliary strictures. Endoscopy 38:561–565
Disclosures
Janek Binek, Nadja Lindenmann, Christa M. Meyenberger, Margarete Hell, Hanno Ulmer, Peter Spieler, and Jan Borovicka have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binek, J., Lindenmann, N., Meyenberger, C.M. et al. Malignant biliary stenosis: conventional cytology versus DNA image cytometry. Surg Endosc 25, 1808–1813 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1469-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1469-0