Abstract
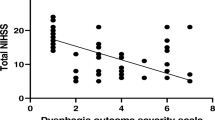
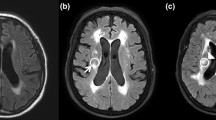
The subcortex is an important region in terms of swallowing function that passes fibers from the swallowing center to the cortex. However, studies on the relationship between the hemorrhage size and characteristics of dysphagia were lacking. In the present study, the relationship between subcortical hemorrhage size and characteristics of dysphagia was assessed in patients with subcortical hemorrhage. This study recruited retrospectively 49 subcortical hemorrhage patients with dysphagia. The hemorrhage size was measured and the clinical dysphagia scale (CDS) was used to evaluate the severity of dysphagia. The relationship between CDS score and hemorrhage size was analyzed. Subjects were divided into 2 groups according to average hemorrhage size of the subjects. The CDS scores of the 2 groups were compared and the relationship between each CDS item and hemorrhage size was analyzed. A significant positive correlation was observed between hemorrhage size and total CDS score. Also, a significant correlation was observed when patients over 70 years of age were excluded. The total CDS score in the large hemorrhage group was significantly higher than the CDS score in the small hemorrhage group. The CDS items including tracheostomy, lip sealing, tongue protrusion, laryngeal elevation, and reflex coughing were significantly correlated with hemorrhage size. In this study, the hemorrhage size in patients with subcortical hemorrhage correlated with the severity of dysphagia. In addition, the hemorrhage size was correlated with specific CDS items. These findings should be considered when treating subcortical hemorrhage patients with dysphagia in a clinical setting.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CDS:
-
Clinical dysphagia scale
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- VFSS:
-
Videofluoroscopic swallowing study
- IQR:
-
Interquantile range
References
Singh S, Hamdy S. Dysphagia in stroke patients. Postgrad Med J. 2006;82:383–91.
Holas MA, DePippo KL, Reding MJ. Aspiration and relative risk of medical complications following stroke. Arch Neurol. 1994;51:1051–3.
Kidd D, Lawson J, Nesbitt R, MacMahon J. The natural history and clinical consequences of aspiration in acute stroke. QJM. 1995;88:409–13.
Katzan IL, Cebul RD, Husak SH, Dawson NV, Baker DW. The effect of pneumonia on mortality among patients hospitalized for acute stroke. Neurology. 2003;60:620–5.
Horner J, Massey EW. Silent aspiration following stroke. Neurology. 1988;38:317–9.
Paciaroni M, Mazzotta G, Corea F, Caso V, Venti M, Milia P, Silvestrelli G, Palmerini F, Parnetti L, Gallai V. Dysphagia following stroke. Eur Neurol. 2004;51:162–7.
Robbins J, Levine RL, Maser A, Rosenbek JC, Kempster GB. Swallowing after unilateral stroke of the cerebral cortex. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993;74:1295–300.
Daniels SK, Foundas AL. Lesion localization in acute stroke patients with risk of aspiration. J Neuroimaging. 1999;9:91–8.
Steinhagen V, Grossmann A, Benecke R, Walter U. Swallowing disturbance pattern relates to brain lesion location in acute stroke patients. Stroke. 2009;40:1903–6.
Logemann JA, Shanahan T, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ, Lazar R, Halper A. Oropharyngeal swallowing after stroke in the left basal ganglion/internal capsule. Dysphagia. 1993;8:230–4.
Wan P, Chen X, Zhu L, Xu S, Huang L, Li X, Ye Q, Ding R. Dysphagia post subcortical and supratentorial stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;25:74–82.
Nakagawa T, Sekizawa K, Arai H, Kikuchi R, Manabe K, Sasaki H. High incidence of pneumonia in elderly patients with basal ganglia infarction. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:321–4.
Broderick JP, Brott TG, Duldner JE, Tomsick T, Huster G. Volume of intracerebral hemorrhage. A powerful and easy-to-use predictor of 30-day mortality. Stroke. 1993;24:987–93.
Franke CL, Versteege CW, van Gijn J. The best fit method. A simple way for measuring the volume of an intracerebral haematoma. Neuroradiology. 1988;30:73–5.
Steiner I, Gomori JM, Melamed E. The prognostic value of the CT scan in conservatively treated patients with intracerebral hematoma. Stroke. 1984;15:279–82.
Tuhrim S, Dambrosia JM, Price TR, Mohr JP, Wolf PA, Hier DB, Kase CS. Intracerebral hemorrhage: external validation and extension of a model for prediction of 30-day survival. Ann Neurol. 1991;29:658–63.
Kothari RU, Brott T, Broderick JP, Barsan WG, Sauerbeck LR, Zuccarello M, Khoury J. The ABCs of measuring intracerebral hemorrhage volumes. Stroke. 1996;27:1304–5.
Han T, Paik N, Park J. The clinical functional scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Korean J Stroke. 2001;3:153–7.
Chun SW, Lee SA, Jung IY, Beom J, Han TR, Oh BM. Inter-rater agreement for the clinical dysphagia scale. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011;35:470–6.
Jung SH, Lee KJ, Hong JB, Han TR. Validation of clinical dysphagia scale: based on videofluoroscopic swallowing study. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005;29:343–50.
Daniels SK, Brailey K, Foundas AL. Lingual discoordination and dysphagia following acute stroke: analyses of lesion localization. Dysphagia. 1999;14:85–92.
Daniels SK, Foundas AL. The role of the insular cortex in dysphagia. Dysphagia. 1997;12:146–56.
Martin RE, Goodyear BG, Gati JS, Menon RS. Cerebral cortical representation of automatic and volitional swallowing in humans. J Neurophysiol. 2001;85:938–50.
Mosier K, Bereznaya I. Parallel cortical networks for volitional control of swallowing in humans. Exp Brain Res. 2001;140:280–9.
Cola MG, Daniels SK, Corey DM, Lemen LC, Romero M, Foundas AL. Relevance of subcortical stroke in dysphagia. Stroke. 2010;41:482–6.
Lee CK, Kim JA. Pattern of post-stroke swallowing disorder according to the brain lesion. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001;25:193–201.
Alberts MJ, Horner J, Gray L, Brazer SR. Aspiration after stroke: lesion analysis by brain MRI. Dysphagia. 1992;7:170–3.
Kim J, Oh BM, Kim JY, Lee GJ, Lee SA, Han TR. Validation of the videofluoroscopic dysphagia scale in various etiologies. Dysphagia. 2014;29:438–43.
Splaingard ML, Hutchins B, Sulton LD, Chaudhuri G. Aspiration in rehabilitation patients: videofluoroscopy vs bedside clinical assessment. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1988;69:637–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.Y., Han, S.H. Relationship Between Subcortical Hemorrhage Size and Characteristics of Dysphagia. Dysphagia 34, 155–160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-018-9938-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-018-9938-z