Abstract
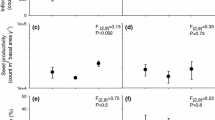
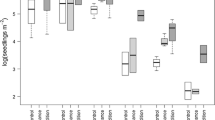
Plants with limited resources adjust partitioning among growth, survival, and reproduction. We tested the effects of water and nutrient amendments on seed production, size, and quality in Sarcobatus vermiculatus (greasewood) to assess the magnitude and importance of changes in reproductive partitioning. In addition, we assessed interactions among the environment of seed-producing plants (adult plant scale), seed size, and seedling microenvironment (seedling scale) on successful seedling establishment. Interactions of these factors determine the scale of resource heterogeneity that affects seedling establishment in deserts. Both total number of seeds produced per plant and seed quality (weight and germination) increased significantly in the enriched treatment in a 3-year field experiment. Seedling length 3 days after germination and seed N concentration, other measures of seed quality, were higher for seed from both irrigated and enriched plants than for seed from control plants. Field S. vermiculatus seed production and quality can be substantially increased with irrigation and nutrient enrichment at the adult plant scale and this allows management of seed availability for restoration. However, based on a greenhouse study, seedling environment, not the environment of the seed-producing plant or seed size, was the most important factor affecting seedling germination, survival, and growth. Thus it appears that production of more seed may be more important than improved seed quality, because higher quality seed did not compensate for a low-resource seedling environment. For both natural establishment and restoration this suggests that heterogeneity at the scale of seedling microsites, perhaps combined with fertilization of adult shrubs (or multi-plant patches), would produce the greatest benefit for establishing seedlings in the field.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker HG (1972) Seed weight in relation to environmental conditions in California. Ecology 53:997–1009
Cheplick GP, Sung LY (1998) Effects of maternal nutrient environment and maturation position on seed heteromorphism, germination, and seedling growth in Triplasis purpurea (Poaceae). Int J Plant Sci 159:338–350
Dahlgren RA, Richards JH, Yu Z (1997) Soil and groundwater chemistry and vegetation distribution in a desert playa, Owens Lake, California. Arid Soil Res Rehabil 11:221–244
Dickey J, Hall M, Madison M, Smesrud J, Griswold M, Cotton Q, Heilmann M, Roland G, Jordahl J, Harasick R, Bamossy W, Coles R, Wheeler L, Brown P, Burton K, Fornelli R, Anderson I, Riedel-Lehrke M, Tiller R, Richards J (2005) Managing salt to stabilize the Owens Playa with saltgrass. In: Proceedings of the International Salinity Forum, Riverside, pp 147–150
Dodd GL, Donovan LA (1999) Water potential and ionic effects on germination and seedling growth of two cold desert shrubs. Am J Bot 86:1146–1153
Dolan RW (1984) The effect of seed size and maternal source on individual size in a population of Ludwigia leptocarpa (Onagraceae). Am J Bot 71:1302–1307
Donovan LA, Richards JH (2000) Juvenile shrubs show differences in stress tolerance, but no competition or facilitation, along a stress gradient. J Ecol 88:1–16
Donovan LA, Richards JH, Schaber EJ (1997) Nutrient relations of the halophytic shrub, Sarcobatus vermiculatus, along a soil salinity gradient. Plant Soil 190:105–117
Drenovsky RE, Richards JH (2005) Nitrogen addition increases fecundity in the desert shrub Sarcobatus vermiculatus. Oecologia 143:349–356
Fort KP, Richards JH (1998) Does seed dispersal limit initiation of primary succession in desert playas? Am J Bot 85:1722–1731
Green PT, Juniper PA (2004) Seed-seedling allometry in tropical rain forest trees: seed mass-related patterns of resource allocation and the ‘reserve effect’. J Ecol 92:397–408
Harper JL (1977) Population biology of plants. Academic Press, New York
Hou JQ, Romo JT (1998) Seed weight and germination time affect growth of 2 shrubs. J Range Manage 51:699–703
James JJ, Tiller RL, Richards JH (2005) Multiple resources limit plant growth and function in a saline-alkaline desert community. J Ecol 93:113–126
Janzen DH (1977) Variation in seed size within a crop of a Costa Rican Mucana andreana (Leguminosae). Am J Bot 64:347–349
Kristensen L (2003) Maternal effects due to organic and conventional growing conditions in spring barley (Hordeum vulgare). Biol Agric Hortic 21:195–208
Martincic J, Guberac V, Maric S (1997) Influence of winter rye seed size (Secale cereale L.) on germ and rootlet length, and grain yield. Rost Vyroba 43:95–100
Moles AT, Westoby M (2004) Seedling survival and seed size: a synthesis of the literature. J Ecol 92:372–383
Neter J, Kutner MH, Nachtsheim CJ, Wassermen W (1996) Applied linear statistical models, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, Boston
Petersen JL, Ueckert DN (2005) Fourwing saltbush seed yield and quality: irrigation, fertilization, and ecotype effects. Rangeland Ecol Manage 58:299–307
Roach DA, Wulff RD (1987) Maternal effects in plants. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 18:209–235
SAS (2001) SAS STAT user’s guide, version 6, eth edn, vol 2. SAS, Cary
Scheiner SM, Gurevitch J (1993) Design and analysis of ecological experiments. Chapman and Hall, New York
Schimpf DJ (1977) Seed weight of Amaranthus retroflexus in relation to moisture and length of growing season. Ecology 58:450–453
Sills GR, Nienhuis J (1995) Maternal phenotypic effects due to soil nutrient levels and sink removal in Arabidopsis thaliana (Brassicaceae). Am J Bot 82:491–495
Singh DK, Singh V (2003) Seed size and adventitious (nodal) roots as factors influencing the tolerance of wheat to waterlogging. Aust J Agric Res 54:969–977
Snyder KA, Donovan LA, James JJ, Tiller RL, Richards JH (2004) Extensive summer water pulses do not necessarily lead to canopy growth of Great Basin and northern Mojave Desert shrubs. Oecologia 141:325–334
Sousa WP, Kennedy PG, Mitchell BJ (2003) Propagule size and predispersal damage by insects affect establishment and early growth of mangrove seedlings. Oecologia 135:564–575
Stanton ML (1984) Seed variation in wild radish—effect of seed size on components of seedling and adult fitness. Ecology 65:1105–1112
Stanton ML, Thiede DA (2005) Statistical convenience vs. biological insight: consequences of data transformation for the analysis of fitness variation in heterogeneous environments. New Phytol 166:319–337
Stougaard RN, Xue QW (2004) Spring wheat seed size and seeding rate effects on yield loss due to wild oat (Avena fatua) interference. Weed Sci 52:133–141
Triboi E, Martre P, Triboi-Blondel AM (2003) Environmentally-induced changes in protein composition in developing grains of wheat are related to changes in total protein content. J Exp Bot 54:1731–1742
Ungar IA (1978) Halophyte seed germination. Bot Rev 44:233–264
Valencia-Diaz S, Montana C (2005) Temporal variability in the maternal environment and its effect on seed size and seed quality in Flourensia cernua DC (Asteraceae). J Arid Environ 63:686–695
Waller DM (1982) Factors influencing seed weight in Impatiens capensis (Balsaminaceae). Am J Bot 69:1470–1475
Weiner J, Martinez S, MullerScharer H, Stoll P, Schmid B (1997) How important are environmental maternal effects in plants? A study with Centaurea maculosa. J Ecol 85:133–142
Whitford WG, Rapport DJ, deSoyza AG (1999) Using resistance and resilience measurements for ‘fitness’ tests in ecosystem health. J Environ Manage 57:21–29
Yanful M, Maun MA (1996) Effects of burial of seeds and seedlings from different seed sires on the emergence and growth of Strophostyles helvola. Can J Bot 74:1322–1330
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship to A. N. B., the California State Lands Commission (C-99017), and the California Agricultural Experiment Station. We thank Los Angeles Department of Water and Power and US Borax (Lake Minerals Operation) for cooperation. Research assistance provided by members of the Richards’ lab is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by John Keeley.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breen, A.N., Richards, J.H. Irrigation and fertilization effects on seed number, size, germination and seedling growth: implications for desert shrub establishment. Oecologia 157, 13–19 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-008-1049-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-008-1049-3