Abstract
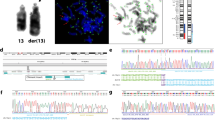
Genome rearrangements are caused by the erroneous repair of DNA double-strand breaks, leading to several alterations that result in loss or gain of the structural genomic of a dosage-sensitive genes. However, the mechanisms that promote the complexity of rearrangements of congenital or developmental defects in human disease are unclear. The investigation of complex genomic abnormalities could help to elucidate the mechanisms and causes for the formation and facilitate the understanding of congenital or developmental defects in human disease. We here report one case of a patient with atypical clinical features of the 1p36 syndrome and the use of cytogenomic techniques to characterize the genomic alterations. Analysis by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification and array revealed a complex rearrangement in the 1p36.3 region with deletions and duplication interspaced by normal sequences. We also suggest that chromoanagenesis could be a possible mechanism involved in the repair and stabilization of this rearrangement.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen E, Obolensky E, Rauen KA, Shaffer LG, Li X (2008) Cytogenetic and array CGH characterization of de novo 1p36 duplications and deletion in a patient with congenital cataracts, hearing loss, choanal atresia, and mental retardation. Am J Med Genet A 146A(21):2785–2790
Chiang C, Jacobsen JC, Ernst C, Hanscom C, Heilbut A, Blumenthal I, Mills RE, Kirby A, Lindgren AM, Rudiger SR, McLaughlan CJ, Bawden CS, Reid SJ, Faull RL, Snell RG, Hall IM, Shen Y, Ohsumi TK, Borowsky ML, Daly MJ, Lee C, Morton CC, MacDonald ME, Gusella JF, Talkowski ME (2012) Complex reorganization and predominant non-homologous repair following chromosomal breakage in karyotypically balanced germline rearrangements and transgenic integration. Nat Genet 44(4):390–397
Colnaghi R, Carpenter G, Volker M, O’Driscoll M (2011) The consequences of structural genomic alterations in humans: genomic disorders, genomic instability and cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22(8):875–885
D’Angelo CS, Gajecka M, Kim CA, Gentles AJ, Glotzbach CD, Shaffer LG, Koiffmann CP (2009) Further delineation of nonhomologous-based recombination and evidence for subtelomeric segmental duplications in 1p36 rearrangements. Hum Genet 125(5–6):551–563
Fitzgibbon GJ, Clayton-Smith J, Banka S, Hamilton SJ, Needham MM, Dore JK, Miller JT, Pawson GD, Gaunt L (2008) Array comparative genomic hybridisation-based identification of two imbalances of chromosome 1p in a 9-year-old girl with a monosomy 1p36 related phenotype and a family history of learning difficulties: a case report. J Med Case Rep 2:355
Forment JV, Kaidi A, Jackson SP (2012) Chromothripsis and cancer: causes and consequences of chromosome shattering. Nat Rev Cancer 12(10):663–670
Gajecka M, Mackay KL, Shaffer LG (2007) Monosomy 1p36 deletion syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 145C(4):346–356
Giannikou K, Fryssira H, Oikonomakis V, Syrmou A, Kosma K, Tzetis M, Kitsiou-Tzeli S, Kanavakis E (2012) Further delineation of novel 1p36 rearrangements by array-CGH analysis: narrowing the breakpoints and clarifying the “extended” phenotype. Gene 506(2):360–368
Hastings PJ, Lupski JR, Rosenberg SM, Ira G (2009) Mechanisms of change in gene copy number. Nat Rev Genet 10(8):551–564
Heilstedt HA, Ballif BC, Howard LA, Lewis RA, Stal S, Kashork CD, Bacino CA, Shapira SK, Shaffer LG (2003) Physical map of 1p36, placement of breakpoints in monosomy 1p36, and clinical characterization of the syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 72(5):1200–1212
Holland AJ, Cleveland DW (2012) Chromoanagenesis and cancer: mechanisms and consequences of localized, complex chromosomal rearrangements. Nat Med 18(11):1630–1638
Kloosterman WP, Guryev V, van Roosmalen M, Duran KJ, de Bruijn E, Bakker SC, Letteboer T, van Nesselrooij B, Hochstenbach R, Poot M, Cuppen E (2011) Chromothripsis as a mechanism driving complex de novo structural rearrangements in the germline. Hum Mol Genet 20(10):1916–1924
Liu P, Erez A, Nagamani SC, Dhar SU, Kołodziejska KE, Dharmadhikari AV, Cooper ML, Wiszniewska J, Zhang F, Withers MA, Bacino CA, Campos-Acevedo LD, Delgado MR, Freedenberg D, Garnica A, Grebe TA, Hernández-Almaguer D, Immken L, Lalani SR, McLean SD, Northrup H, Scaglia F, Strathearn L, Trapane P, Kang SH, Patel A, Cheung SW, Hastings PJ, Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR, Bi W (2011) Chromosome catastrophes involve replication mechanisms generating complex genomic rearrangements. Cell 146(6):889–903
Maher CA, Wilson RK (2012) Chromothripsis and human disease: piecing together the shattering process. Cell 148(1–2):29–32
Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2012) Characterizing complex structural variation in germline and somatic genomes. Trends Genet 28(1):43–53
Schouten JP, McElgunn CJ, Waaijer R, Zwijnenburg D, Diepvens F, Pals G (2002) Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acids Res 30(12):e57
Shaffer LG, Kashork CD, Saleki R, Rorem E, Sundin K, Ballif BC, Bejjani BA (2006) Targeted genomic microarray analysis for identification of chromosome abnormalities in 1500 consecutive clinical cases. J Pediatr 149(1):98–102
Sobreira NL, Gnanakkan V, Walsh M, Marosy B, Wohler E, Thomas G, Hoover-Fong JE, Hamosh A, Wheelan SJ, Valle D (2011) Characterization of complex chromosomal rearrangements by targeted capture and next-generation sequencing. Genome Res 21(10):1720–1727
Stephens PJ, Greenman CD, Fu B, Yang F, Bignell GR, Mudie LJ, Pleasance ED, Lau KW, Beare D, Stebbings LA, McLaren S, Lin ML, McBride DJ, Varela I, Nik-Zainal S, Leroy C, Jia M, Menzies A, Butler AP, Teague JW, Quail MA, Burton J, Swerdlow H, Carter NP, Morsberger LA, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Follows GA, Green AR, Flanagan AM, Stratton MR, Futreal PA, Campbell PJ (2011) Massive genomic rearrangement acquired in a single catastrophic event during cancer development. Cell 144(1):27–40
Zhang F, Carvalho CM, Lupski JR (2009) Complex human chromosomal and genomic rearrangements. Trends Genet 25(7):298–307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zanardo, É.A., Piazzon, F.B., Dutra, R.L. et al. Complex structural rearrangement features suggesting chromoanagenesis mechanism in a case of 1p36 deletion syndrome. Mol Genet Genomics 289, 1037–1043 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0876-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0876-7