Abstract
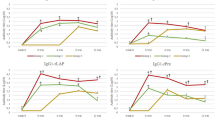
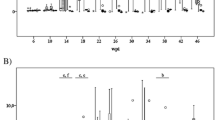
Buffaloes, as highly susceptible definitive hosts of Fasciola gigantica, suffer from a high infection rate of fasciolosis, which causes enormous economic losses. Repeat infection is responsible for this high rate; thus, elucidating the protective immunity mechanism in repeat infection is decisive in fasciolosis prevention. Herein, a secondary experimental infection model was established to preliminarily reveal the protective immunity that occurs in repeat infection. In brief, animals were assigned to three groups: group A (uninfected control), group B (primary infection) and group C (secondary infection). Buffaloes were autopsied 20 weeks post-infection for measurements of the recovered flukes and hepatic examination. In addition, the detection of specific antibody (IgG) responses to F. gigantica excretory-secretory product (FgESP) throughout the whole period and weight gain throughout the first 4 months as a percentage (%) of the starting weight were also determined. The serum hepatic enzyme gamma glutathione transferase (GGT) levels were monitored to assess hepatic damage throughout the study period. Infection establishment was compared between group B and group C. Similar specific IgG patterns were observed between group B and group C, and hepatic damage was more severe in group C than group B. Significant differences in weight gain as a percentage of the start weight were observed between group A and group B at the 3rd and 4th months postprimary infection, while significant differences were not observed between group A and group C or group B and group C. Our results suggest that challenge infection cannot induce resistance against F. gigantica in buffaloes, which is consistent with the protective immunity against Fasciola hepatica reinfection observed in sheep and goats.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boray JC (1967) The effect of host reaction to experimental Fasciola hepatica infections in sheep and cattle. In: Soulsby EJL (ed) The reaction of the host to parasitism. Elwert, Marburg, pp 84–96
Chauvin A, Bouvet G, Boulard C (1995) Humoral and cellular immune responses to Fasciola hepatica experimental primary and secondary infection in sheep. Int J Parasitol 25(10):1227. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-60366-7_11
Chiezey NP, Adama JY, Ajanusi J, Lawal I (2013) Disruption of estrus and conception in the acute phase of Fasciola gigantica infections in Yankasa ewes. Acad J 5(8):206–214. https://doi.org/10.5897/JVMAH2013.0227
Dalton RJP (2009) Zoonotic helminth infections with particular emphasis on fasciolosis and other trematodiases. Philos Trans Biol Sci 364(1530):2763–2776. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0089
Fagbemi BO, Guobadia E (1995) Immunodiagnosis of fasciolosis in ruminants using a 28-kDa cysteine protease of Fasciola gigantica adult worms. Vet Parasitol 57(4):309–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4017(94)00684-5
Gupta SC, Yadav SC (1994) Emergence of Fasciola gigantica cercariae from naturally infected Lymnaea auricularia. J Parasit Dis 18(1):53–56
Hanna REB, Gordon AW, Moffett D, Edgar HWJ, Oliver LF, McConnell S, Shaw L, Brennan GP, Fairweather I (2011) Fasciola hepatica: comparative effects of host resistance and parasite intra-specific interactions on size and reproductive histology in flukes from rats infected with isolates differing in triclabendazole sensitivity. Vet Parasitol 178(3):251–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.01.045
Hansen DS, Clery DG, Estuningsih SE, Widjajanti S, Partoutomo S, Spithill TW (1999) Immune responses in Indonesian thin tail and Merino sheep during a primary infection with Fasciola gigantica: lack of a specific IgG2 antibody response is associated with increased resistance to infection in Indonesian sheep. Int J Parasitol 29(7):1027–1035. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.80.2.406
Hillyer S (1988) Antibody profiles by EITB and ELISA of cattle and sheep infected with Fasciola hepatica. J Parasitol 74(5):810–818. https://doi.org/10.2307/3282259
Huo KL, Lu CY, Bai AB, Zhou XZ, Zhang JL, Zhang JY, Wu JM (2018) An epidemiological survey of the Fasciola spp. of bovine in Guangxi province. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine 054(009):32–33,36,124 doi:CNKI:SUN:ZSYZ.0.2018–09–010
Liao D (1996) Study on a new egg count technique for Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus and Ascaris suum. Vet Parasitol 61(1–2):113–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4017(94)00767-5
Liu G-H, Gasser RB, Young ND, Song H-Q, Ai L, Zhu X-Q (2014) Complete mitochondrial genomes of the ‘intermediate form’ of Fasciola and Fasciola gigantica, and their comparison with F hepatica. Parasites Vectors 7(1):150. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-150
Martı́nez-Moreno A, Jiménez-Luque V, Moreno T, Redondo ESH, de las Mulas JMn, Pérez J (1999) Liver pathology and immune response in experimental Fasciola hepatica infections of goats. Vet Parasitol 82(1):19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4017(98)00262-3
Martínez-Moreno A, Martínez-Moreno FJ, Acosta I, Gutiérrez PN, Becerra C, Hernández S (1997) Humoral and cellular immune responses to experimental Fasciola hepatica infections in goats. Parasitol Res 83(7):680–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050319
Meemon K, Sobhon P (2015) Juvenile-specific cathepsin proteases in Fasciola spp.: their characteristics and vaccine efficacies. Parasitol Res 114(8):2807–2813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4589-6
Molina EC, Gonzaga EA, Sinolinding EO, Lumbao LA, Peralta AA, Barraca AP (2005) Differences in susceptibility between cattle and swamp buffaloes to infection with Fasciola gigantica. Trop Anim Health Prod 37(8):611–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-005-4301-4
Mulcahy G, Joyce P, Dalton JP (1999) Immunology of Fasciola hepatica infection. In: Dalton JP (ed) Fasciolosis. CAB International Publishing, Wallingford, pp 341–375
Raadsma HW, Kingsford NM, Suharyanta, Spithill TW, Piedrafita D (2007) Host responses during experimental infection with Fasciola gigantica or Fasciola hepatica in Merino sheep: I. Comparative immunological and plasma biochemical changes during early infection. Vet Parasitol 143(3):275–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.09.008
Roberts JA, Estuningsih E, Widjayanti S, Wiedosari E, Partoutomo S, Spithill TW (1997) Resistance of Indonesian thin tail sheep against Fasciola gigantica and F. hepatica. Vet Parasitol 68(1):69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4017(96)01027-8
Roberts JA, Widjayanti S, Estuningsih E (1996) Acquired resistance of merino sheep against Fasciola gigantica. Parasitol Res 82(8):743–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050196
Ross JG (1967) Studies of immunity to Fasciola hepatica: acquired immunity in cattle, sheep and rabbits following natural infection and vaccine procedures. J Helminthol 41(4):393–399. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X0002191X
Sharma RL, TlDN D, Raina OK (1989) Studies on the prevalence and laboratory transmission of fascioliasis in animals in the Kashmir valley. Br Vet J 145(1):57–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/0007-1935(89)90010-9
Vercruysse J, Claerebout E (2001) Treatment vs non-treatment of helminth infections in cattle: defining the threshold. Vet Parasitol 98(1):195–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4017(01)00431-9
Walsh TR, Ainsworth S, Armstrong S, Hodgkinson J, Williams D (2021) Differences in the antibody response to adult Fasciola hepatica excretory/secretory products in experimentally and naturally infected cattle and sheep. Vet Parasitol 289:109321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2020.109321
Windon RG, Chaplin PJ, McWaters P, Tavarnesi M, Tzatzaris M, Kimpton WG, Cahill RNP, Beezum L, Coulter A, Drane D, Sjölander A, Pearse M, Scheerlinck JPY, Tennent JM (2001) Local immune responses to influenza antigen are synergistically enhanced by the adjuvant ISCOMATRIX®. Vaccine 20(3):490–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-410X(01)00332-2
Wu ZJ, Wang JH, Meng Z, Jin WK, He KX, Zhang WY, Di WD (2021) Identification of Fasciola spp. based on ITS-2 reveals the Fasciola gigantica infection in buffaloes in Nanning city, South China. Vet Parasitol 300:109585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2021.109585
Yadav SC, Sharma RL, Kalicharan A, Mehra UR, Dass RS, Verma AK (1999) Primary experimental infection of riverine buffaloes with Fasciola gigantica. Vet Parasitol 82(4):285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4017(99)00005-9
Yoshihara S, Nakagawa M, Suda H (1985) Protection against Fasciola gigantica infection in rats administered metacercarial antigens. Res Vet Sci 39(3):383–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-5288(18)31730-2
Zhang WY, Moreau E, Yang BZ, Li ZQ, Hope JC, Howard CJ, Huang WY, Chauvin A (2006) Humoral and cellular immune responses to Fasciola gigantica experimental infection in buffaloes. Res Vet Sci 80(3):299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2005.07.003
Zhong HP, Liu XY, Li H, Huang J, Tang ZZ, Yu NQ, Zeng LH, Cheng JR, Qin GS, Wang XL (2021) Studies on serum biochemical indices of different subspecies of riverine buffaloes. Chin J Anim Sci 57(9):70–73. https://doi.org/10.19556/j.0258-7033.20201111-06
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the researchers and farming staff of the Buffalo Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and Guangxi Zhuang Nationality Autonomous Region, for their assistance and collaboration.
Funding
Project financial support was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31960706).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wei-Yu Zhang conceived and designed the study. Wen-Da Di critically revised the manuscript. Jin-Hui Wang performed the experiment, analysed the data and drafted the manuscript. Kang-Xin He, Zhen-Di Wang, Xiao-Ge Han, Zhen Meng, Xiang-Xiang Yuan and Zheng-Jiao Wu helped in the implementation of the study. Chong-Li Wen helped in buffalo feeding of the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The animal study and experimental procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Animal Science and Technology, Guangxi University. The animals used in this study were handled in accordance with good animal practices as required by the Animal Ethics Procedures and Guidelines of the People’s Republic of China.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Section Editor: Dante Zarlenga
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JH., He, KX., Wang, ZD. et al. Effect of primary and secondary Fasciola gigantica infection on specific IgG responses, hepatic enzyme levels and weight gain in buffaloes. Parasitol Res 121, 1709–1718 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-022-07519-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-022-07519-2