Abstract
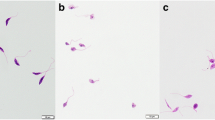
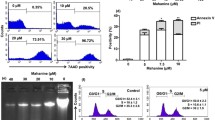
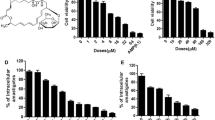
Leishmaniasis is one of the most neglected parasitic infections of the world and current therapeutic options show several limitations. In the search for more effective drugs, plant compounds represent a powerful natural source. Artemisinin is a sesquiterpene lactone extracted from Artemisia annua L. leaves, from which dihydroartemisinin (DQHS) and artesunic acid (AA)/artesunate are examples of active derivatives. These lactones have been applied successfully on malaria therapy for decades. Herein, we investigated the sensitivity of Leishmania braziliensis, one of the most prevalent Leishmania species that cause cutaneous manifestations in the New World, to artemisinin, DQHS, and AA. L. braziliensis promastigotes and the stage that is targeted for therapy, intracelular amastigotes, were more sensitive to DQHS, showing EC50 of 62.3 ± 1.8 and 8.9 ± 0.9 μM, respectively. Cytotoxicity assays showed that 50% of bone marrow-derived macrophages cultures were inhibited with 292.8 ± 3.8 μM of artemisinin, 236.2 ± 4.0 μM of DQHS, and 396.8 ± 6.7 μM of AA. The control of intracellular infection may not be essentially attributed to the production of nitric oxide. However, direct effects on mitochondrial bioenergetics and H2O2 production appear to be associated with the leishmanicidal effect of DQHS. Our data provide support for further studies of artemisinin and derivatives repositioning for experimental leishmaniasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcântara LM, Ferreira TCS, Gadelha FR, Miguel DC (2018) Challenges in drug discovery targeting TriTryp diseases with an emphasis on leishmaniasis. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist 8(3):430–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpddr.2018.09.006
Aldiere E, Atragene D, Bergandi L, Riganti C, Costamagna C, Bosia A, Ghugo D (2003) Artemisinin inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and nuclear fator NF-kB activation. FEBS Lett 552(2–3):141–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00905-0
Alvar J, Vélez ID, Bern C, Herrero M, Desjeux P, Cano J, Jannin J, Boer M, the WHO Leishmaniasis Control Team (2012) Leishmaniasis worldwide and global estimates of its incidence. PLoS One 7(5):e35671. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035671
Amato VS, Tuon FF, Siqueira AM, Nicodemo AC, Neto VA (2007) Treatment of mucosal leishmaniasis in Latin America: systematic review. Am J Trop Med Hyg 77:266–274. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2007.77.266
Ansari MT, Saify ZS, Sultana N, Ahmad I, Saeed-Ul-Hassan S, Tariq I, Khanum M (2013) Malaria and artemisinin derivatives: an updated review. Mini Rev Med Chem 13(13):1879–1902. https://doi.org/10.2174/13895575113136660097
Balint GA (2001) Artemisinin and its derivatives: an important new class of antimalarial agents. Pharmacol Ther 90(2–3):261–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0163-7258(01)00140-1
Barreiros ALBS, David JM, David JP (2006) Estresse oxidativo: relação entre gerações de espécies reativas e defesa do organismo. Química Nova 29(1):113–123. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422006000100021
Brito AMG, Santos D, Rodrigues AS, Brito R, Xavier-Filho L (2013) Plants with anti-Leishmania activity: integrative review from 2000 to 2011. Pharmacogn Rev 7(13):34–41. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.112840
Brossi A, Venugolapan B, Gerpe LD, Yeh HJC, Flippen-Anderson JL, Buchs P, Luo XD, Milhous W, Peters W (1988) Arteether, a new antimalarial drug: synthesis and antimalarial properties. J Med Chem 31(3):645–650. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00398a026
Callaway E, Cyranoski D (2015) Anti-parasite drugs sweep Nobel prize in medicine 2015. Nature. 526(7572):174–175. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2015.18507
Charlton R, Rossi-Bergmann DPW, Steel PG (2018) Repurposing as a strategy for the discovery of new anti-leishmanials: the state of the art. Parasitology. 145(2):219–236. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182017000993
Chen Y, Li R, Zhu Y, Zhong S, Qian J, Yang D, Jurczyszyn A, Beksac M, Gu C, Yang Y (2020) Dihydroartemisinin induces growth arrest and overcomes dexamethasone resistance in multiple myeloma. Front Oncol 15(10):767. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00767
Cohen BE, Benaim G, Ruiz M, Michelangeli F (1990) Increased calcium permeability is not responsible for the rapid lethal effects of amphotericin B on Leishmania sp. FEBS Lett 259(2):286–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(90)80028-H
Cortes S, Albuquerque A, Cabral LIL, Lopes L, Campino L, Cristiano MLS (2015) In vitro susceptibility of Leishmania infantum to artemisinin derivatives and selected trioxolanes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59(8):5032–5035. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00298-15
Das P, Lahiri A, Lahiri A, Chakravortty D (2010) Modulation of the arginase pathway in the context of microbial pathogenesis: a metabolic enzyme moonlighting as an immune modulator. PLoS Pathog 6(6):e1000899. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000899
Ebrahimisadr P, Ghaffarifar F, Mohammad Hassan Z (2013) In-vitro evaluation of antileishmanial activity and toxicity of artemether with focus on its apoptotic effect. Iran J Pharm Res 12(4):903–909. https://doi.org/10.22037/IJPR.2013.1406
Esavand Heydari F, Ghaffarifar F, Soflaei S, Dalimi A (2013) Comparison between in vitro effects of aqueous extract of Artemisia seiberi and artemisinin on Leishmania major. Jundishapur J Nat pharm prod. 8(2):70-5. https://doi.org/10.17795/jjnpp-9513
Geroldinger G, Tonner M, Quirgst J, Walter M, De Sarkar S, Machín L, Monzote L, Bein H, Stolze K, Duvigneau K, Staniek K, Chatterjee M, Gille L (2020) Activation of artemisinin and heme degradation in Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes: a possible link? Biochem Pharmacol 173:113737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113737
Greenwood BM, Fidock DA, Kyle DE, Kappe SHI, Alonso PL, Collins FH, Duffy PE (2008) Malaria: progress, perils, and prospects for eradication. J Clin Invest 118(4):1266–1276. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI33996
Haynes RK, Chan HW, Cheung MK, Lam WL, Soo MK, Tsang HW, Voerste A, Williams ID (2002) C-10 ester and ether derivatives of dihydroartemisinin – 10-α artesunate, preparation of authentic 10-β artesunate, and of other ester and ether derivatives bearing potential aromatic intercalating groups at C-10. Eur J Org Chem. (1):113–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-0690(20021)2002
Islamuddin M, Chouhan G, Tyagi M, Abdin MZ, Sahal D, Afrin F (2014) Leishmanicidal activities of Artemisia annua leaf essential oil against visceral leishmaniasis. Front Microbiol 5:626. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00626
Kapler GM, Coburn CM, Beverly SM (1990) Stable transfection of the human parasite Leishmania major delineates a 30-kilobase region suficiente for extrachromosomal replication and expression. Mol Cell Biol 10(3):1084–1094. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.10.3.1084
Kardono LBS, Wikara T, Tursiloadi H, Tursiloadi S (2014) Synthesis of dihydroartemisinin using Ni/TiO2 catalyst prepared by sol gel method. J Appl Pharm Sci 4(01):1–8. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2014.40101
Klayman DL (1985) Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China. Science. 228(4703):1049–1055. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3887571
Konkimalla VB, Blunder M, Korn B, Soomro A, Jansen H, Chang W, Posner G, Bauer R, Efferth T (2008) Effect of artemisinins and other endoperoxides on nitric oxide-related signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cells. Nitric Oxide-Biol Ch 19(2):184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2008.04.008
Li Y (2012) Qinghaosu (artemisinin): chemistry and pharmacology. Acta Pharmacol Sin B. 33(9):1141-1146. 10.1038%2Faps.2012.104
Li Y, Yu PL, Chen YX, Li LQ, Gai YZ, Wang DS, Zheng YP (1981) Studies on analogs of artemisinin. I. The synthesis of ethers, carboxylic esters and carbonates of dihydroartemisinin. Acta Pharm Sin B 16(6):429–439
Loo CS, Lam NS, Yu D, Su XZ, Lu F (2017) Artemisinin and its derivatives in treating protozoan infections beyond malaria. Pharmacol Res 117:192–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.012
Luo XD, Shen CC (1987) The chemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications of qinghaosu (artemisinin) and its derivatives. Med Res Rev 7(1):29–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.2610070103
Mendes B, Almeida JR, Vale N, Gomes P, Gadelha FR, Silva SL, Miguel DC (2019) Potential use of 13-mer peptides based on phospholipase and oligoarginine as leishmanicidal agents. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 226:108612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2019.108612
Mesa EL, Vasquez D, Lutgen P, Vélez ID, Restrepo AM, Ortiz I, Robledo SR (2017) In vitro and in vivo antileishmanial activity of Artemisia annua L leaf powder and its potential usefulness in the treatment of uncomplicated cutaneous leishmaniasis in humans Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 50(1). https://doi.org/10.1590/0037-8682-0457-2016
Miguel DC, Zauli-Nascimento RC, Yokoyama-Yasunaka JKU, Pereira LIA, Jerônimo SMB, Ribeiro-Dias F, Dorta ML, Uliana SRB (2011) Clinical isolates of New World Leishmania from cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis patients are uniformly sensitive to tamoxifen. Int J Antimicrob Agents 38(1):93–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.03.012
Minori K, Rosa LB, Bonsignore R, Casini A, Miguel DC (2020) Comparing the antileishmanial activity of gold(I) and gold(III) compounds in L. amazonensis and L. braziliensis in vitro. ChemMedChem. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202000536
Mutiso JM, Macharia JG, Barasa M, Taracha E, Bourdichon AJ, Gicheru MM (2011) In vitro and in vivo antileishmanial efficacy of a combination therapy of diminazene and artesunate against Leishmania donovani in BALB/c mice. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 53(3):129–132. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0036-46652011000300003
Oliveira LF, Schubach AO, Martins MM, Passos SL, Oliveira RV, Marzochi MC, Andrade CA (2011) Systematic review of the adverse effects of cutaneous leishmaniasis treatment in the New World. Acta Trop 118:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2011.02.007
Pandey N, Ray SP (2016) Updates on artemisinin: an insight to mode of actions and strategies for enhanced global production. Protoplasma. 253(1):15–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0805-6
Peloso EF, Vitor SC, Ribeiro LHG, Piñeyro MD, Robello C, Gadelha FR (2011) Role of Trypanosoma cruzi peroxiredoxins in mitochondrial bioenergetics. J Bioenerg Biomembr 43:419–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-011-9365-4
Peloso EF, Gonçalves CC, Silva TM, Ribeiro LHG, Piñeyro MD, Robello C, Gadelha FR (2012) Tryparedoxin peroxidases and superoxide dismutases expression as well as ROS release are related to Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes growth phases. Arch Biochem Biophys 520:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2012.02.020
Sarkar SD, Sarkar D, Sarjar A, Dighal A, Chakrabarti S, Staniek K, Gille L, Cratterjee (2019) The leishmanicidal activity of artemisinin is mediated by cleavage of the endoperoxide bridge and mitochondrial dysfunction. Parasitology 146(4):511–520. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118201800183X
Sen R, Bandyopadhyay S, Dutta A, Mandal G, Ganguly S, Saha P, Chatterjee M (2007) Artemisinin triggers induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in Leishmania Donovani promastigotes. J Med Microbiol 56(9):1213–1218. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.47364-0
Sen R, Ganguly S, Saha P, Chatterjee M (2010) Efficacy of artemisinin in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 36(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.03.008
Sun C, Zhou B (2016) The molecular and cellular action properties of artemisinins: what has yeast told us? Microb Cell 14;3(5):196–205. https://doi.org/10.15698/mic2016.05.498
World Health Organization - WHO (2020a) Leishmaniasis (cutaneous, mucosal and visceral forms) https://www.who.int/ith/diseases/leishmaniasis/en/. Acessed 06 july 2020
World Health Organization - WHO (2020b) Malaria: retreat of a centuries-old scourge. https://www.who.int/publications/10-year-review/malaria/en/index6.html. Acessed 06 july 2020
Yu WY, Kan WJ, Yu PX, Li MM, Song JS, Zhao F (2012) Anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of artemisinin and dihydroartemisinin. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi 37(17):2618–2621
Funding
N.G. received a master scholarship from CAPES (Programa Demanda Social). D.C.M. is supported by a FAPESP Young Investigator Award (#2014/21129-4) and FAEPEX-Pesquisa, Pró-Reitoria de Pesquisa – UNICAMP (#519.292).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Julia Walochnik
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grazzia, N., Boaventura, S., Garcia, V.L. et al. Dihydroartemisinin, an active metabolite of artemisinin, interferes with Leishmania braziliensis mitochondrial bioenergetics and survival. Parasitol Res 120, 705–713 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-07019-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-07019-1