Abstract
Over the last 60 years, accumulating evidence has suggested that acute, chronic, and maternal Toxoplasma gondii infections predispose to schizophrenia. More recent evidence suggests that chronically infected patients with schizophrenia present with more severe disease. After acute infection, parasites form walled cysts in the brain, leading to lifelong chronic infection and drug resistance to commonly used antiparasitics. Chronic infection is the most studied and closely linked with development and severity of schizophrenia. There are currently four published randomized controlled trials evaluating antiparasitic drugs, specifically azithromycin, trimethoprim, artemisinin, and artemether, in patients with schizophrenia. No trials have demonstrated a change in psychopathology with adjunctive treatment. Published trials have either selected drugs without evidence against chronic infection or used them at doses too low to reduce brain cyst burden. Furthermore, trials have failed to achieve sufficient power or account for confounders such as previous antipsychotic treatment, sex, age, or rhesus status on antiparasitic effect. There are currently no ongoing trials of anti-Toxoplasma therapy in schizophrenia despite ample evidence to justify further testing.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
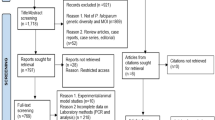
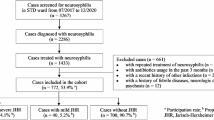
Search strategy included querying Medline, Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, PsychInfo, and Embase with query “Toxoplasm* AND schizophreni*”. Resulting abstracts were screened for relevant randomized controlled trials in humans. Reference lists of included trials were screened for additional trials.
References
Amminger GP, McGorry PD, Berger GE et al (2007) Antibodies to infectious agents in individuals at ultrahigh risk for psychosis. Biol Psychiatry 61:1215–1217. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.09.034
Araujo FG, Remington JS (1974) Effect of clindamycin on acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 5:647–651. doi:10.1128/AAC.5.6.647
Araujo FG, Shepard RM, Remington JS (1991) In vivo activity of the macrolide antibiotics azithromycin, roxithromycin and spiramycin against Toxoplasma gondii. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 10:519–524. doi:10.1007/BF01963942
Buentello E (1958) Preliminary observations on the relationship between toxoplasmosis, lysergic acid and schizophrenia. Gac Med Mex 88:693–710
Çelik T, Kartalci Ş, Aytaş Ö et al (2015) Association between latent toxoplasmosis and clinical course of schizophrenia—continuous course of the disease is characteristic for Toxoplasma gondii-infected patients. Folia Parasitol 62:15. doi:10.14411/fp.2015.015
Chang HR, Arsenijevic D, Comte R et al (1994) Activity of epiroprim (Ro 11-8958), a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, alone and in combination with dapsone against Toxoplasma gondii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:1803–1807. doi:10.1128/AAC.38.8.1803
Chang HR, Comte R, Piguet PF, Pechère JC (1991) Activity of minocycline against Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. J Antimicrob Chemother 27:639–645. doi:10.1093/jac/27.5.639
Chew WK, Segarra I, Ambu S, Mak JW (2012) Significant reduction of brain cysts caused by Toxoplasma gondii after treatment with spiramycin coadministered with metronidazole in a mouse model of chronic toxoplasmosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:1762–1768. doi:10.1128/AAC.05183-11
Dickerson FB, Stallings CR, Boronow JJ et al (2009) A double-blind trial of adjunctive azithromycin in individuals with schizophrenia who are seropositive for Toxoplasma gondii. Schizophr Res 112:198–199. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2009.05.005
Dickerson F, Stallings CR, Vaughan C et al (2011) Artemisinin reduces the level of antibodies to gliadin in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 129:196–200. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2011.04.010
Djurković-Djaković O, Milenković V, Nikolić A et al (2002) Efficacy of atovaquone combined with clindamycin against murine infection with a cystogenic (Me49) strain of Toxoplasma gondii. J Antimicrob Chemother 50:981–987. doi:10.1093/jac/dkf251
Dumas JL, Chang R, Mermillod B et al (1994) Evaluation of the efficacy of prolonged administration of azithromycin in a murine model of chronic toxoplasmosis. J Antimicrob Chemother 34:111–118. doi:10.1093/jac/34.1.111
Dumas JL, Pizzolato G, Pechère JC (1999) Evaluation of trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole as monotherapy or in combination in the management of toxoplasmosis in murine models. Int J Antimicrob Agents 13:35–39. doi:10.1016/S0924-8579(99)00073-4
Dunay IR, Chan WC, Haynes RK, Sibley LD (2009) Artemisone and artemiside control acute and reactivated toxoplasmosis in a murine model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:4450–4456. doi:10.1128/AAC.00502-09
Eissa MM, Barakat AMA, Amer EI, Younis LK (2015) Could miltefosine be used as a therapy for toxoplasmosis? Exp Parasitol 157:12–22. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2015.06.005
Elsheikha HM, Büsselberg D, Zhu XQ (2016) The known and missing links between Toxoplasma gondii and schizophrenia. Metab Brain Dis 31:749–759. doi:10.1007/s11011-016-9822-1
Flegr J (2013) Influence of latent Toxoplasma infection on human personality, physiology and morphology: pros and cons of the Toxoplasma–human model in studying the manipulation hypothesis. J Exp Biol 216:127–133. doi:10.1242/jeb.073635
Flegr J (2015) Schizophrenia and Toxoplasma gondii: an undervalued association? Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 13:817–820. doi:10.1586/14787210.2015.1051033
Fond G, Boyer L, Gaman A et al (2015) Treatment with anti-toxoplasmic activity (TATA) for Toxoplasma positive patients with bipolar disorders or schizophrenia: a cross-sectional study. J Psychiatr Res 63:58–64. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.02.011
Fond G, Macgregor A, Tamouza R et al (2014) Comparative analysis of anti-toxoplasmic activity of antipsychotic drugs and valproate. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 264:179–183. doi:10.1007/s00406-013-0413-4
Fujita Y, Ishima T, Kunitachi S et al (2008) Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice are improved by subsequent subchronic administration of the antibiotic drug minocycline. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:336–339. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.08.031
Goodwin DG, Strobl JS, Lindsay DS (2011) Evaluation of five antischizophrenic agents against Toxoplasma gondii in human cell cultures. J Parasitol 97:148–151. doi:10.1645/GE-2536.1
Hencken CP, Jones-Brando L, Bordón C et al (2010) Thiazole, oxadiazole, and carboxamide derivatives of artemisinin are highly selective and potent inhibitors of Toxoplasma gondii. J Med Chem 53:3594. doi:10.1021/jm901857d
Holub D, Flegr J, Dragomirecká E et al (2013) Differences in onset of disease and severity of psychopathology between toxoplasmosis-related and toxoplasmosis-unrelated schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 127:227–238. doi:10.1111/acps.12031
Holub D, Motlová L, Dragomirecká E et al (2011) Possible protective function of Rh factor in schizophrenia. Psychiatrie 15:37–42
Horacek J, Flegr J, Tintera J et al (2012) Latent toxoplasmosis reduces gray matter density in schizophrenia but not in controls: voxel-based-morphometry (VBM) study. World J Biol Psychiatry 13:501–509. doi:10.3109/15622975.2011.573809
Huskinson-Mark J, Araujo FG, Remington JS (1991) Evaluation of the effect of drugs on the cyst form of Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis 164:170–171. doi:10.1093/infdis/164.1.170
Jones-Brando L, Torrey EF, Yolken R (2003) Drugs used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder inhibit the replication of Toxoplasma gondii. Schizophr Res 62:237–244. doi:10.1016/S0920-9964(02)00357-2
Lainson R (1958) Observations on the development and nature of pseudocysts and cysts of Toxoplasma gondii. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 52:396–407. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(58)90123-8
Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W et al (2005) What does the PANSS mean? Schizophr Res 79:231–238. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2005.04.008
Lindová J, Kuběna AA, Šturcová H et al (2013) Pattern of money allocation in experimental games supports the stress hypothesis of gender differences in Toxoplasma gondii-induced behavioural changes. Folia Parasitol 57:136–142. doi:10.14411/fp.2010.017
Lindová J, Novotná M, Havlícek J et al (2006) Gender differences in behavioural changes induced by latent toxoplasmosis. Int J Parasitol 36:1485–1492. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.07.008
Loo CSN, Lam NSK, Yu D et al (2017) Artemisinin and its derivatives in treating protozoan infections beyond malaria. Pharmacol Res 117:192–217. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.012
Mahmoud SS (2006) Azithromycin macrolids with a potent activity on chronic experimental toxopiasmosis. Iraqi J Pharm 6:1–5
Monroe JM, Buckley PF, Miller BJ (2015) Meta-analysis of anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM antibodies in acute psychosis. Schizophr Bull 41:989–998. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbu159
Munić V, Kelnerić Ž, Mikac L, Eraković Haber V (2010) Differences in assessment of macrolide interaction with human MDR1 (ABCB1, P-gp) using rhodamine-123 efflux, ATPase activity and cellular accumulation assays. Eur J Pharm Sci 41:86–95. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2010.05.016
Nair AB, Jacob S (2016) A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm 7:27–31. doi:10.4103/0976-0105.177703
Neville AJ, Zach SJ, Wang X et al (2015) Clinically available medicines demonstrating anti-Toxoplasma activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:7161–7169. doi:10.1128/AAC.02009-15
Nguyen B, Stadtsbaeder S (1983) Comparative effects of cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole), pyrimethamine-sulphadiazine and spiramycin during avirulent infection with Toxoplasma gondii (Beverley strain) in mice. Br J Pharmacol 79:923–928. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10537.x
Oya K, Kishi T, Iwata N (2014) Efficacy and tolerability of minocycline augmentation therapy in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hum Psychopharmacol 29:483–491. doi:10.1002/hup.2426
Panel on Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Infected Adults and Adolescents (2017) Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in HIV-infected adults and adolescents: recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/adult_oi.pdf. Accessed 18 Feb 2017
Pappas G, Roussos N, Falagas ME (2009) Toxoplasmosis snapshots: global status of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and implications for pregnancy and congenital toxoplasmosis. Int J Parasitol 39:1385–1394. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.04.003
Roberts CW, Walker W, Alexander J (2001) Sex-associated hormones and immunity to protozoan parasites. Clin Microbiol Rev 14:476–488. doi:10.1128/CMR.14.3.476-488.2001
Sarciron ME, Lawton P, Saccharin C et al (1997) Effects of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine on Toxoplasma gondii cysts in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41:1531–1536
Schultz TL, Hencken CP, Woodard LE et al (2014) A thiazole derivative of artemisinin moderately reduces Toxoplasma gondii cyst burden in infected mice. J Parasitol 100:516–521. doi:10.1645/13-451.1
Sharif M, Sarvi S, Pagheh AS et al (2016) The efficacy of herbal medicines against Toxoplasma gondii during the last 3 decades: a systematic review. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 94:1237–1248. doi:10.1139/cjpp-2016-0039
Shibre T, Alem A, Abdulahi A et al (2010) Trimethoprim as adjuvant treatment in schizophrenia: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Schizophr Bull 36:846–851. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbn191
Sugie M, Asakura E, Zhao YL et al (2004) Possible involvement of the drug transporters P glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein Mrp2 in disposition of azithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:809–814. doi:10.1128/AAC.48.3.809-814.2004
Sutterland AL, Fond G, Kuin A et al (2015) Beyond the association. Toxoplasma gondii in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and addiction: systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand 132:161–179. doi:10.1111/acps.12423
Vos T, Allen C, Arora M et al (2016) Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388:1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6
Wang HL, Wang GH, Li QW et al (2006) Prevalence of Toxoplasma infection in first-episode schizophrenia and comparison between Toxoplasma-seropositive and Toxoplasma-seronegative schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 114:40–48. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2006.00780.x
Wang HL, Xiang YT, Li QY et al (2014) The effect of artemether on psychotic symptoms and cognitive impairment in first-episode, antipsychotic drug-naive persons with schizophrenia seropositive to Toxoplasma gondii. J Psychiatr Res 53:119–124. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.02.016
Webster JP, Lamberton PHL, Donnelly CA, Torrey EF (2006) Parasites as causative agents of human affective disorders? The impact of anti-psychotic, mood-stabilizer and anti-parasite medication on Toxoplasma gondii’s ability to alter host behaviour. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 273:1023–1030. doi:10.1098/rspb.2005.3413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chorlton, S.D. Toxoplasma gondii and schizophrenia: a review of published RCTs. Parasitol Res 116, 1793–1799 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5478-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5478-y