Abstract
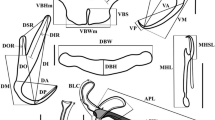
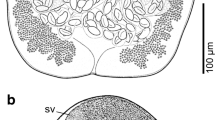
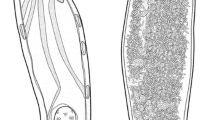
M aritrema corai n. sp. is described based on material from the intestine of the white ibis Eudocimus albus (L.) (Threskiornithidae) in Mexico. The new species can be distinguished morphologically from all congeners by the unique combination of the following morphological features: a very long cirrus sac attenuated distally [cirrus sac to body length ratio 1:0.90–1.29 (mean 1:1.07)]; a large, elongate-oval seminal receptacle, located dorsally between the cirrus sac and ovary; and long, filiform, unarmed, evaginable cirrus. Phylogenetic analyses of 28S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequences for the new species and for Maritrema spp. and Microphallus spp. depicted strong support for the two genera (excluding Microphallus fusiformis) and revealed close relationships between Ma. corai n. sp. and the clade formed by Maritrema novaezealandense Martorelli, Fredensborg, Mouritsen & Poulin, 2004, Maritrema heardi (Kinsella & Deblock, 1994) and Maritrema cf. eroliae.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera E, Ramo C, Busto B (1993) Food habits of the scarlet and white ibis in the Orinoco Plains. Condor 95(3):739–741
Al-Kandari WY, Al-Bustan SA, Alnaqeeb M (2011) Ribosomal DNA sequence characterization of Maritrema cf. eroliae Yamaguti, 1939 (Digenea: Microphallidae) and its life cycle. J Parasitol 97(6):1067–1074
Bush AO (1990) Helminth communities in avian hosts: determinants of pattern. In: Esch GW, Bush AO, Aho JM (eds) Parasite communities: patterns and processes. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 197–232
Cable RM, Connor RS, Balling JW (1960) Digenetic trematodes of Puerto Rican shore birds. SurveyPR Virgin Islands 17:187–255
Canaris AG, Kinsella JM, Didyk AS (2012) Helminth parasites of the western willet, Tringa semipalmata inornata, from Montana and Texas with a checklist of helminth parasites. J Parasitol 98(1):216–221
Ching HL (1963) The description and life cycle of Maritrema laricola sp. n. (Trematoda: Microphallidae). Can J Zool 41(5):881–888
Ching HL (1974) Two new species of Maritrema (Trematoda: Microphallidae) from the Pacific Coast of North America. Can J Zool 52(7):865–869
Ching HL (1978) New marine hosts for Parorchis acanthus, Cryptocotyle lingua, Maritrema megametrios, and Maritrema gratiosum, trematodes of birds from British Columbia, Canada. Can J Zool 56(8):1877–1879
Ching HL (1990) Some helminths of dunlin (Calidris alpina) and western willet (Catoptrophorus semipalmatus inornatus) from California. J Helminthol Soc Wash 57(1):44–50
Coil WH (1955) Notes on the genus Maritrema Nicoll, 1907 (Trematoda: Microphallidae) with the description of two new species. J Parasitol 41(5):533–537
Deblock S (1971) Contribution à l’étude des Microphallidae Travassos, 1920. XXIV. Tentative de phylogénie et de taxonomie. Bull Mus Nat Hist Nat Paris Ser 7(3):353–468
Deblock S (2008) Family Microphallidae Ward, 1901. In: Bray RA, Gibson DI, Jones A (eds) Keys to the Trematoda, vol 3. CABI, Wallingford, pp 451–492
Deblock S, Canaris A (1996) Microphallidae Trematoda: XLVIII Quatre Maritrema du groupe Eroliae; parasites d’oiseaux australiens. Parasite 4:357–361
Deblock S, Canaris AG (1992) Contribution à l’étude des Microphallidae Travassos, 1920 (Trematoda). XLIII. De six espèces d’Afrique du Sud dont une d’un genre nouveau. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 67:204–218
Deblock S, Combes C (1965) Contribution à l’étude des Microphallidae Travassos, 1920 (Trematoda). X. Maritrema pyrenaica n.sp. parasite du desman (Mammifère Insectivore). Essai de clé diagnostique des espèces du genre. Bull Soc Zool Fr 90(1):101–117
Deblock S, Heard RW (1969) Contribution à l’étude des Microphallidae Travassos, 1920 (Trematoda). XIX. Description de Maritrema prosthometra n. sp. et de Longiductotrema nov. gen., parasites d’Oiseaux Ralliformes d’Amérique du Nord. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 44:415–424
Deblock S, Rausch RL (1968) Contribution à l’étude des Microphallidae Travassos, 1920 (Trematoda). XVI. Description de Maritrema megametrios n. sp., parasite d’oiseaux de la côte ouest d’Amérique du Nord. Bull Soc Zool France 93:317–323
Deblock S, Rausch RL (1972) Contribution à l’étude des Microphallidae Travassos, 1920 (Trematoda) XXVI De quelques espèces d’Alaska. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 47(5):701–715
Dery DW (1958) A description of Maritreminoides raminellae, n. sp. (Trematoda: Microphallidae). Proc Helrninthol Soc Wash 25(1):40–44
Diaz JI, Cremonte F (2010) Development from metacercaria to adult of a new species of Maritrema (Digenea: Microphallidae) parasitic in the kelp gull, Larus dominicanus, from the Patagonian coast, Argentina. J Parasitol 96(4):740–745
Diaz JI, Gilardoni C, Cremonte F (2012) Description of Maritrema formicae sp. nov. (Digenea, Microphallidae) parasitic in the kelp gull, Larus dominicanus, from the Patagonian coast, Argentina. Acta Parasitol 57(2):149–153
Didyk AS, Canaris AG, Kinsella JM (2007a) Intestinal helminths of the spotted sandpiper, Actitis macularius (L.), during fall migration in New Brunswick, Canada, with a checklist of helminths reported from this host. Comp Parasitol 74(2):359–363
Didyk AS, Kinsella JM, Canaris AG (2007b) Intestinal helminths of fall-migrating ruddy turnstones, Arenaria interpres (L.), from New Brunswick, Canada, with a checklist of helminths reported from this host. Comp Parasitol 74(2):364–371
Dronen NO, Badley JE (1979) Helminths of shorebirds from the Texas Gulf coast. I. Digenetic trematodes from the long-billed curlew, Numenius americanus. J Parasitol 65(4):645–649
Dronen NO, Blend CK (2008) Patagifer lamothei n. sp. (Digenea: Echinostomatidae: Nephrostominae) from the white ibis Eudocimus albus (Threskiornithidae) from Texas, USA. Rev Mex Biodiv 79:23S–32S
Etchegoin JA, Martorelli SR (1997) Description of a new species of Maritrema (Digenea:Microphallidae) from Mar Chiquita coastal lagoon (Buenos Aires, Argentina) with notes on its life cycle. J Parasitol 83(4):709–713
Ewart MJ, McLaughlin JD (1989) Helminths from spring and fall migrant bufflehead ducks (Bucephala albeola) at Delta, Manitoba, Canada. Can J Zool 68(10):2230–2233
Fay FH, Williamson FSL (1962) Studies on the helminth fauna of Alaska XXXIX. Echinococcus multilocularis Leuckart, 1863, and other helminths of foxes on the Pribilof Islands. Can J Zool 40(5):767–772
Fedynich AM, Pence DB, Gray PN, Bergan JF (1996) Helminth community structure and pattern in two allopatric populations of a nonmigratory waterfowl species (Anas fulvigula). Can J Zool 74(7):1253–1259
Forrester DJ, Spalding MG (2003) Parasites and diseases of wild birds in Florida. University Press of Florida, Florida
Galaktionov KV, Blasco-Costa I, Olson PD (2012) Life cycles, molecular phylogeny and historical biogeography of the ‘pygmaeus’ microphallids (Digenea: Microphallidae): widespread parasites of marine and coastal birds in the Holarctic. Parasitology 139(10):1346–1360
García-Varela M, Nadler SA (2005) Phylogenetic relationships of Palaeacanthocephala (Acanthocephala) inferred from SSU and LSU rDNA gene sequences. J Parasitol 91(6):1401–1409
Hadley CE, Castle RM (1940) Description of a new species of Maritrema Nicoll 1907, Maritrema arenaria, with studies of the life history. Biol Bull 78(2):338–348
Harkema R, Miller GC (1962) Helminths of Procyon lotor solutus from Cape Island, South Carolina. J Parasitol 48(2):333–335
Heath JA, Frederick P, Kushlan JA, Bildstein KL (2009) White Ibis (Eudocimus albus). In: Poole A (ed) The birds of North America online. Ithaca: Cornell Lab of Ornithology. http://bna.birds.cornell.edu/bna/species/009. Accessed 13 June 2015
Martin G-V, Hernández-Mena D, García-Prieto L (2014) Morphological and molecular differentiation of Parastrigea (Trematoda: Strigeidae) from Mexico, with the description of a new species. Parasitol Int 63(2):315–323
Howell SNG, Webb S (1995) A guide to the birds of Mexico and Northern Central America. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17(8):754–755
Kinsella JM (1998) Comparison of helminths of rice rats, Oryzomys palustris, from freshwater and saltwater marshes in Florida. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 55(2):275–280
Kinsella JM, Deblock S (1994) Contribution à l’étude des Microphallidae Travassos, 1920 (Trematoda). XLVI. Description de Floridatrema heardi n. gen., n. sp., parasite d’Oryzomys palustres (Mammifere) des États-Unis. Parasite 1(1):39–44
Kinsella JM, Deblock S (1997) Contribution à l’étude des Microphallidae (Trematoda). LI. De cinq espèces du plongeon imbrin Gavia immer (Aves) des Etats-Unis, dont Microphallus forresteri n. sp. Pluralité vraisemblable de l’espèce Microphallus nicolli (Cable & Hunninen, 1938). Syst Parasitol 37(2):139–148
Luton K, Walker D, Blair D (1992) Comparisons of ribosomal internal transcribed spacers from two congeneric species of flukes (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda: Digenea). Mol Biochem Parasitol 56(2):323–327
Martorelli SR, Fredensborg BL, Mouritsen KN, Poulin R (2004) Description and proposed life cycle ofMaritrema novaezealandensis n. sp. (Microphallidae) parasitic in red-billed gulls, Larus novaehollandiae scopulinus, from Otago Harbor, South Island, New Zealand. J Parasitol 90(2):2720–277
Ortega-Olivares MP, Hernández-Mena DI, Pérez-Ponce de León G, García-Varela M (2011) Helminths of the white ibis, Eudocimus albus (Aves: Threskiornithidae) in Mexico. Zootaxa 3088:15–26
Patten MA (2012) The White Ibis Eudocimus albus subspecies of South America. Bull BOC 132(2):128–132
Posada D (2008) jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25(7):1253–1256
Presswell B, Blasco-Costa I, Kostadinova A (2014) Two new species of Maritrema Nicoll, 1907 (Digenea: Microphallidae) from New Zealand: morphological and molecular characterisation. Parasitol Res 113(5):1641–1656
Rambaut A (2006) FigTree v1.3.1. Institute of Evolutionary Biology. University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh
Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2007) Tracer v1.4. http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer. Accessed 13 June 2015
Ramirez JL, Miyaki CY, Frederick PC, del Lama SN (2014) Species delimitation in the genus Eudocimus (Threskiornithidae: Pelecaniformes): first genetic approach. Waterbirds 37(4):419–425
Rankin JS Jr (1939) Studies on the trematode family Microphallidae Travassos, 1921. I. The genus Levinseniella Stiles and Hassall, 1901, and description of a new genus, Cornucopula. Trans Am Micr Soc 58(4):431–447
Rausch RL, Fay FH, Williamson FS (1990) The ecology of Echinococcus multilocularis (Cestoda: Taeniidae) on St. Lawrence Island Alaska II Helminth populations in the definitive host. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 65(3):131–140
Riggins MA (1953) A study of the helminth parasites of certain shore-inhabiting birds from Lake Texoma, Oklahoma. Proc Okla Acad Sci 34:57–59
Smith SJ (1983) Three new species and a new record of microphallid trematodes from Tasmania, with observations on their in vitro development. Pap Proc R Soc Tasm 117:105–123
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22(21):2688–2690
Stock SP, Campbell JF, Nadler SA (2001) Phylogeny of Steinernema Travassos, 1927 (Cephalobina: Steinernematidae) inferred from ribosomal DNA sequences and morphological characters. J Parasitol 87(4):877–889
Swales WE (1933) On Streptovitella acadiae (gen. et spec. nov.). A Trematode of the family Heterophyidæ from the Black Duck (Anas rubripes). J Helminthol 11(2):115–118
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4673–4380
Tkach V, Pawlowski J, Mariaux J (2000) Phylogenetic analysis of the suborder Plagiorchiata (Platyhelminthes, Digenea) based on partial lsrDNA sequences. Int J Parasitol 30(1):83–93
Tkach V, Littlewood TJ, Olson PD, Kinsella JM, Swiderski Z (2003) Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the Microphalloidea Ward, 1901 (Trematoda: Digenea). Syst Parasitol 56(1):1–15
Underwood HT, Dronen NO (1986) Neocyclustera rally gen. et sp. n. (Cestoidea: Dilepididae) and other endohelminths from clapper rails, Rallus longirostris, from a marsh in Galveston County, Texas. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 53(1):59–62
Underwood HT (1990) Determination of feeding habits from endohelminth fauna. Amer Zool 30(1):114A
Wilgenbusch JC, Warren DL, Swofford DL (2004) AWTY: a system for graphical exploration of MCMC convergence in Bayesian phylogenetic inference. http://ceb.csit.fsu.edu/awty. Accessed 13 June 2015
Yamaguti S (1939) Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan. Part 25. Trematodes of birds, IV. Jap J Zool 8:129–210
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to the staff of the Laboratorio de Rotíferos y Acantocéfalos of the Instituto de Biología, UNAM, for their assistance in the collection and parasitological examination of white ibis and to G. Pérez-Ponce de León for his comments on the morphological identification of the specimens. We also thank to B. Mendoza Garfias for her assistance with the use of the SEM.
Funding
This study was funded by the Programa de Apoyo a Proyectos de Investigación e Inovación Tecnológica (PAPIIT No IN207213) and the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT No. 179048) and partially supported by the Czech Science Foundation (project P506/12/1632). JSHO benefited from a Postdoctoral Fellowship of the Dirección General Asuntos del Personal Académico (DGAPA-UNAM). CDPP benefited from a PhD student grant of the Programa de Posgrado en Ciencias Biológicas, UNAM, and CONACYT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Birds were collected under the collecting permit FAUT 0202 issued by the Mexican government through the Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT) to MGV.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández-Orts, J.S., Pinacho-Pinacho, C.D., García-Varela, M. et al. M aritrema corai n. sp. (Digenea: Microphallidae) from the white ibis Eudocimus albus (Linnaeus) (Aves: Threskiornithidae) in Mexico. Parasitol Res 115, 547–559 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4771-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4771-x