Abstract
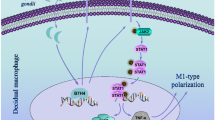
Toxoplasma gondii is an apicomplexan parasite capable of transplacental transmission to cause spontaneous abortion or significant disease in the surviving neonate. Different from the dominant genotypes of T. gondii strains in European and North American which belong to three distinct clonal lineages, type I, type II, and type III, isolates from China possess the predominant genotype of China 1(ToxoDB#9) with a different virulence. The genotype-associated pathogenesis has been investigated previously. Based on two isolates of T. gondii from Chinese wild cats, a murine model of pregnancy and one transwell system in vitro, here we reported differentially polarized activation of macrophages induced by genotype China 1 strains, TgCtwh3 and TgCtwh6 with different virulence to mice, and its impact on trophoblast apoptosis. The results showed that macrophages were alternatively activated when infected with virulent TgCtwh3 while classically activated when infected with low virulent (cyst-forming) TgCtwh6 both in vitro and in vivo. By the analysis of flow cytometry, the percentage of the Th1 cells in two infection groups decreased significantly, and the Th2 cells from spleen escalated only in the virulent TgCtwh3 group. Interestingly, the high parasite burden was noted in the placenta of TgCtwh3-infected group whereas the inflammatory cells infiltration predominates in the TgCtwh6-infected group. In vivo trophoblast apoptosis in TgCtwh3 group was found to be more obvious when compared with TgCtwh6 although it was present in both. The present observations indicate that polarization of macrophages and modulation of Th subsets induced by the isolates with identical genotype but different virulence could contribute to trophoblast apoptosis through different mechanisms, suggesting a virulence-associated pathogenesis of T. gondii in abnormal pregnant outcome.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi M, Kowalewska-Grochowska K, Bahar MA, Kilani RT, Winkler-Lowen B, Guilbert LJ (2003) Infection of placental trophoblasts by Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis 188(4):608–616
Chen ZW, Gao JM, Huo XX, Wang L, Yu L, Halm-Lai F, Xu YH, Song WJ, Hide G, Shen JL, Lun ZR (2011) Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from cats in different geographic regions of China. Vet Parasitol 183(1–2):166–170
Cook T, Roos D, Morada M, Zhu G, Keithly JS, Feagin JE, Wu G, Yarlett N (2007) Divergent polyamine metabolism in the Apicomplexa. Microbiology 153(Pt 4):1123–1130
Dalton DK, Haynes L, Chu CQ, Swain SL, Wittmer S (2000) Interferon gamma eliminates responding CD4 T cells during mycobacterial infection by inducing apoptosis of activated CD4 T cells. J Exp Med 192(1):117–122
Desmonts G, Couvreur J (1974) Congenital toxoplasmosis. A prospective study of 378 pregnancies. N Engl J Med 290(20):1110–1116
dos Santos SA, de Andrade Junior DR, de Andrade DR (2011) TNF-alpha production and apoptosis in hepatocytes after Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium invasion. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 53(2):107–112
El Kasmi KC, Qualls JE, Pesce JT, Smith AM, Thompson RW, Henao-Tamayo M, Basaraba RJ, Konig T, Schleicher U, Koo MS, Kaplan G, Fitzgerald KA, Tuomanen EI, Orme IM, Kanneganti TD, Bogdan C, Wynn TA, Murray PJ (2008) Toll-like receptor-induced arginase 1 in macrophages thwarts effective immunity against intracellular pathogens. Nat Immunol 9(12):1399–1406
Gao XJ, Zhao ZJ, He ZH, Wang T, Yang TB, Chen XG, Shen JL, Wang Y, Lv FL, Hide G, Lun ZR (2012) Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnant women in China. Parasitology 139(2):139–147
Hill D, Dubey JP (2002) Toxoplasma gondii: transmission, diagnosis and prevention. Clin Microbiol Infect 8(10):634–640
Howe DK, Sibley LD (1995) Toxoplasma gondii comprises three clonal lineages: correlation of parasite genotype with human disease. J Infect Dis 172(6):1561–1566
Iniesta V, Gomez-Nieto LC, Corraliza I (2001) The inhibition of arginase by N(omega)-hydroxy-l-arginine controls the growth of Leishmania inside macrophages. J Exp Med 193(6):777–784
Jensen KD, Wang Y, Wojno ED, Shastri AJ, Hu K, Cornel L, Boedec E, Ong YC, Chien YH, Hunter CA, Boothroyd JC, Saeij JP (2011) Toxoplasma polymorphic effectors determine macrophage polarization and intestinal inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 9(6):472–483
Li Z, Zhao ZJ, Zhu XQ, Ren QS, Nie FF, Gao JM, Gao XJ, Yang TB, Zhou WL, Shen JL, Wang Y, Lu FL, Chen XG, Hide G, Ayala FJ, Lun ZR (2012) Differences in iNOS and arginase expression and activity in the macrophages of rats are responsible for the resistance against T. gondii infection. PLoS One 7(4):e35834
Liesenfeld O, Kosek J, Remington JS, Suzuki Y (1996) Association of CD4+ T cell-dependent, interferon-gamma-mediated necrosis of the small intestine with genetic susceptibility of mice to peroral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med 184(2):597–607
Loke P, Nair MG, Parkinson J, Guiliano D, Blaxter M, Allen JE (2002) IL-4 dependent alternatively-activated macrophages have a distinctive in vivo gene expression phenotype. BMC Immunol 3:7
Mantovani A (2008) From phagocyte diversity and activation to probiotics: back to Metchnikoff. Eur J Immunol 38(12):3269–3273
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M (2004) The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol 25(12):677–686
Melo MB, Jensen KD, Saeij JP (2011) Toxoplasma gondii effectors are master regulators of the inflammatory response. Trends Parasitol 27(11):487–495
Pappas G, Roussos N, Falagas ME (2009) Toxoplasmosis snapshots: global status of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and implications for pregnancy and congenital toxoplasmosis. Int J Parasitol 39(12):1385–1394
Polgar K, Hill JA (2002) Identification of the white blood cell populations responsible for Th1 immunity to trophoblast and the timing of the response in women with recurrent pregnancy loss. Gynecol Obstet Invest 53(1):59–64
Raes G, Brys L, Dahal BK, Brandt J, Grooten J, Brombacher F, Vanham G, Noel W, Bogaert P, Boonefaes T, Kindt A, Van den Bergh R, Leenen PJ, De Baetselier P, Ghassabeh GH (2005) Macrophage galactose-type C-type lectins as novel markers for alternatively activated macrophages elicited by parasitic infections and allergic airway inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 77(3):321–327
Ramos JM, Milla A, Rodriguez JC, Padilla S, Masia M, Gutierrez F (2011) Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection among immigrant and native pregnant women in Eastern Spain. Parasitol Res 109(5):1447–1452
Robben PM, Mordue DG, Truscott SM, Takeda K, Akira S, Sibley LD (2004) Production of IL-12 by macrophages infected with Toxoplasma gondii depends on the parasite genotype. J Immunol 172(6):3686–3694
Sibley LD, Boothroyd JC (1992) Virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii comprise a single clonal lineage. Nature 359(6390):82–85
Sindrilaru A, Peters T, Wieschalka S, Baican C, Baican A, Peter H, Hainzl A, Schatz S, Qi Y, Schlecht A, Weiss JM, Wlaschek M, Sunderkotter C, Scharffetter-Kochanek K (2011) An unrestrained proinflammatory M1 macrophage population induced by iron impairs wound healing in humans and mice. J Clin Invest 121(3):985–997
Van den Bossche J, Bogaert P, van Hengel J, Guerin CJ, Berx G, Movahedi K, Van den Bergh R, Pereira-Fernandes A, Geuns JM, Pircher H, Dorny P, Grooten J, De Baetselier P, Van Ginderachter JA (2009) Alternatively activated macrophages engage in homotypic and heterotypic interactions through IL-4 and polyamine-induced E-cadherin/catenin complexes. Blood 114(21):4664–4674
Wang L, Chen H, Liu D, Huo X, Gao J, Song X, Xu X, Huang K, Liu W, Wang Y, Lu F, Lun ZR, Luo Q, Wang X, Shen J (2013) Genotypes and mouse virulence of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from animals and humans in China. PLoS One 8(1):e53483
Welch JS, Escoubet-Lozach L, Sykes DB, Liddiard K, Greaves DR, Glass CK (2002) TH2 cytokines and allergic challenge induce Ym1 expression in macrophages by a STAT6-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 277(45):42821–42829
Wong SY, Remington JS (1994) Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy. Clin Infect Dis 18(6):853–861, quiz 862
Wood KJ, Sawitzki B (2006) Interferon gamma: a crucial role in the function of induced regulatory T cells in vivo. Trends Immunol 27(4):183–187
Xiao W, Hong H, Kawakami Y, Lowell CA, Kawakami T (2008) Regulation of myeloproliferation and M2 macrophage programming in mice by Lyn/Hck, SHIP, and Stat5. J Clin Invest 118(3):924–934
Xu X, Liu T, Zhang A, Huo X, Luo Q, Chen Z, Yu L, Li Q, Liu L, Lun ZR, Shen J (2012) Reactive oxygen species-triggered trophoblast apoptosis is initiated by endoplasmic reticulum stress via activation of caspase-12, CHOP, and the JNK pathway in Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. Infect Immun 80(6):2121–2132
Yu L, Shen J, Su C, Sundermann CA (2013) Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in wildlife from Alabama, USA. Parasitol Res 112(3):1333–1336
Zhou DH, Yuan ZG, Zhao FR, Li HL, Zhou Y, Lin RQ, Zou FC, Song HQ, Xu MJ, Zhu XQ (2011) Modulation of mouse macrophage proteome induced by Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites in vivo. Parasitol Res 109(6):1637–1646
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Natural Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2010CB530001) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 81171605 and 81101272). Our thanks are given to Prof. Geoff Hide at Center for Parasitology and Disease, School of Environment and Life Sciences, University of Salford, UK for polishing the language in the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Tingting Liu and Qian Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Zhang, Q., Liu, L. et al. Trophoblast apoptosis through polarization of macrophages induced by Chinese Toxoplasma gondii isolates with different virulence in pregnant mice. Parasitol Res 112, 3019–3027 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3475-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3475-3