Abstract
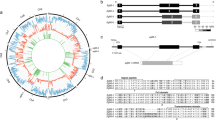
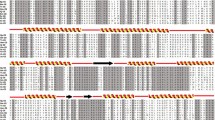
Members of the 14-3-3 protein family have been identified as regulatory molecules in intracellular signaling pathways and cell cycle control. Previously, the first Echinococcus 14-3-3 isoform (E14-3-3.1) was isolated from E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestode stages. Hyperexpression of this isoform was claimed to be associated with non-restricted tumor-like growth of the E. multilocularis metacestode. In this report, we describe the characterization of a 14-3-3 cDNA from E. granulosus and E. multilocularis corresponding to a second isoform of this family, E14-3-3.2. The characterized 14-3-3 gene was interrupted by two introns whose sequence and positions were conserved in both Echinococcus species. The deduced amino acid sequence of E14-3-3.2 showed 88% identity to the E14-3-3.1 isoform and 52% identity to a third Echinococcus isoform (E14-3-3.3) described by other authors. These findings, coupled to Southern blot analysis, suggest the presence of more than one 14-3-3 gene in Echinococcus. Phylogenenetically, the Echinococcus 14-3-3.1 and 14-3-3.2 isoforms appeared to cluster with zeta-type (“pro-tumorigenic”) 14-3-3 isoforms from closely related organisms, whereas the E14-3-3.3 isoform grouped with 14-3-3 epsilon isoforms. The presence of more than one 14-3-3 isoform might indicate isoform-specific roles in the different parasite stages of Echinococcus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken A, Collinge DB, Heusden BP van, Isobe T, Roseboom PH, Rosenfeld G, Soll J (1992) 14-3-3 proteins: a highly conserved, widespread family of eukaryotic proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 17:498–501
Al-Khedery B, Barnwell JW, Galinski MR (1999) Stage-specific expression of 14-3-3 in asexual blood-stage Plasmodium. Mol Biochem Parasitol 102:117–130
Beitz E (2000) TEXshade shading and labeling multiple sequence alignments using LaTeX2E. Bioinformatics 16:135–139
DeLille JM, Sehnke PC, Ferl RJ (2001) The Arabidopsis 14-3-3 family of signaling regulators. Plant Physiol 126:35–38
De Vetten NC, Ferl RJ (1994) Two genes encoding GF14 (14-3-3) proteins in Zea mays. Structure, expression, and potential regulation by the G-box binding complex. Plant Physiol 106:1593–1604
Ferl RJ, Manak MS, Reyes MF (2002) The 14-3-3s. Genome Biol 3:3010.1–3010.7
Fernández C, Gregory WF, Loke P, Maizels RM (2002) Full-length-enriched cDNA libraries from Echinococcus granulosus contain separate populations of oligo-capped and trans-spliced transcripts and a high level of predicted signal peptide sequences. Mol Biochem Parasitol 122:171–180
Jones DH, Ley S, Aitken A (1995) Isoforms of 14-3-3 protein can form homo- and heterodimers in vivo and in vitro: implications for function as adapter proteins. FEBS Lett 368:55–58
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
McGonigle S, Beall MJ, Feeney EL, Pearce EJ (2001) Conserved role for 14-3-3 epsilon downstream of type I TGF beta receptors. FEBS Lett 490:65–69
McGonigle S, Loschiavo M, Pearce EJ (2002) 14-3-3 proteins in Schistosoma mansoni: identification of a second epsilon isoform. Int J Parasitol 32:685–693
McManus DP, Knight M, Simpson AJ (1985) Isolation and characterisation of nucleic acids from the hydatid organisms, Echinococcus spp (Cestoda). Mol Biochem Parasitol 16:251–266
Muratake T, Hayashi S, Ichikawa T, Kumanishi T, Ichimura Y, Kuwano R, Isobe T, Wang Y, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Takahashi Y (1996) Structural organization and chromosomal assignment of the human 14-3-3 eta chain gene (YWHAH). Genomics 36:63–69
Rosenquist M, Sehnke P, Ferl RJ, Sommarin M, Larsson C (2000) Evolution of the 14-3-3 protein family: does the large number of isoforms in multicellular organisms reflect functional specificity? J Mol Evol 51:446–458
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Sanger R, Nicklen S, Coulson AX (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Schechtman D, Ram D, Tarrab-Hazdai R, Arnon R, Schechter I (1995) Stage-specific expression of the mRNA encoding a 14-3-3 protein during the life cycle of Schistosoma mansoni. Mol Biochem Parasitol 73:275–278
Siles-Lucas M, Felleisen RS, Hemphill A, Wilson W, Gottstein B (1998) Stage-specific expression of the 14-3-3 gene in Echinococcus multilocularis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 91:281–293
Siles-Lucas M, Nunes CP, Zaha A, Breijo M (2000) The 14-3-3 protein is secreted by the adult worm of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasite Immunol 22:521–528
Siles-Lucas M, Nunes CP, Zaha A (2001) Comparative analysis of the 14-3-3 gene and its expression in Echinococcus granulosus and Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes. Parasitology 122:281–287
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acid Res 24:4876–4882
Thompson RCA (1995) Biology and systematics of Echinococcus. In: Thompson RCA, Lymbery AJ (eds) Echinococcus and hydatid disease. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 1–50
Toyooka K, Muratake T, Watanabe H, Hayashi S, Ichikawa T, Usui H, Washiyama K, Kumanishi T, Takahashi Y (2002) Isolation and structure of the mouse 14-3-3 eta chain gene and the distribution of 14-3-3 eta mRNA in the mouse brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 100:13–20
Voigt J, Liebich I, Wostemeyer J, Adam KH, Marquardt O (2000) Nucleotide sequence, genomic organization and cell-cycle-dependent expression of a Chlamydomonas 14-3-3 gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1492:395–405
Wang W, Shakes DC (1996) Molecular evolution of the 14-3-3 protein family. J Mol Evol 43:384–398
Wang W, Shakes DC (1997) Expression patterns and transcript processing of ftt-1 and ftt-2, two C. elegans 14-3-3 homologues. J Mol Biol 268:619–630
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by PADCT (620081/95-3), CNPq, FAPERGS, the Swiss National Science Foundation (Project 31-63615.00) and the Ministry of Science and Technology in Spain (Project AGL2002-00644). M.S.L. is the holder of a “Ramón y Cajal” contract. We acknowledge the financial contributions made by the Interreg II project BWA 30.027 and the EU EchinoRisk project QLK2-CT-2001-01995 (BBW 00.0586-1) and also thank J.J. Arenzon for a critical reading of the manuscript and A.P. Nunes for help with the figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nunes, C.P., Zaha, A., Gottstein, B. et al. 14-3-3 gene characterization and description of a second 14-3-3 isoform in both Echinococcus granulosus and E. multilocularis. Parasitol Res 93, 403–409 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1147-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1147-z