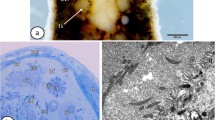
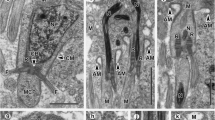
Abstract
The ultrastructure of the testes in two representatives of the enigmatic taxon Nemertodermatida was studied using transmission electron microscopy. Nemertoderma westbladi has paired testes, which are delineated by lining cells. Within each testis, different follicles, each surrounded by a membrane-like structure, are found. Flagellophora apelti has genuinely follicular testes, consisting of several follicles, each containing a certain stage of spermatogenesis. As the gametes are not enclosed by a structure that can be called a true gonad, the structure of the testes differs from most bilaterian animals, but resembles the organization of gametogenic areas of ctenophores. Each stage of spermatogenesis in F. apelti is described, enabling the inference of the origin of the structures seen in mature spermatozoa. The overall structure of the mature spermatozoa is similar in all nemertodermatids and unique within the Metazoa: an elongated head containing the nucleus; a middle piece containing an axoneme, mitochondrial derivatives and in F. apelti granular derivatives; and a flagellar tail.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baguñà J, Martinez P, Paps J, Riutort M (2008) The dawn of bilaterian animals: the case of acoelomorph flatworms. Bioessays 26:1046–1057
Boone M, Willems M, Claeys M, Artois T (2011) Spermatogenesis and the structure of the testes in Isodiametra pulchra (Isodiametridae, Acoela). Acta Zool 92:101–108
Campbell RD (1974) Cnidaria. In: Giese AC, Pearse JS (eds) Reproduction of marine invertebrates volume I: acoelomate and pseudocoelomate metazoans. Academic Press, New York, pp 133–199
Edgecombe GD, Giribet G, Dunn CW, Hejnol A, Kristensen RM, Neves RC, Rouse GW, Worsaae K, Sorensen MV (2011) Higher-level metazoan relationships: recent progress and remaining questions. Org Div Evol 11:151–172
Ehlers U (1985) Das phylogenetische system der plathelminthes. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart
Eisenman EA, Alfert M (1982) A new fixation procedure for preserving the ultrastructure of marine invertebrate tissues. J Microsc 125:117–120
Faubel A, Dörjes J (1978) Flagellophora apelti gen.n.sp.n.: a remarcable representative of the order Nemertodermatida (Turbellaria: Archoophora). Senckenbergiana marit 10:1–13
Franzén Å (1956) On spermiogenesis, morphology of the spermatozoon, and biology of fertilization among invertebrates. Zool bidrag Uppsala 31:355–482
Hejnol A, Obst M, Stamatakis A, Ott M, Rouse GW, Edgecombe GD, Martinez P et al (2009) Assessing the root of bilaterian animals with scalable phylogenomic methods. Proc R Soc B 276:4261–4270
Hendelberg J (1977) Comparative morphology of turbellarian spermatozoa studied by electron microscopy. Acta Zool Fenn 154:149–162
Hernandez-Nicaise ML (1991) Ctenophora. In: Harrison FW, Westfall JA (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates volume 2: Placozoa, Porifera, Cnidaria and Ctenophora. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 359–418
Jondelius U, Ruiz-Trillo I, Baguñà J, Riutort M (2002) The Nemertodermatida are basal bilaterians and not members of the Platyhelminthes. Zool Scr 31:201–215
Lundin K (1997) Comparative ultrastructure of the epidermal ciliary rootlets and associated structures in species of the Nemertodermatida and Acoela (Plathelminthes). Zoomorphology 117:81–92
Lundin K (1998) Symbiotic bacteria on the epidermis of species of the Nemertodermatida (Platyhelminthes, Acoelomorpha). Acta Zool 79:187–191
Lundin K (2000) Phylogeny of the Nemertodermatida (Acoelomorpha, Platyhelminthes). A cladistic analysis. Zool Scr 29:65–74
Lundin K (2001) Degenerating epidermal cells in Xenoturbella bocki (phylum uncertain), Nemertodermatida and Acoela (Platyhelminthes). Belg J Zool 131:153–157
Lundin K, Hendelberg J (1995) Ultrastructure of the epidermis of Meara stichopi (Platyhelminthes, Nemertodermatida) and associated extra-epidermal bacteria. Hydrobiologia 305:161–165
Lundin K, Hendelberg J (1996) Degenerating epidermal bodies (‘‘pulsatile bodies’’) in Meara stichopi (Plathelminthes, Nemertodermatida). Zoomorphology 116:1–5
Lundin K, Hendelberg J (1998) Is the sperm type of the Nemertodermatida close to that of the ancestral Platyhelminthes? Hydrobiologia 383:197–205
Lundin K, Sterrer W (2001) The Nemertodermatida. In: Littlewood DTJ, Bray RA (eds) Interrelationships of the Platyhelminthes. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 24–27
Mwinyi A, Bailly X, Bourlat S, Jondelius U, Littlewood DTH, Podsiadlowski L (2010) The phylogenetic position of Acoela as revealed by the complete mitochondrial genome of Symsagittifera roscoffensis. BMC Evol Biol 10:309
Obst M, Nakano H, Bourlat SJ, Thorndyke MC, Telford MJ, Nyengaard JR, Funch P (2011) Spermatozoon ultrastructure of Xenoturbella bocki (Westblad 1949). Acta Zool 92:109–115
Philippe H, Brinkmann H, Copley RR, Moroz LL, Nakano H, Poustka AJ, Wallberg A, Peterson KJ, Telford MJ (2011) Acoelomorph flatworms are deuterostomes related to Xenoturbella. Nature 470:255–258
Pianka HD (1974) Ctenophora. In: Giese AC, Pearse JS (eds) Reproduction of marine invertebrates volume I: acoelomate and pseudocoelomate metazoans. Academic Press, New York, pp 201–265
Raikova OI, Justine JL (1994) Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis and spermatozoa in three acoels (Platyhelminthes). Annales des Sciences Naturelles-Zoologie et Biologie Animale 15:63–75
Raikova OI, Justine JL (1999) Microtubular system during spermiogenesis and in the spermatozoon of Convoluta saliens (Platyhelminthes, Acoela): tubulin immunocytochemistry and electron microscopy. Mol Reprod Dev 52:74–85
Raikova OI, Falleni A, Justine JL (1997) Spermiogenesis in Paratomella rubra (Platyhelminthes, Acoela): ultrastructural, immunocytochemical, cytochemical studies and phylogenetic implications. Acta Zool 78:295–307
Raikova OI, Reuter M, Jondelius U, Gustafsson MKS (2000) The brain of the Nemertodermatida (Platyhelminthes) as revealed by anti-5HT and anti-FMRFamide immunostainings. Tissue Cell 32:358–365
Raikova OI, Reuter M, Gustafsson MKS, Maule A, Halton DW, Jondelius U (2004) Basiepidermal nervous system in Nemertoderma westbladi (Nemertodermatida): GYIRFamide immunoreactivity. Zoology 107:75–86
Reuter M, Raikova OI, Jondelius U, Gustafsson MKS, Maule AG, Halton DW (2001) Organisation of the nervous system in the Acoela: an immunocytochemical study. Tissue Cell 33:119–128
Rieger RM, Tyler S, Smith JPS, Rieger GE (1991) Platyhelminthes and Nemertinea. In: Harrison F, Bogitsh BJ (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 3. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 7–140
Ruiz-Trillo I, Paps J, Loukota M, Ribera C, Jondelius U, Baguñà J (2002) A phylogenetic analysis of myosin heavy chain type II sequences corroborates that Acoela and Nemertodermatida are basal bilaterians. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11246–11251
Schmidt-Rhaesa A (2007) The evolution of organ systems. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Steinböck O (1930–1931) Ergebnisse einer von E. Reisinger and O. Steinböck mit Hilfe des Rask-Orsted Fonds durchgeführten Reise in Grönland 1926. 2. Nemertoderma bathycola nov. Gen. nov. spec., eine eigenartige Turbellarie aus der Tiefe der Diskobay; nebst einem Beitrag zur Kenntnis des Nemertinenepithels. Vidensk Medd Dan Naturhist Foren 90:47–84
Sterrer W (1998) New and known Nemertodermatida (Platyhelminthes-Acoelomorpha)—a revision. Belg J Zool 128:55–92
Tyler S, Rieger RM (1975) Uniflagellate spermatozoa in Nemertoderma (Turbellaria) and their phylogenetic significance. Science 188(4189):730–732
Tyler S, Rieger RM (1977) Ultrastructural evidence for the systematic position of the Nemertodermatida (Turbellaria). Acta Zool Fenn 54:193–207
Wallberg A, Curini-Galletti M, Ahmadzadeh A, Jondelius U (2007) Dismissal of Acoelomorpha: Acoela and Nemertodermatida are separate early bilaterian clades. Zool Scr 36:509–523
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Flemish Marine Institute (VLIZ) for the use of the research vessel “Zeeleeuw” and the assistance of its crew for the collection of F. apelti. We acknowledge Prof. Dr. Ulf Jondelius for the assistance during the collection of N. westbladi, and thank the crew at the Sven Lovén Centre for Marine Sciences (Kristineberg). We thank Prof. Dr. Ernest Schockaert for useful discussions and Dr. Nikki Watson (Australia) for linguistic corrections. This research was funded by an aspirant grant to MB provided by the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen), the samplings were carried out in the framework of project G.08.208, also financed by the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen). We gratefully acknowledge the reviewers for their valuable comments, which helped us to improve this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Seth Tyler.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boone, M., Bert, W., Claeys, M. et al. Spermatogenesis and the structure of the testes in Nemertodermatida. Zoomorphology 130, 273–282 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-011-0137-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-011-0137-9