Abstract
Background
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a malignant epithelial tumor characterized by a dismal prognosis. Given the lack of therapeutic strategies and durable treatment options currently available, identifying innovative treatments for CCA is an urgent unmet clinical need. Cucurbitacin C (CuC) is a distinct variant of the cucurbitacin family, displaying promising anti-cancer activity against various tumor types. The primary objective of our research is to elucidate the promising effects of CuC on CCA.
Methods
The impact of CuC on CCA cell lines was assessed by cell count kit-8 assay, EdU staining assay, colony formation assay, wound-healing assay, and Transwell assay. Flow cytometric analysis was conducted to explore the function of CuC treatments on cell-cycle distribution and apoptosis in CCA cells. Computational biology and network pharmacology approaches were utilized to predict potential targets of CuC. Furthermore, a tumor xenograft mouse model was established using CCA cells to explore the anti-cancer effects of CuC in vivo.
Results
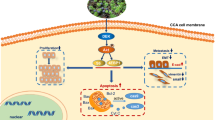
Our research findings revealed that CuC exerted a suppressive effect on CCA cell progression. Cell viability assays, EdU staining assays, and colony formation assays demonstrated that CuC effectively suppressed viability and proliferation of CCA cells. Wound-healing assays and Transwell assays indicated that CuC effectively inhibits the migratory and invasive capabilities of CCA cells. Flow cytometry analysis elucidated that CuC played its anti-proliferative role in CCA cells by arresting G0/G1 phase and increasing apoptosis. Through bioinformatics and network pharmacology analysis, in conjunction with western blot analysis, we demonstrated CuC mediated the inhibition of CCA cell progression through modulation of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Additionally, the CCA xenograft tumor model was established, and the results supported the inhibition of CuC treatment against CCA progression in vivo.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that CuC possesses notable capabilities to suppress cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in CCA. Importantly, the inhibitory effects of CuC on CCA progression are attributed to its modulation of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Altogether, our study demonstrated that CuC holds promise as a prospective therapeutic agent for treating CCA.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Banales JM, Marin JJG, Lamarca A, Rodrigues PM, Khan SA, Roberts LR et al (2020) Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: the next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 17(9):557–588. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-020-0310-z
Benavides M, Antón A, Gallego J, Gómez MA, Jiménez-Gordo A, La Casta A et al (2015) Biliary tract cancers: SEOM clinical guidelines. Clin Transl Oncol 17(12):982–987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1436-2
Bergquist A, von Seth E (2015) Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 29(2):221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2015.02.003
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Brindley PJ, Bachini M, Ilyas SI, Khan SA, Loukas A, Sirica AE et al (2021) Cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7(1):65. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-021-00300-2
Chan KT, Li K, Liu SL, Chu KH, Toh M, Xie WD (2010) Cucurbitacin B inhibits STAT3 and the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in leukemia cell line K562. Cancer Lett 289(1):46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2009.07.015
Deng C, Zhang B, Zhang S, Duan C, Cao Y, Kang W et al (2016) Low nanomolar concentrations of Cucurbitacin-I induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis by perturbing redox homeostasis in gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis 7(2):e2106. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.13
Ding N, Yamashita U, Matsuoka H, Sugiura T, Tsukada J, Noguchi J et al (2011) Apoptosis induction through proteasome inhibitory activity of cucurbitacin D in human T-cell leukemia. Cancer 117(12):2735–2746. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.25711
Gao Y, Islam MS, Tian J, Lui VW, Xiao D (2014) Inactivation of ATP citrate lyase by Cucurbitacin B: a bioactive compound from cucumber, inhibits prostate cancer growth. Cancer Lett 349(1):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.03.015
Hogdall D, Lewinska M, Andersen JB (2018) Desmoplastic tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy in Cholangiocarcinoma. Trends Cancer 4(3):239–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2018.01.007
Hong SH, Ku JM, Lim YS, Lee SY, Kim JH, Cheon C et al (2020) Cucurbitacin D overcomes Gefitinib resistance by blocking EGF binding to EGFR and inducing cell death in NSCLCs. Front Oncol 10:62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00062
Hsu YC, Huang TY, Chen MJ (2014) Therapeutic ROS targeting of GADD45γ in the induction of G2/M arrest in primary human colorectal cancer cell lines by cucurbitacin E. Cell Death Dis 5(4):e1198. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.151
Kausar H, Munagala R, Bansal SS, Aqil F, Vadhanam MV, Gupta RC (2013) Cucurbitacin B potently suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer growth: identification of intracellular thiols as critical targets. Cancer Lett 332(1):35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.01.008
Lendvai G, Szekerczes T, Illyes I, Dora R, Kontsek E, Gogl A et al (2020) Cholangiocarcinoma: Classification, Histopathology and Molecular Carcinogenesis. Pathol Oncol Res 26(1):3–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-018-0491-8
Lin X, Farooqi AA (2021) Cucurbitacin mediated regulation of deregulated oncogenic signaling cascades and non-coding RNAs in different cancers: spotlight on JAK/STAT, Wnt/β-catenin, mTOR, TRAIL-Mediated Pathways. Seminars Cancer Biol 73:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.10.012
Nakamura H, Arai Y, Totoki Y, Shirota T, Elzawahry A, Kato M et al (2015) Genomic spectra of biliary tract cancer. Nat Genet 47(9):1003–1010. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3375
Qing ZX, Zhou Y, Liu XB, Cheng P, Zeng JG (2014) 23,24-Dihydrocucurbitacin C: a new compound regarded as the next metabolite of cucurbitacin C. Nat Prod Res 28(15):1165–1170. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2014.921787
Qing Z, Shi Y, Han L, Li P, Zha Z, Liu C et al (2022) Identification of seven undescribed cucurbitacins in Cucumis sativus (cucumber) and their cytotoxic activity. Phytochemistry 197:113123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113123
Rizvi S, Khan SA, Hallemeier CL, Kelley RK, Gores GJ (2018) Cholangiocarcinoma—evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15(2):95–111. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.157
Rodrigues PM, Olaizola P, Paiva NA, Olaizola I, Agirre-Lizaso A, Landa A et al (2021) Pathogenesis of Cholangiocarcinoma. Annu Rev Pathol 16:433–463. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-030220-020455
Ruzzenente A, Fassan M, Conci S, Simbolo M, Lawlor RT, Pedrazzani C et al (2015) Cholangiocarcinoma heterogeneity revealed by multigene mutational profiling: clinical and prognostic relevance in surgically resected patients. Ann Surg Oncol 23(5):1699–1707. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-5046-6
Sikander M, Malik S, Chauhan N, Khan P, Kumari S, Kashyap VK et al (2019) Cucurbitacin D reprograms glucose metabolic network in prostate cancer. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030364
Sikander M, Malik S, Khan S, Kumari S, Chauhan N, Khan P et al (2019) Novel Mechanistic Insight into the Anticancer Activity of Cucurbitacin D against Pancreatic Cancer (Cuc D Attenuates Pancreatic Cancer). Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010103
Thoennissen NH, Iwanski GB, Doan NB, Okamoto R, Lin P, Abbassi S et al (2009) Cucurbitacin B induces apoptosis by inhibition of the JAK/STAT pathway and potentiates antiproliferative effects of gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 69(14):5876–5884. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-09-0536
Ueno M, Kariya R, Sittithumcharee G, Okada S (2021) Cucurbitacin B induces apoptosis of primary effusion lymphoma via disruption of cytoskeletal organization. Phytomedicine 85:153545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153545
Valle JW, Kelley RK, Nervi B, Oh D-Y, Zhu AX (2021) Biliary tract cancer. The Lancet 397(10272):428–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00153-7
Wei J, Chen X, Li Y, Li R, Bao K, Liao L et al (2022) Cucurbitacin B-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest of conjunctival melanoma cells mediated by GRP78-FOXM1-KIF20A pathway. Acta Pharm Sin b 12(10):3861–3876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2022.05.021
Wu D, Wang Z, Lin M, Shang Y, Wang F, Zhou J et al (2019) In vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of Cucurbitacin C, a novel natural product from cucumber. Front Pharmacol 10:1287. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01287
Yang P, Lian Q, Fu R, Ding GB, Amin S, Li Z et al (2022) Cucurbitacin E triggers cellular senescence in colon cancer cells via regulating the miR-371b-5p/TFAP4 signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem 70(9):2936–2947. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07952
You L, Lin J, Yu Z, Qian Y, Bi Y, Wang F et al (2022) Nobiletin suppresses cholangiocarcinoma proliferation via inhibiting GSK3β. Int J Biol Sci 18(15):5698–5712. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.78345
Yuan R, Zhao W, Wang QQ, He J, Han S, Gao H et al (2021) Cucurbitacin B inhibits non-small cell lung cancer in vivo and in vitro by triggering TLR4/NLRP3/GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis. Pharmacol Res 170:105748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105748
Zhang YZ, Wang CF, Zhang LF (2018) Cucurbitacin D impedes gastric cancer cell survival via activation of the iNOS/NO and inhibition of the Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Rep 39(6):2595–2603. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6361
Acknowledgements
Fig. 6A were adapted and created by Figdraw (www.figdraw.com).
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Zhejiang Health Committee (2021ZH003), Hangzhou Science and Technology Commission (202004A14), and the Construction Fund of Medical Key Disciplines of Hangzhou (OO20190001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WC and JY conceived and designed the experiments. WC performed laboratory experiments, wrote the manuscript, and prepared the figures. ZH and CL conducted data collection and analysis. QL, YW, and JY edited and revised the manuscript. YW and JY provided direction and guidance throughout the writing of this manuscript and shared senior authorship. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
The animal study was reviewed and approved by Animal Ethical and Welfare Committee of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Approval Number: No. SYXK (Zhejiang) 2018-0012).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Liu, Q., Huang, Z. et al. Cucurbitacin C as an effective anti-cancer agent: unveiling its potential role against cholangiocarcinoma and mechanistic insights. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 13123–13136 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05188-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05188-x