Abstract
Purpose
To assess the effects of metformin use on lung cancer (LC) survival according to summarized results from observational studies (OBs) and randomized clinical trials (RCTs).
Methods
We systematically searched electronic databases and, to our knowledge, for the first time, RCTs were included in a systematic review and meta-analysis about the role of metformin on LC survival. We carried out meta-analyses separately for OBs and RCTs. Analyses for overall survival (OS) concerning OBs were stratified by studies with and without time-dependent approach. Subgroup analyses were adopted for OBs to identify the sources of heterogeneity. Included studies were assessed for quality.
Results
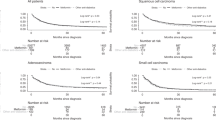
We identified ten OBs and four RCTs. For OBs, metformin use was associated with improved OS for LC patients. Only two studies used time-dependent approach in which a higher ratio was found when compared to the non-use of the time-dependent analysis in eight studies. OBs were classified as high quality but the risk of bias was “unclear” in eight OBs due to absence of the time-dependent analysis. For RCTs, metformin use was not beneficial for OS and neither for progression-free survival. Heterogeneous quality was found among RCTs. Sources of bias that could alter significantly the results or raise doubts were identified in RCTs.
Conclusion
Time-dependent analysis should be considered an appropriate strategy for OBs focused on the metformin use for LC patients’ survival, and further studies applying this approach are required. More well-designed RCTs are needed to provide consistent results for the association between metformin use and LC survival.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AMPK:
-
Adenosine monophosphate-active protein kinase
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- LC:
-
Lung cancer
- LCSS:
-
Lung cancer-specific survival
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- RCT:
-
Randomized clinical trial
- RR:
-
Relative risk
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- SCLC:
-
Small cell lung carcinoma
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- 95% CI:
-
95% Confidence interval
References
Ahmed I, Ferro A, Cohler A, Langenfeld J, Surakanti SG, Aisner J et al (2015) Impact of metformin use on survival in locally-advanced, inoperable non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive chemoradiation. J Thorac Dis 7(3):346–355
Arrieta O, Varela-Santoyo E, Soto-Perez-de-Celis E, Sánchez-Reyes R, De la Torre-Vallejo M, Muñiz-Hernández S et al (2016) Metformin use and its effect on survival in diabetic patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 16:633
Arrieta O, Barrón F, Padilla MS, Avilés-Salas A, Ramírez-Tirado LA, Arguelles Jiménez MJ et al (2019) Effect of metformin plus tyrosine kinase inhibitors compared with tyrosine kinase inhibitors alone in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated lung adenocarcinoma: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 5(11):e192553
Bugge AS, Lund MB, Valberg M, Brustugun OT, Solberg S, Kongerud J (2018) Cause-specific death after surgical resection for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 53(1):221–227
Burns PB (2011) The levels of evidence and their role in evidence-based medicine. Plast Reconstr Surg 128(1):305–310
Cao X, Wen ZS, Wang XD, Li Y, Liu KY, Wang X (2017) The clinical effect of metformin on the survival of lung cancer patients with diabetes: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies. J Cancer 8(13):2532–2541
Chen H, Yao W, Chu Q, Han R, Wang Y, Sun J et al (2015) Synergistic effects of metformin in combination with EGFR-TKI in the treatment of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and type 2 diabetes. Cancer Lett 369(1):97–102
Chuang MC, Yang YH, Tsai YH, Hsieh MJ, Lin YC, Lin CK et al (2018) Survival benefit associated with metformin use in inoperable non-small cell lung cancer patients with diabetes: a population-based retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 13(1):e0191129
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7(3):177–188
Downs SH, Black N (1998) The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health 52(6):377–384
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD et al (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:d5928
Hooper P, Jutai JW, Strong G, Russell-Minda E (2008) Age-related macular degeneration and low-vision rehabilitation: a systematic review. Can J Ophthalmol 43(2):180–187
Li C, Xue Y, Xi YR, Xie K (2017) Progress in the application and mechanism of metformin in treating non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett 13(5):2873–2880
Li L, Jiang L, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Zhang XJ, Wu G et al (2019) Combination of metformin and gefitinib as first-line therapy for nondiabetic advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations: a randomized, double-blind phase II trial. Clin Cancer Res 25(23):6967–6975
Lin JJ, Gallagher EJ, Sigel K, Mhango G, Galsky MD, Smith CB et al (2015) Survival of patients with stage IV lung cancer with diabetes treated with metformin. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 191(4):448–454
Lin J, Gill A, Zahm SH, Carter CA, Shriver CD, Nations JA et al (2017) Metformin use and survival after non-small cell lung cancer: a cohort study in the US Military health system. Int J Cancer 141(2):254–263
Luo J, Hendryx M, Qi L, Ho GY, Margolis KL (2016) Pre-existing diabetes and lung cancer prognosis. Br J Cancer 115(1):76–79
Lydon S, Power M, McSharry J, Byrne M, Madden C, Squires JE et al (2017) Interventions to improve hand hygiene compliance in the ICU: a systematic review. Crit Care Med 45(11):e1165–e1172
Ma S, Zheng Y, Xiao Y, Zhou P, Tan H (2017) Meta-analysis of studies using metformin as a reducer for liver cancer risk in diabetic patients. Medicine (baltim) 96(19):e6888
Marrone KA, Zhou X, Forde PM, Purtell M, Brahmer JR, Hann CL et al (2018) A randomized phase II study of metformin plus paclitaxel/carboplatin/bevacizumab in patients with chemotherapy-naive advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist 23(7):859–865
Medairos RA, Clark J, Holoubek S, Kubasiak JC, Pithadia R, Hamid F et al (2016) Metformin exposure is associated with improved progression-free survival in diabetic patients after resection for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 152(1):55-61.e1
Menamin Ú, Cardwell CR, Hughes CM, Murray LM (2016) Metformin use and survival from lung cancer: a population-based cohort study. Lung Cancer 94:35–39
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M et al (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev 4:1
Pereira M, Galvão TF (2014) Heterogeneity and publication bias in systematic reviews. Epidemiol Serv Saúde 23(4):775–778
Richardson M, Garner P, Donegan S (2019) Interpretation of subgroup analyses in systematic reviews: a tutorial. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health 7:192–198
Rocha JS, Arima LY, Werneck RI, Moysés SJ, Baldani MH (2018) Determinants of dental care attendance during pregnancy: a systematic review. Caries Res 52(1–2):139–152
Sayed R, Saad AS, El Wakeel L, Elkholy E, Badary O (2015) Metformin addition to chemotherapy in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: an open label randomized controlled study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16(15):6621–6626
Spratt DE, Beadle BM, Zumsteg ZS, Rivera A, Skinner HD, Osborne JR et al (2016) The influence of diabetes mellitus and metformin on distant metastases in oropharyngeal cancer: a multicenter study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 94(3):523–531
Suissa S (2008) Immortal time bias in pharmaco-epidemiology. Am J Epidemiol 167(4):492–499
Suissa S, Azoulay L (2012) Metformin and the risk of cancer: time-related biases in observational studies. Diabetes Care 35(12):2665–2673
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Szklo M (1998) Population-based cohort studies. Epidemiol Rev 20(1):81–90
Tian RH, Zhang YG, Wu Z, Liu X, Yang JW, Ji HL (2016) Effects of metformin on survival outcomes of lung cancer patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Clin Transl Oncol 18(6):641–649
Wen-Xiu X, Xiao-Wei Z, Hai-Ying D, Ying-Hui T, Si-Si K, Xiao-Fang Z et al (2018) Impact of metformin use on survival outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer treated with platinum. Medicine (baltim) 97(51):e13652
Wink KC, Belderbos JS, Dieleman EM, Rossi M, Rasch CR, Damhuis RA et al (2016) Improved progression free survival for patients with diabetes and locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) using metformin during concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 118(3):453–459
Xin WX, Fang L, Fang QL, Zheng XW, Ding HY, Huang P (2018) Effect of hypoglycemic agents on survival outcomes of lung cancer patients with diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Medicine (baltim) 97(9):e0035
Xu T, Li D, He Y, Zhang F, Qiao M, Chen Y (2018) Prognostic value of metformin for non-small cell lung cancer patients with diabetes. World J Surg Oncol 16(1):60
Yousef M, Tsiani E (2017) Metformin in lung cancer: review of in vitro and in vivo animal studies. Cancers (basel) 9(5):45
Zeng S, Gan HX, Xu JX, Liu JY (2019) Metformin improves survival in lung cancer patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Med Clin (barc) 152(8):291–297
Zhang J, Wu J, He Q, Liang W, He J (2018) The prognostic value of metformin for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res 7(3):389–396
Zhong S, Wu Y, Yan X, Tang J, Zhao J (2017) Metformin use and survival of lung cancer patients: meta-analysis findings. Indian J Cancer 54(1):63–67
Funding
No relevant funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TNT, SB and EW were responsible for the conception of the study. SB and AER contributed to the data collection and extracted the data. SB and TNT assessed the eligibility of each article, independently. SB conducted the analysis and produced the results, figures and tables. AER and TNT provided statistical support. TNT and EW contributed to data interpretation. SB wrote the manuscript. TNT, AER and EW revised the manuscript. AER contributed to manuscript editing at the moment of submission. All authors were involved in the manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Disclaimer
Where authors are identified as personnel of the International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization, the authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this article and they do not necessarily represent the decisions, policy or views of International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brancher, S., Ribeiro, A.E., Toporcov, T.N. et al. The role of metformin on lung cancer survival: the first systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized clinical trials. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 2819–2836 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03728-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03728-x