Abstract
Background
Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS) is a sarcoma with a poor prognosis. A clinical trial, SARC028, revealed that treatment with anti-PD-1 drugs was effective against UPS. Studies have reported that UPS expresses PD-L1, sometimes strongly (≥ 50%). However, the mechanism of PD-L1 expression in UPS has remained unclear. CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 6 (CMTM6) was identified as a novel regulator of PD-L1 expression. The positive relationship between PD-L1 and CMTM6 has been reported in several studies. The aim of this study was thus to examine CMTM6 expression in UPS and evaluate the relationship between PD-L1 and CMTM6 in this disease.
Materials and methods
Fifty-one primary UPS samples were subjected to CMTM6 and PD-L1 immunostaining. CMTM6 expression was assessed using proportion and intensity scores. CMTM6 gene copy number was also evaluated using a real-time PCR-based copy number assay. We also analyzed the mRNA expression and copy number variation of PD-L1 and CMTM6 in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data.
Results
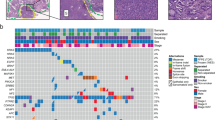
TCGA data indicated that the mRNAs encoded by genes located around 3p22 were coexpressed with CMTM6 mRNA in UPS. Both proportion and intensity scores of CMTM6 positively correlated with strong PD-L1 expression (≥ 50%) (both p = 0.023). CMTM6 copy number gain increased CMTM6 expression. Patients with UPS with a high CMTM6 intensity score had a worse prognosis for overall survival.
Conclusions
UPS showed variation in CMTM6 copy number and CMTM6 expression. CMTM6 expression was significantly correlated with PD-L1 expression, especially with strong PD-L1 expression.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CMTM6:
-
CKLF like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 6
- FFPE:
-
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded
- IS:
-
Intensity score
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed death-ligand 1
- PS:
-
Proportion score
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- TIL:
-
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
- UPS:
-
Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma
References
Boxberg M, Steiger K, Lenze U et al (2018) PD-L1 and PD-1 and characterization of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in high grade sarcomas of soft tissue—prognostic implications and rationale for immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2017.1389366
Burr ML, Sparbier CE, Chan Y-C et al (2017) CMTM6 maintains the expression of PD-L1 and regulates anti-tumour immunity. Nature 549:101–105. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23643
Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F (2013) WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. IARC Press, Lyon
Cerami et al (2017) The CBio cancer genomics. Cancer Discov 32:736–740. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U et al (2014) Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal complementary data sources and analysis options. Sci Signal 6:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2004088
Ishihara S, Yamada Y, Iwasaki T et al (2020) PD-L1 and IDO-1 expression in undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma: the associations with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, dMMR and HLA class I. Oncol Rep. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7837
Keung EZ, Burgess M, Salazar R et al (2020) Correlative analyses of the SARC028 trial reveal an association between sarcoma-associated immune infiltrate and response to pembrolizumab. Clin Cancer Res 26:1258–1266. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1824
Koh YW, Han JH, Haam S et al (2019) Increased CMTM6 can predict the clinical response to PD-1 inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 8:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2019.1629261
Li X, Chen L, Gu C et al (2020) CMTM6 significantly relates to PD-L1 and predicts the prognosis of gastric cancer patients. PeerJ 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9536
Liu LL, Zhang SW, Chao X et al (2020) Coexpression of CMTM6 and PD-L1 as a predictor of poor prognosis in macrotrabecular-massive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02691-9
Martinez-Morilla S, Zugazagoitia J, Wong PF et al (2020) Quantitative analysis of CMTM6 expression in tumor microenvironment in metastatic melanoma and association with outcome on immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 10:1864909. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2020.1864909
Mezzadra R, Sun C, Jae LT et al (2017) Identification of CMTM6 and CMTM4 as PD-L1 protein regulators. Nature 549:106–110. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23669
Schalper KA, Carvajal-Hausdorf D, McLaughlin J et al (2017) Differential expression and significance of PD-L1, IDO-1, and B7–H4 in human lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 23:370–378. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0150
Tawbi HA, Burgess M, Bolejack V et al (2017) Pembrolizumab in advanced soft-tissue sarcoma and bone sarcoma (SARC028): a multicentre, two-cohort, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1493–1501. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30624-1
WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (2020) Soft tissue and bone tumours. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon (France). https://publications.iarc.fr/588
Zugazagoitia J, Liu Y, Toki M et al (2019) Quantitative assessment of CMTM6 in the tumor microenvironment and association with response to PD-1 pathway blockade in advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 14:2084–2096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.09.014
Acknowledgements
The results shown here are in part based upon data generated by the TCGA Research Network: https://www.cancer.gov/tcga. We appreciate M. Tomita and M. Nakamizo at the Department of Anatomic Pathology, Kyushu University for providing technical support. We additionally thank the Research Support Center, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, for providing the experimental devices.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (19H03444).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SI, TI, KK, HY and YO designed this study and wrote the manuscript. SI, TI performed the experiments. SI, YT, YI, YS, TM, SK, DT, IK, TM, DK, TF, NS, ME, YM and YN collected the materials. SI, TI, KK, YY IK and YO performed histological re-evaluation of the samples and confirmed the diagnosis. SI, TI and YO supervised the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The present study was approved by the Kyushu University Committee of Bioethics (approval no. 29-429 and 29-625; 2017).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2021_3616_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file1Supplementary Figure 1 Validations of PD-L1 and CMTM6 are shown. HE and IHC images of ×100 and ×400 for PD-L1 and CMTM6 are presented. For PD-L1 and CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 6 (CMTM6), the images show that the stromal cells were negative, while the tumor cells were positive. For CMTM6, UPS cells were not stained as strongly as the positive control of fallopian tube. Supplementary Figure 2 ROC curve of CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) presented in a previous study. A cut-off of 25 was used. Supplementary Figure 3 Integrative Genomics Viewer of the copy number segment of undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS) cases in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) was obtained by using cBioPortal. Regarding the copy numbers of genes around chromosome 3p22 listed in Figure 1b and CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 6 (CMTM6), these appeared to exhibit copy number variation. Supplementary Figure 4 The relationship between PD-L1 and CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 6 (CMTM6) expression. Supplementary Figure 5 ROC curves. (a) Strong PD-L1 expression (≥ 50%) and proportion score (PS) of CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 6 (CMTM6). (b) Strong PD-L1 expression (≥ 50%) and intensity score (IS) of CMTM6. (c) PD-L1 expression (≥ 1%) and PS of CMTM6. (d) PD-L1 expression (≥ 1%) and IS of CMTM6. (DOCX 4138 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishihara, S., Iwasaki, T., Kohashi, K. et al. The association between the expression of PD-L1 and CMTM6 in undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 2003–2011 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03616-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03616-4