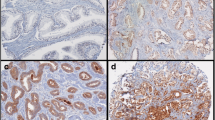
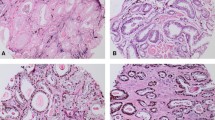
Abstract
Background
To investigate the incidence and prognostication of ERG, PTEN and SPINK1 protein expressions in prostate cancer cohort of Middle Eastern descent in comparison to published data from Western population.
Methods
Immunohistochemistry for ERG, PTEN and SPINK1 was performed in a cohort of localized PCA (n = 340). The data were correlated to pathological and clinical outcomes and compared to Western populations.
Results
ERG expression and PTEN loss were noted in 123/288 (42.7%) and 91/297 (30.6%) of patients, respectively. SPINK1 expression was assessed in a subset of cases, noted in 6/150 (4%) of patients. Only ERG expression was associated with grade groups, being more common in the lower grade groups (1–3 vs 4–5; p = 0.04). In contrast to the Western population, PTEN loss foci were more likely to be ERG negative, observed in 81% of tumor foci and patients with PTEN neg/ERG pos were more likely to exhibit biochemical recurrence (OR 2.831; 95% CI 1.10–726, p = 0.03). This association remained significant in multivariate analysis (OR 2.68; 95% CI 0.98–7.33, p = 0.05), after adjusting for GG, path stage and surgical margin.
Conclusion
This study documents significant differences in key molecular events in PCA in Middle Eastern population compared to Western populations that could explain differences in PCA incidence, progression and prognostication. ERG, PTEN and SPINK1 genomic alteration occur less frequently and the enrichment of ERG for PTEN loss is not observed. Additionally, patients with combined PTEN loss/ERG positive are at highest risk for BCR vs North American Caucasian population where PTEN loss alone seems to be associated with the worst clinical outcome. The data presented here further support differences in clonal evolution between Middle Eastern and Western population in relation to PCA and add further insight to understanding PCA molecular pathways.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PCA:
-
Prostate cancer
- CRPC:
-
Castrate-resistant prostate cancer
- ETS:
-
Erythroblast transformation-specific
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- SPINK1:
-
Serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 1
- BCR:
-
Biochemical recurrence
References
Abou-Ouf H, Zhao L, Bismar TA (2016) ERG expression in prostate cancer: biological relevance and clinical implication. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142:1781–1793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2096-x
Ahearn TU, Pettersson A, Ebot EM, Gerke T, Graff RE, Morais CL, Hicks JL, Wilson KM, Rider JR, Sesso HD, Fiorentino M, Flavin R, Finn S, Giovannucci EL, Loda M, Stampfer MJ, De Marzo AM, Mucci LA, Lotan TL (2016) A Prospective investigation of PTEN Loss and ERG expression in lethal prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv346
Aldaoud N, Abdo N, Al Bashir S, Alqudah M, Marji N, Alzou'bi H, Alazab R, Trpkov K (2017) Prostate cancer in Jordanian-Arab population: ERG status and relationship with clinicopathologic characteristics. Virchows Arch 471:753–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-017-2160-9
Ateeq B, Kunju LP, Carskadon SL, Pandey SK, Singh G, Pradeep I, Tandon V, Singhai A, Goel A, Amit S, Agarwal A, Dinda AK, Seth A, Tsodikov A, Chinnaiyan AM, Palanisamy N (2015) Molecular profiling of ETS and non-ETS aberrations in prostate cancer patients from northern India. Prostate 75:1051–1062. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22989
Ateeq B, Tomlins SA, Laxman B, Asangani IA, Cao Q, Cao X, Li Y, Wang X, Feng FY, Pienta KJ, Varambally S, Chinnaiyan AM (2011) Therapeutic targeting of SPINK1-positive prostate cancer. Sci Transl Med 3:72ra17. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001498
Attard G, Swennenhuis JF, Olmos D, Reid AH, Vickers E, A'Hern R, Levink R, Coumans F, Moreira J, Riisnaes R, Oommen NB, Hawche G, Jameson C, Thompson E, Sipkema R, Carden CP, Parker C, Dearnaley D, Kaye SB, Cooper CS, Molina A, Cox ME, Terstappen LW, de Bono JS (2009) Characterization of ERG, AR and PTEN gene status in circulating tumor cells from patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Can Res 69:2912–2918. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3667
Bhalla R, Kunju LP, Tomlins SA, Christopherson K, Cortez C, Carskadon S, Siddiqui J, Park K, Mosquera JM, Pestano GA, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM, Palanisamy N (2013) Novel dual-color immunohistochemical methods for detecting ERG-PTEN and ERG-SPINK1 status in prostate carcinoma. Mod Pathol 26:835–848. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2012.234
Bismar TA, Dolph M, Teng LH, Liu S, Donnelly B (2012) ERG protein expression reflects hormonal treatment response and is associated with Gleason score and prostate cancer specific mortality. Eur J Cancer 48:538–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2012.01.001
Bismar TA, Hegazy S, Feng Z, Yu D, Donnelly B, Palanisamy N, Trock BJ (2018) Clinical utility of assessing PTEN and ERG protein expression in prostate cancer patients: a proposed method for risk stratification. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144:2117–2125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2730-5
Bismar TA, Yoshimoto M, Vollmer RT, Duan Q, Firszt M, Corcos J, Squire JA (2011) PTEN genomic deletion is an early event associated with ERG gene rearrangements in prostate cancer. BJU Int 107:477–485. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09470.x
Braun M, Scheble VJ, Menon R, Scharf G, Wilbertz T, Petersen K, Beschorner C, Reischl M, Kuefer R, Schilling D, Stenzl A, Kristiansen G, Rubin MA, Fend F, Perner S (2011) Relevance of cohort design for studying the frequency of the ERG rearrangement in prostate cancer. Histopathology 58:1028–1036. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.03862.x
Dal Pra A, Lalonde E, Sykes J, Warde F, Ishkanian A, Meng A, Maloff C, Srigley J, Joshua AM, Petrovics G, van der Kwast T, Evans A, Milosevic M, Saad F, Collins C, Squire J, Lam W, Bismar TA, Boutros PC, Bristow RG (2013) TMPRSS2-ERG status is not prognostic following prostate cancer radiotherapy: implications for fusion status and DSB repair. Clin Cancer Res 19:5202–5209. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1049
Darnel AD, Lafargue CJ, Vollmer RT, Corcos J, Bismar TA (2009) TMPRSS2-ERG fusion is frequently observed in Gleason pattern 3 prostate cancer in a Canadian cohort. Cancer Biol Ther 8:125–130
Demichelis F, Fall K, Perner S, Andren O, Schmidt F, Setlur SR, Hoshida Y, Mosquera JM, Pawitan Y, Lee C, Adami HO, Mucci LA, Kantoff PW, Andersson SO, Chinnaiyan AM, Johansson JE, Rubin MA (2007) TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion associated with lethal prostate cancer in a watchful waiting cohort. Oncogene 26:4596–4599. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210237
Dong J, Xiao L, Sheng L, Xu J, Sun ZQ (2014) TMPRSS2:ETS fusions and clinicopathologic characteristics of prostate cancer patients from Eastern China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:3099–3103
Facher EA, Law JC (1998) PTEN and prostate cancer. J Med Genet 35:790
Flavin R, Pettersson A, Hendrickson WK, Fiorentino M, Finn S, Kunz L, Judson GL, Lis R, Bailey D, Fiore C, Nuttall E, Martin NE, Stack E, Penney KL, Rider JR, Sinnott J, Sweeney C, Sesso HD, Fall K, Giovannucci E, Kantoff P, Stampfer M, Loda M, Mucci LA (2014) SPINK1 protein expression and prostate cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 20:4904–4911. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1341
Furusato B, van Leenders GJ, Trapman J, Kimura T, Egawa S, Takahashi H, Furusato M, Visakorpi T, Hano H (2011) Immunohistochemical ETS-related gene detection in a Japanese prostate cancer cohort: diagnostic use in Japanese prostate cancer patients. Pathol Int 61:409–414. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1827.2011.02675.x
Grasso CS, Wu YM, Robinson DR, Cao X, Dhanasekaran SM, Khan AP, Quist MJ, Jing X, Lonigro RJ, Brenner JC, Asangani IA, Ateeq B, Chun SY, Siddiqui J, Sam L, Anstett M, Mehra R, Prensner JR, Palanisamy N, Ryslik GA, Vandin F, Raphael BJ, Kunju LP, Rhodes DR, Pienta KJ, Chinnaiyan AM, Tomlins SA (2012) The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature 487:239–243. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11125
Guedes LB, Tosoian JJ, Hicks J, Ross AE, Lotan TL (2017) PTEN loss in gleason score 3 + 4 = 7 prostate biopsies is associated with nonorgan confined disease at radical prostatectomy. J Urol 197:1054–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2016.09.084
Han B, Mehra R, Suleman K, Tomlins SA, Wang L, Singhal N, Linetzky KA, Palanisamy N, Zhou M, Chinnaiyan AM, Shah RB (2009) Characterization of ETS gene aberrations in select histologic variants of prostate carcinoma. Mod Pathol 22:1176–1185
Hilal L, Shahait M, Mukherji D, Charafeddine M, Farhat Z, Temraz S, Khauli R, Shamseddine A (2015) Prostate cancer in the arab world: a view from the inside. Clin Genitourin Cancer 13:505–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2015.05.010
Huang KC, Alshalalfa M, Hegazy SA, Dolph M, Donnelly B, Bismar TA (2014a) The prognostic significance of combined ERG and androgen receptor expression in patients with prostate cancer managed by androgen deprivation therapy. Cancer Biol Ther 15:1120–1128. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.29689
Huang KC, Begin LR, Palanisamy N, Donnelly B, Bismar TA (2016) SPINK1 expression in relation to PTEN and ERG in matched primary and lymph node metastatic prostate cancer: Implications for biomarker development. Urol Oncol 34(235):e231–e210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2015.11.015
Huang KC, Dolph M, Donnelly B, Bismar TA (2014b) ERG expression is associated with increased risk of biochemical relapse following radical prostatectomy in early onset prostate cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 16:973–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1182-x
Huang KC, Evans A, Donnelly B, Bismar TA (2017) SPINK1 overexpression in localized prostate cancer: a rare event inversely associated with ERG expression and exclusive of homozygous PTEN deletion. Pathol Oncol Res 23:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-016-0119-9
Hyun T, Yam A, Pece S, Xie X, Zhang J, Miki T, Gutkind JS, Li W (2000) Loss of PTEN expression leading to high Akt activation in human multiple myelomas. Blood 96:3560–3568
Jiang H, Mao X, Huang X, Zhao J, Wang L, Xu J, Zhang H, Lu Y, Yu Y (2016) TMPRSS2:ERG fusion gene occurs less frequently in Chinese patients with prostate cancer. Tumour Biol 37:12397–12402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5116-9
Khani F, Mosquera JM, Park K, Blattner M, O'Reilly C, MacDonald TY, Chen Z, Srivastava A, Tewari AK, Barbieri CE, Rubin MA, Robinson BD (2014) Evidence for molecular differences in prostate cancer between African American and Caucasian men. Clin Cancer Res 20:4925–4934. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2265
Lee SL, Yu D, Wang C, Saba R, Liu S, Trpkov K, Donnelly B, Bismar TA (2015) ERG expression in prostate needle biopsy: potential diagnostic and prognostic implications. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 23:499–505. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAI.0000000000000119
Leinonen KA, Tolonen TT, Bracken H, Stenman UH, Tammela TL, Saramaki OR, Visakorpi T (2010) Association of SPINK1 expression and TMPRSS2:ERG fusion with prognosis in endocrine-treated prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:2845–2851. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2505
Lippolis G, Edsjo A, Stenman UH, Bjartell A (2013) A high-density tissue microarray from patients with clinically localized prostate cancer reveals ERG and TATI exclusivity in tumor cells. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 16:145–150. https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2013.7
Liu S, Yoshimoto M, Trpkov K, Duan Q, Firszt M, Corcos J, Squire JA, Bismar TA (2011) Detection of ERG gene rearrangements and PTEN deletions in unsuspected prostate cancer of the transition zone. Cancer Biol Ther 11:562–566
Lotan TL, Carvalho FL, Peskoe SB, Hicks JL, Good J, Fedor H, Humphreys E, Han M, Platz EA, Squire JA, De Marzo AM, Berman DM (2015) PTEN loss is associated with upgrading of prostate cancer from biopsy to radical prostatectomy. Mod Pathol 28:128–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2014.85
Mani RS, Iyer MK, Cao Q, Brenner JC, Wang L, Ghosh A, Cao X, Lonigro RJ, Tomlins SA, Varambally S, Chinnaiyan AM (2011) TMPRSS2-ERG-mediated feed-forward regulation of wild-type ERG in human prostate cancers. Can Res 71:5387–5392. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0876
Marrone M, Potosky AL, Penson D, Freedman AN (2015) A 22 gene-expression assay, Decipher(R) (GenomeDx Biosciences) to predict five-year risk of metastatic prostate cancer in men treated with radical prostatectomy. PLoS Curr. https://doi.org/10.1371/currents.eogt.761b81608129ed61b0b48d42c04f92a4
Ornish D, Magbanua MJ, Weidner G, Weinberg V, Kemp C, Green C, Mattie MD, Marlin R, Simko J, Shinohara K, Haqq CM, Carroll PR (2008) Changes in prostate gene expression in men undergoing an intensive nutrition and lifestyle intervention. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:8369–8374. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0803080105
Patil PA, McKenney JK, Reynolds JP, Przybycin CG, Magi-Galluzzi C (2019) Clinical significance and EZH2, ERG and SPINK1 protein expression in pure and mixed ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Histol Histopathol 34:381–390. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-18-046
Perner S, Demichelis F, Beroukhim R, Schmidt FH, Mosquera JM, Setlur S, Tchinda J, Tomlins SA, Hofer MD, Pienta KG, Kuefer R, Vessella R, Sun XW, Meyerson M, Lee C, Sellers WR, Chinnaiyan AM, Rubin MA (2006) TMPRSS2:ERG fusion-associated deletions provide insight into the heterogeneity of prostate cancer. Can Res 66:8337–8341
Perner S, Mosquera JM, Demichelis F, Hofer MD, Paris PL, Simko J, Collins C, Bismar TA, Chinnaiyan AM, De Marzo AM, Rubin MA (2007) TMPRSS2-ERG fusion prostate cancer: an early molecular event associated with invasion. Am J Surg Pathol 31:882–888
Reid AH, Attard G, Ambroisine L, Fisher G, Kovacs G, Brewer D, Clark J, Flohr P, Edwards S, Berney DM, Foster CS, Fletcher A, Gerald WL, Moller H, Reuter VE, Scardino PT, Cuzick J, de Bono JS, Cooper CS (2010) Molecular characterisation of ERG, ETV1 and PTEN gene loci identifies patients at low and high risk of death from prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 102:678–684. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605554
Shan J, Al-Rumaihi K, Chouchane K, Al-Bozom I, Rabah D, Farhat K, Chouchane L (2017) Prostate cancer small non-coding RNA transcriptome in Arabs. J Transl Med 15:260. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1362-x
Shoag J, Barbieri CE (2016) Clinical variability and molecular heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Asian J Androl 18:543–548. https://doi.org/10.4103/1008-682X.178852
Teng LH, Wang C, Begin LR, Dolph M, Yilmaz A, Trpkov K, Donnelly B, Bismar TA (2013a) ERG protein expression and gene rearrangements are present at lower rates in metastatic and locally advanced castration-resistant prostate cancer compared to localized disease. Urology 82:394–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2013.03.029
Teng LH, Wang C, Dolph M, Donnelly B, Bismar TA (2013b) ERG protein expression is of limited prognostic value in men with localized prostate cancer. ISRN Urol 2013:786545. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/786545
Tomlins SA, Palanisamy N, Siddiqui J, Chinnaiyan AM, Kunju LP (2012) Antibody-based detection of ERG rearrangements in prostate core biopsies, including diagnostically challenging cases: ERG staining in prostate core biopsies. Arch Pathol Lab Med 136:935–946. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2011-0424-OA
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW, Varambally S, Cao X, Tchinda J, Kuefer R, Lee C, Montie JE, Shah RB, Pienta KJ, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM (2005) Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science 310:644–648
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Yu J, Varambally S, Mehra R, Perner S, Demichelis F, Helgeson BE, Laxman B, Morris DS, Cao Q, Cao X, Andren O, Fall K, Johnson L, Wei JT, Shah RB, Al-Ahmadie H, Eastham JA, Eggener SE, Fine SW, Hotakainen K, Stenman UH, Tsodikov A, Gerald WL, Lilja H, Reuter VE, Kantoff PW, Scardino PT, Rubin MA, Bjartell AS, Chinnaiyan AM (2008) The role of SPINK1 in ETS rearrangement-negative prostate cancers. Cancer Cell 13:519–528
Vinceneux A, Bruyere F, Haillot O, Charles T, de la Taille A, Salomon L, Allory Y, Ouzaid I, Choudat L, Roupret M, Comperat E, Houede N, Beauval JB, Vourc'h P, Fromont G (2017) Ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: clinical and biological profiles. Prostate 77:1242–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23383
Yoshimoto M, Joshua AM, Cunha IW, Coudry RA, Fonseca FP, Ludkovski O, Zielenska M, Soares FA, Squire JA (2008) Absence of TMPRSS2:ERG fusions and PTEN losses in prostate cancer is associated with a favorable outcome. Mod Pathol 21(12):1451–1460. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2008.96
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Ruby Reyes for her technical assistance in preparing this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Prostate Cancer Foundation, USA. Young Investigator Award and Prostate Cancer Canada, Translational Acceleration Grant and by funds from Calgary Laboratory Services (T.A.B). The Agency provides operating cost funds with no effect on actual research design or outcome.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RA, AB, MK, HA performed analysis. IK, TL, MS collected data and performed analysis. SG performed statistical analysis. NP performed, supervised and provided input for manuscript and marker staining. TAB supervised and planned study. All authors have approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the University of Calgary Cumming School of Medicine ethics review board and in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Patient consent was waived by the ethics review board, due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Availability of data and materials
The study is retrospective with samples available from 1998–2008. Data sharing is not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelsalam, R.A., Khalifeh, I., Box, A. et al. Molecular characterization of prostate cancer in Middle Eastern population highlights differences with Western populations with prognostic implication. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146, 1701–1709 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03221-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03221-x