Abstract
Purpose
The hydrophobic bile acid, deoxycholic acid (DC), can induce apoptosis in hepatocytes. The roles of DC and its transporter are not yet established in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. We investigated DC-induced alterations in HCC cell growth, with a particular focus on the effect of the expression of bile acid (BA)-transporting Na+-dependent taurocholic cotransporting polypeptides (NTCPs).
Methods
We determined NTCP expression in four human HCC cell lines: Huh-BAT, Huh-7, SNU-761, and SNU-475. NTCP expression and apoptotic signaling cascades were examined by immunoblot analyses. Cell viability was assessed using the 3,4-(5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium salt assay. Wound healing and invasion assays were performed to evaluate cell migration and invasion abilities. Real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed to measure IL-8 expression levels. Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activity was evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results
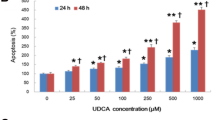
The HCC cell lines revealed varying NTCP expression levels, and DC treatment had dual effects, depending on NTCP expression. DC induced apoptosis in NTCP-positive HCC cells, especially under hypoxic conditions. In NTCP-negative HCC cells, simultaneous treatment with DC and cyclooxygenase inhibitor markedly decreased aggressive cellular behaviors via the inhibition of NF-κB/COX-2/IL-8 pathways.
Conclusion
Hydrophobic bile acid offers therapeutic potential for patients with advanced HCC via different mechanisms depending on NTCP expression levels within the tumor.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
Bile acid
- DC:
-
Deoxycholic acid
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- NTCP:
-
Na+-dependent taurocholic cotransporting polypeptides
- COX:
-
Cyclooxygenase
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- TACE:
-
Transarterial chemoembolization
- CDC:
-
Chenodeoxycholate
- DC:
-
Deoxycholate
- GCDC:
-
Glycochenodeoxycholate
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- TGR5:
-
G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor
- FXR:
-
Farnesoid-X-receptor
- NFκB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- RPMI:
-
Roswell Park Memorial Institute
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- eIF2α:
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal Kinase
- siRNAs:
-
Small interfering RNA
- MTS:
-
3,4-(5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium salt
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- HBSS:
-
Hank’s balanced salt solution
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- cDNA:
-
Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid
- MoMLV:
-
Moloney murine leukemia virus
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- Mcl-1:
-
Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein
References
Alrefai WA, Gill RK (2007) Bile acid transporters: structure, function, regulation and pathophysiological implications. Pharm Res 24(10):1803–1823. doi:10.1007/s11095-007-9289-1
Bernstein C, Holubec H, Bhattacharyya AK, Nguyen H, Payne CM, Zaitlin B, Bernstein H (2011) Carcinogenicity of deoxycholate, a secondary bile acid. Arch Toxicol 85(8):863–871. doi:10.1007/s00204-011-0648-7
Breinig M, Schirmacher P, Kern MA (2007) Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-a therapeutic target in liver cancer? Curr Pharm Des 13(32):3305–3315. doi:10.2174/138161207782360627
Cencioni MT, Chiurchiu V, Catanzaro G, Borsellino G, Bernardi G, Battistini L, Maccarrone M (2010) Anandamide suppresses proliferation and cytokine release from primary human T-lymphocytes mainly via CB2 receptors. PLoS ONE 5(1):e8688. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008688
Cervello M, Montalto G (2006) Cyclooxygenases in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 12 (32):5113–5121. http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/12/5113.asp
Cui J, Huang L, Zhao A, Lew JL, Yu J, Sahoo S, Meinke PT, Royo I, Pelaez F, Wright SD (2003) Guggulsterone is a farnesoid X receptor antagonist in coactivator association assays but acts to enhance transcription of bile salt export pump. J Biol Chem 278(12):10214–10220. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209323200
Fukase K, Ohtsuka H, Onogawa T, Oshio H, Ii T, Mutoh M, Katayose Y, Rikiyama T, Oikawa M, Motoi F, Egawa S, Abe T, Unno M (2008) Bile acids repress E-cadherin through the induction of snail and increase cancer invasiveness in human hepatobiliary carcinoma. Cancer Sci 99(9):1785–1792. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00898.x
Gadaleta RM, van Mil SW, Oldenburg B, Siersema PD, Klomp LW, van Erpecum KJ (2010) Bile acids and their nuclear receptor FXR: relevance for hepatobiliary and gastrointestinal disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801(7):683–692. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.04.006
Gorman AM, Healy SJ, Jager R, Samali A (2012) Stress management at the ER: regulators of ER stress-induced apoptosis. Pharmacol Ther 134(3):306–316. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.02.003
Gumpricht E, Dahl R, Yerushalmi B, Devereaux MW, Sokol RJ (2002) Nitric oxide ameliorates hydrophobic bile acid-induced apoptosis in isolated rat hepatocytes by non-mitochondrial pathways. J Biol Chem 277(28):25823–25830. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112305200
Gwak GY, Yoon JH, Kim KM, Lee HS, Chung JW, Gores GJ (2005) Hypoxia stimulates proliferation of human hepatoma cells through the induction of hexokinase II expression. J Hepatol 42(3):358–364. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2004.11.020
Higuchi H, Bronk SF, Takikawa Y, Werneburg N, Takimoto R, El-Deiry W, Gores GJ (2001) The bile acid glycochenodeoxycholate induces trail-receptor 2/DR5 expression and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276(42):38610–38618. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105300200
Higuchi H, Grambihler A, Canbay A, Bronk SF, Gores GJ (2004) Bile acids up-regulate death receptor 5/TRAIL-receptor 2 expression via a c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent pathway involving Sp1. J Biol Chem 279(1):51–60. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309476200
Hill MJ (1990) Bile flow and colon cancer. Mutat Res 238(3):313–320
Hohenester S, Gates A, Wimmer R, Beuers U, Anwer MS, Rust C, Webster CR (2010) Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase p110gamma contributes to bile salt-induced apoptosis in primary rat hepatocytes and human hepatoma cells. J Hepatol 53(5):918–926. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.05.015
Jensen OM, MacLennan R, Wahrendorf J (1982) Diet, bowel function, fecal characteristics, and large bowel cancer in Denmark and Finland. Nutr Cancer 4(1):5–19. doi:10.1080/01635588209513733
Kawamori T, Rao CV, Seibert K, Reddy BS (1998) Chemopreventive activity of celecoxib, a specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, against colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 58(3):409–412
Knisely AS, Strautnieks SS, Meier Y, Stieger B, Byrne JA, Portmann BC, Bull LN, Pawlikowska L, Bilezikci B, Ozcay F, Laszlo A, Tiszlavicz L, Moore L, Raftos J, Arnell H, Fischler B, Nemeth A, Papadogiannakis N, Cielecka-Kuszyk J, Jankowska I, Pawlowska J, Melin-Aldana H, Emerick KM, Whitington PF, Mieli-Vergani G, Thompson RJ (2006) Hepatocellular carcinoma in ten children under five years of age with bile salt export pump deficiency. Hepatology 44(2):478–486. doi:10.1002/hep.21287
Kubo F, Ueno S, Hiwatashi K, Sakoda M, Kawaida K, Nuruki K, Aikou T (2005) Interleukin 8 in human hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with cancer cell invasion of vessels but not with tumor angiogenesis. Ann Surg Oncol 12(10):800–807. doi:10.1245/ASO.2005.07.015
Kullak-Ublick GA, Glasa J, Boker C, Oswald M, Grutzner U, Hagenbuch B, Stieger B, Meier PJ, Beuers U, Kramer W, Wess G, Paumgartner G (1997) Chlorambucil-taurocholate is transported by bile acid carriers expressed in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Gastroenterology 113(4):1295–1305. doi:10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9322525
Kullak-Ublick GA, Stieger B, Meier PJ (2004) Enterohepatic bile salt transporters in normal physiology and liver disease. Gastroenterology 126(1):322–342. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2003.06.005
Lee JH, Ku JL, Park YJ, Lee KU, Kim WH, Park JG (1999) Establishment and characterization of four human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines containing hepatitis B virus DNA. World J Gastroenterol 5 (4):289–295. http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v5/i4/289.htm
Lee HY, Crawley S, Hokari R, Kwon S, Kim YS (2010) Bile acid regulates MUC2 transcription in colon cancer cells via positive EGFR/PKC/Ras/ERK/CREB, PI3 K/Akt/IkappaB/NF-kappaB and p38/MSK1/CREB pathways and negative JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 pathway. Int J Oncol 36(4):941–953. doi:10.3892/ijo_00000573
Leng J, Han C, Demetris AJ, Michalopoulos GK, Wu T (2003) Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth through Akt activation: evidence for Akt inhibition in celecoxib-induced apoptosis. Hepatology 38(3):756–768. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50380
Liang CC, Park AY, Guan JL (2007) In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc 2(2):329–333. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.30
Liao M, Zhao J, Wang T, Duan J, Zhang Y, Deng X (2011) Role of bile salt in regulating Mcl-1 phosphorylation and chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer 10:44. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-10-44
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359(4):378–390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
Lv N, Song MY, Kim EK, Park JW, Kwon KB, Park BH (2008) Guggulsterone, a plant sterol, inhibits NF-kappaB activation and protects pancreatic beta cells from cytokine toxicity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 289(1–2):49–59. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2008.02.001
Nakabayashi H, Taketa K, Miyano K, Yamane T, Sato J (1982) Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res 42(9):3858–3863
Nakao S, Ogtata Y, Shimizu E, Yamazaki M, Furuyama S, Sugiya H (2002) Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced prostaglandin E2 release is mediated by the activation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) transcription via NFkappaB in human gingival fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem 238(1–2):11–18. doi:10.1023/A:1019927616000
Ning Y, Manegold PC, Hong YK, Zhang W, Pohl A, Lurje G, Winder T, Yang D, Labonte MJ, Wilson PM, Ladner RD, Lenz HJ (2011) Interleukin-8 is associated with proliferation, migration, angiogenesis and chemosensitivity in vitro and in vivo in colon cancer cell line models. Int J Cancer 128(9):2038–2049. doi:10.1002/ijc.25562
Park JG, Lee JH, Kang MS, Park KJ, Jeon YM, Lee HJ, Kwon HS, Park HS, Yeo KS, Lee KU et al (1995) Characterization of cell lines established from human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 62(3):276–282. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910620308
Park SE, Lee SW, Hossain MA, Kim MY, Kim MN, Ahn EY, Park YC, Suh H, Kim GY, Choi YH, Kim ND (2008) A chenodeoxycholic derivative, HS-1200, induces apoptosis and cell cycle modulation via Egr-1 gene expression control on human hepatoma cells. Cancer Lett 270(1):77–86. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.04.038
Perez MJ, Briz O (2009) Bile-acid-induced cell injury and protection. World J Gastroenterol 15(14):1677–1689. doi:10.3748/wjg.15.1677
Plummer SM, Holloway KA, Manson MM, Munks RJ, Kaptein A, Farrow S, Howells L (1999) Inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-kappaB activation via the NIK/IKK signalling complex. Oncogene 18(44):6013–6020. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202980
Pols TW, Noriega LG, Nomura M, Auwerx J, Schoonjans K (2011) The bile acid membrane receptor TGR5: a valuable metabolic target. Dig Dis 29(1):37–44. doi:10.1159/000324126
Ren Y, Poon RT, Tsui HT, Chen WH, Li Z, Lau C, Yu WC, Fan ST (2003) Interleukin-8 serum levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: correlations with clinicopathological features and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 9(16):5996–6001
Sarfaraz S, Siddiqui IA, Syed DN, Afaq F, Mukhtar H (2008) Guggulsterone modulates MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways and inhibits skin tumorigenesis in SENCAR mice. Carcinogenesis 29(10):2011–2018. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn180
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM, Samali A (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7(9):880–885. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400779
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Chung P, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 287(5453):664–666. doi:10.1126/science.287.5453.664
Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J, de Guevara LL (2010) The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: a global and regional perspective. Oncologist 15(Suppl 4):5–13. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2010-S4-05
Walters JR (2000) Bile acids are physiological ligands for a nuclear receptor. Gut 46(3):308–309
Wang YD, Chen WD, Wang M, Yu D, Forman BM, Huang W (2008) Farnesoid X receptor antagonizes nuclear factor kappaB in hepatic inflammatory response. Hepatology 48(5):1632–1643. doi:10.1002/hep.22519
Waugh DJ, Wilson C (2008) The interleukin-8 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(21):6735–6741. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4843
Wenniger M, Beuers U (2010) Bile salts and cholestasis. Dig Liver Dis 42(6):409–418. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2010.03.015
Wu J, Xia C, Meier J, Li S, Hu X, Lala DS (2002) The hypolipidemic natural product guggulsterone acts as an antagonist of the bile acid receptor. Mol Endocrinol 16(7):1590–1597. doi:10.1210/me.16.7.1590
Yamada T, Osawa S, Hamaya Y, Furuta T, Hishida A, Kajimura M, Ikuma M (2010) Guggulsterone suppresses bile acid-induced and constitutive caudal-related homeobox 2 expression in gut-derived adenocarcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 30(6):1953–1960
Yang F, Huang X, Yi T, Yen Y, Moore DD, Huang W (2007) Spontaneous development of liver tumors in the absence of the bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor. Cancer Res 67(3):863–867. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1078
Yerushalmi B, Dahl R, Devereaux MW, Gumpricht E, Sokol RJ (2001) Bile acid-induced rat hepatocyte apoptosis is inhibited by antioxidants and blockers of the mitochondrial permeability transition. Hepatology 33(3):616–626. doi:10.1053/jhep.2001.22702
Yoon JH, Higuchi H, Werneburg NW, Kaufmann SH, Gores GJ (2002a) Bile acids induce cyclooxygenase-2 expression via the epidermal growth factor receptor in a human cholangiocarcinoma cell line. Gastroenterology 122(4):985–993
Yoon JH, Werneburg NW, Higuchi H, Canbay AE, Kaufmann SH, Akgul C, Edwards SW, Gores GJ (2002b) Bile acids inhibit Mcl-1 protein turnover via an epidermal growth factor receptor/Raf-1-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res 62(22):6500–6505
Yu SJ, Yoon JH, Yang JI, Cho EJ, Kwak MS, Jang ES, Lee JH, Kim YJ, Lee HS, Kim CY (2012) Enhancement of hexokinase II inhibitor-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via augmenting ER stress and anti-angiogenesis by protein disulfide isomerase inhibition. J Bioenerg Biomembr 44(1):101–115. doi:10.1007/s10863-012-9416-5
Yu LX, Zhou L, Li M, Li ZW, Wang DS, Zhang SG (2013) The Notch1/cyclooxygenase-2/Snail/E-cadherin pathway is associated with hypoxia-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and migration. Oncol Rep 29(1):362–370. doi:10.3892/or.2012.2103
Zollner G, Wagner M, Fickert P, Silbert D, Fuchsbichler A, Zatloukal K, Denk H, Trauner M (2005) Hepatobiliary transporter expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 25(2):367–379. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2005.01033.x
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (Grant No. 20100007381) and by the Liver Research Foundation of Korea.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, E.S., Yoon, JH., Lee, SH. et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide mediates dual actions of deoxycholic acid in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells: enhanced apoptosis versus growth stimulation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 133–144 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1554-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1554-6