Abstract
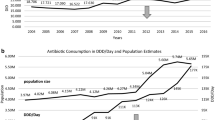
In paediatrics, antibiotics are among the most commonly prescribed drugs. Because of an overall rise in health care costs, lack of uniformity in drug prescribing and the emergence of antibiotic resistance, monitoring and control of antibiotic use is of growing concern and strict antibiotic policies are warranted. Before such a policy can be implemented, detailed knowledge of antibiotic prescribing patterns and related costs is important. In this study a shift of antibiotic prescription patterns over time is described in relation to hospital antibiotic expenditure.
Conclusions A considerable shift in prescription patterns towards more expensive and broader spectrum antibiotics occurs in paediatrics, carrying a risk for the development of antibiotic resistance among the most prevalent micro-organisms in this age group.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 October 1996 and in revised form 15 September 1997 / Accepted: 1 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Houten, M., Laseur, M. & Kimpen, J. Shift in antibiotic prescribing patterns in relation to antibiotic expenditure in paediatrics. Eur J Pediatr 157, 479–481 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310050858
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310050858