Abstract
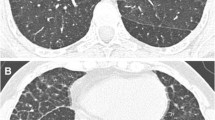
Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in either NPC-1 or NPC-2 genes, resulting in abnormal intracellular cholesterol trafficking. The estimated prevalence of NPC disease is 1: 120,000–150,000. Lung involvement has been described in only few patients with NPC, mostly NPC2. We describe a series of 12 patients, originating from six families all homozygotes to the p.R404Q (c.1211G > A) mutation of NPC1 gene; nine of them had significant pulmonary manifestations. All patients were followed in our medical center. Nine of the patients had pulmonary involvement, with recurrent pneumonia as the first manifestation in most, followed by recurrent wheezing episodes and subsequent development of interstitial lung disease with chronic need for oxygen support. Seven patients were reported of having interstitial disease by various imaging modalities.
Conclusion: Pulmonary involvement in NPC1 is more common than previously reported. It is characterized as primary obstructive and restrictive lung disease and not only as part of neurologic sequel of NPC. It can lead to respiratory insufficiency and death from respiratory failure.
What is Known: • Lung involvement has been described in only few patients with NPC. • Most reported NPC cases with pulmonary involvement were of NPC2. | |
What is New: • Pulmonary involvement in NPC1 is more common than previously reported. • Pulmonary involvement in NPC1 should be considered as part of the disease and be thoroughly assessed and managed. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EM:
-
Electron microscope
- LAMP1:
-
Lysosomal associated membrane protein 1
- NPC:
-
Niemann-Pick disease type C
- PFTs:
-
Pulmonary function tests
- VSGP:
-
Vertical supranuclear gaze palsy
- BAL:
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage
- CT:
-
Computerized tomography
References
Akella A, Deshpande SB (2013) Pulmonary surfactants and their role in pathophysiology of lung disorders. Indian J Exp Biol 51(1):5–22
Bjurulf B, Spetalen S, Erichsen A, Vanier MT, Strøm EH, Strømme P (2008) Niemann-Pick disease type C2 presenting as fatal pulmonary alveolar lipoproteinosis: morphological findings in lung and nervous tissue. Med Sci Monit 14(8):CS71–CS75
Clark J (2008) Wheezing child. Clinical Pediatrics 47:191–198
Deffieu MS, Pfeffer SR (2011) Niemann–Pick type C 1 function requires lumenal domain residues that mediate cholesterol-dependent NPC2 binding. PNAS 108:47
Deutche GH, Young LR, Deterding RR et al (2007) Diffuse lung disease in young children: application of a novel classification scheme. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176:1120–1128
Dinwiddie R, Shrief N, Crawford O (2002) Idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis in children; a national survey in United Kingdom and Ireland. Pediatr Pulmonol 34:23–29
Elleder M, Houstkova H, Zeman J, Ledvinova J, Poupetova H (2001) Pulmonary storage with emphysema as a sign of Niemann-Pick type C2 disease (second complementation group). Report of a case. Virchows Arch 439:206–211
Griese M, Brasch F, Aldana VR, Cabrera MM, Goelnitz U, Ikonen E, Karam BJ, Liebisch G, Linder MD, Lohse P, Meyer W, Schmitz G, Pamir A, Ripper J, Rolfs A, Schams A, Lezana FJ (2010) Respiratory disease in Niemann-Pick type C2 is caused by pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Clin Genet 77:119–130
Guillemot N, Troadec C, de Villemeur TB, Cle’ment A, Fauroux B (2007) Lung disease in Niemann–Pick disease. Pediatr Pulmonol 42:1207–1214
Harwood JL (1987) Lung surfactant. Prog Lipid Res 26(3):211–256
Liu B, Xie C, Richardson JA, Turley SD., Dietschy JM (2007) Receptor-mediated and bulk-phase endocytosis cause macrophage and cholesterol accumulation in Niemann-Pick C disease. J Lipid Res 48:1710–1723
Martinez FD, Wright AL, Taussig LM, Holberg CJ, Halonen M, Morgan WJ (1995) Asthma and wheezing in the first six years of life. N Engl J Med 332:133–138
Meiner V, Shpitzen S, Mandel H, Klar A, Ben-Neriah Z, Zlotogora J, Sagi M, Lossos A, Bargal R, Sury V, Carmi R, Leitersdorf E, Zeigler M (2001) Clinical-biochemical correlation in molecularly characterized patients with Niemann-Pick C. Genet Med 3(5):343–348
Millat G, Marçais C, Tomasetto C, Chikh K, Fensom AH, Harzer K, Wenger DA, Ohno K, Vanier MT (2001) Niemann-Pick C1 disease: correlations between NPC1 mutations, levels of NPC1 protein, and phenotypes emphasize the functional significance of the putative sterol-sensing domain and of the cysteine-rich luminal loop. Am J Hum Genet 68(6):1373–1385
Morisot C, Millat G, Coeslier A, Bourgois B, Fontenoy E, Dobbelaere D, Verot L, Haouari N, Vaillant C, Gottrand F, Bogaert E, Thelliez P, Klosowski S, Djebara A, Bachiri A, Manouvrier S, Vanier MT (2005) Fatal neonatal respiratory distress in Niemann-Pick C2 and prenatal diagnosis with mutations in gene HE1/N PC2. Arch Pediatr 12:434–437
Palmeri S, Tarugi P, Sicurelli F, Buccoliero R, Malandrini A, De Santi MM, Marcianò G, Battisti C, Dotti MT, Calandra S, Federico A (2005) Lung involvement in Niemann-Pick disease type C1: improvement with bronchoalveolar lavage. Neurol Sci 26:171–173
Park WD, O’Brien JF, Lundquist PA, Kraft DL, Vockley CW, Karnes PS, Patterson MC, Snow K (2003) Identification of 58 novel mutations in Niemann-Pick disease type C: correlation with biochemical phenotype and importance of PTC1-like domains in NPC1. Hum Mutat 22:313–325
Patterson MC, Vanier MT, Suzuki K et al (2001) Niemann-Pick type C: a lipid trafficking disorder. In: Scriver CR, Al B, Sly WS, Valle D, Childs B, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease, 8th edn. McGraw Hil, New York, pp 3611–3634
Ramirez CM, Liu B, Le L, Lopez AM, Weinberg AG, Turley SD (2013) Progression of pulmonary disease and related changes in lung cholesterol metabolism in mice Niemann-Pick type C1 deficiency. Abstract 144 Lysosomal Disease Network’s WORLD Symposium™
Ramirez CM, Lopez AM, Le LQ, Posey KS, Weinberg AG, Turley SD (2014 Jan) Ontogenic changes in lung cholesterol metabolism, lipid content, and histology in mice with Niemann-Pick type C disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 184(1):54–61
Roszell BR, Tao JQ, Yu KJ, Huang S, Bates SR (2012) Characterization of the Niemann-Pick C pathway in alveolar type II cells and lamellar bodies of the lung. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 302:L919–L932
Roszell BR, Tao JQ, Yu KJ, Gao L, Huang S, Ning Y, Feinstein SI, Vite CH, Bates SR (2013) Pulmonary abnormalities in animal models due to Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) or C2 (NPC2) disease. PLOS ONE 8(7):e67084
Schofer O, Mischo B, Puschel W, Harzer K, Vanier MT (1998) Early lethal pulmonary form of Niemann-Pick type C disease belonging to a second, rare genetic complementation group. Eur J Pediatr 157:45–49
Vanier MT (2010) Niemann-Pick disease type C. Orphanet J Rare Dis 5:16
Vanier MT, Millat G (1685) Structure and function of the NPC2 protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 2004:14–21
Vanier MT, Millat G (2003) Niemann–Pick disease type C. Clin Genet 64:269–281
Vanier MT, Wenger DA, Comly ME, Rousson R, Brady RO, Pentchev PG (1988) Niemann-Pick disease group C: clinical variability and diagnosis based on defective cholesterol esterification. Clin Genet 33:331–348
Yamamoto T, Nanba E, Ninomiya H, Higaki K, Taniguchi M, Zhang H, Akaboshi S, Watanabe Y, Takeshima T, Inui K, Okada S, Tanaka A, Sakuragawa N, Millat G, Vanier MT, Morris JA, Pentchev PG, Ohno K (1999) NPC1 gene mutations in Japanese patients with Niemann-Pick disease type C. Hum Genet 105(1–2):10–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Orna Staretz Chacham was responsible for planning, conducting, and reporting of the study.
Micha Aviram and Iris Morag contributed for the conducting and reporting of the work.
Aviv Goldbart contributed for reporting of the study.
Eli Hershkovitz contributed for the planning and reporting of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors; therefore, no informed consent was required. The study was approved by the Helsinki Committee of the institution.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Peter de Winter
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Staretz-Chacham, O., Aviram, M., Morag, I. et al. Pulmonary involvement in Niemann-Pick C type 1. Eur J Pediatr 177, 1609–1615 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-018-3219-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-018-3219-6