Abstract
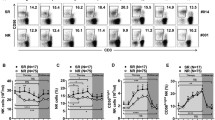
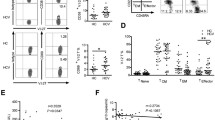
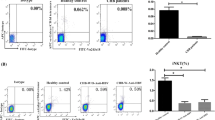
We have characterized the NK/NKT-like cells in patients with self-limiting hepatitis E infection. The distribution of peripheral NK/NKT-like cells, expressions of activation receptors, cytotoxic potential and effector function of NK/NKT-like cells from fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 86 acute patients, 101 recovered and 54 control individuals were assessed. Activated NKT-like (CD16+ CD56+ CD3+) cells were high in the patient groups. On CD56+ CD3− cells, NKp44 and NKp46 expressions were high in the acute patients, whereas NKp30, NKp44, NKp46 and NKG2D were high in the recovered individuals. On CD56+ CD3+ cells, NKp44, NKp46 and NKG2D expressions were high in the recovered but NKp30 was low in both the patient groups. Collectively, the current study elucidates the role of NK/NKT-like cells demonstrating phenotypic alterations of activated NKT-like cells and activation receptors, lack of CD107a expression and functional impairment of peripheral NK/NKT-like cells in self-limiting hepatitis E infection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal R, Jameel S (2011) Hepatitis E. Hepatology 54:2218–2226
Krumbholz A, Mohn U, Lange J et al (2012) Prevalence of hepatitis E virus specific antibodies in humans with occupational exposure to pigs. Med Microbiol Immunol 201:239–244
Dremsek P, Wenzel JJ, Johne R et al (2012) Seroprevalence study in forestry workers from eastern Germany using novel genotype 3-and rat hepatitis E virus-specific immunoglobulin G ELISAs. Med Microbiol Immunol 201:189–200
Srivastava R, Aggarwal R, Jameel S et al (2007) Cellular immune responses in acute hepatitis E virus infection to the viral open reading frame 2 protein. Viral Immunol 20:56–65
Tripathy AS, Das R, Rathod SB, Arankalle VA (2012) Cytokine profiles, CTL response and T cell frequencies in the peripheral blood of acute patients and individuals recovered from Hepatitis E infection. PLoS ONE 7:e31822
Yokoyama WM (2008) Mistaken notions about natural killer cells. Nat Immunol 9:481–485
Lanier LL (2005) NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 23:225–274
Biron CA, Brossay L (2001) NK cells and NKT cells in innate defense against viral infections. Curr Opin Immunol 13:458–464
Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S (2008) Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol 9:503–510
Smyth MJ, Hayakawa Y, Takeda K, Yagita H (2002) New aspects of natural-killer-cell surveillance and therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:850–861
Raulet DH (2003) Roles of the NKG2D immunoreceptor and its ligands. Nat Rev Immunol 3:781–790
Moretta A, Bottino C, Vitale M, Pende D, Cantoni C, Mingari MC, Biassoni R, Moretta L (2001) Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis. Annu Rev Immunol 19:197–223
Moretta L, Bottino C, Pende D, Castriconi R, Mingari MC, Moretta A (2006) Surface NK receptors and their ligands on tumor cells. Semin Immunol 18:151–158
Fukuda M (1991) Lysosomal membrane glycoproteins. Structure, biosynthesis, and intracellular trafficking. J Biol Chem 266:21327–21330
Trapani JA, Smyth MJ (2002) Functional significance of the perforin/granzyme cell death pathway. Nat Rev Immunol 2:735–747
Van Dommelen SL, Degli-Esposti MA (2004) NKT cells and viral immunity. Immunol Cell Biol 82:332–341
Peralbo E, Alonso C, Solana R (2007) Invariant NKT and NKT-like lymphocytes: two different T cell subsets that are differentially affected by ageing. Exp Gerontol 42:703–708
Golden-Mason L, Madrigal-Estebas L, McGrath E, Conroy MJ, Ryan EJ et al (2008) Altered natural killer cell subset distributions in resolved and persistent hepatitis C virus following single source exposure. Gut 57:1121–1128
Srivastava R, Aggarwal R, Bhagat MR, Chowdhury A, Naik S (2008) Alterations in natural killer cells and natural killer T cells during acute viral hepatitis E. J Viral Hepat 15:910–916
Prabhu SB, Gupta P, Durgapal H, Rath S, Gupta SD et al (2010) Study of cellular immune response against Hepatitis E Virus (HEV). J Viral Hepat 18:587–594
Arankalle VA, Lole KS, Deshmukh TM, Chobe LP, Gandhe SS (2007) Evaluation of human (genotype-1) and swine (genotype-4)-ORF-2 based ELISAs for anti-HEV IgM and IgG detection in an endemic country and search for type-4human HEV infections. J Viral Hepat 14:435–445
Saravanabalaji S, Tripathy AS, Dhoot RR, Chadha MS, Kakrani AL, Arankalle VA (2009) Viral load, antibody titers and recombinant open reading frame 2 protein- induced TH1/TH2 cytokines and cellular immune responses in self-limiting and fulminant hepatitis E. Intervirology 52:78–85
Arankalle VA, Lole KS, Deshmukh TM, Srivastava S, Shaligram US (2009) Challenge studies in Rhesus monkeys immunized with candidate hepatitis E vaccines: DNA, DNA-prime-protein-boost and DNA-protein encapsulated in liposomes. Vaccine 27:1032–1039
Tripathy AS, Das R, Chadha MS, Arankalle VA (2011) Epidemic of Hepatitis B with high mortality in India: association of fulminant disease with lack of CCL4 and natural killer T cells. J Viral Hepat. 18:e415–e422
Das R, Rathod SB, Alagarasu K, Arankalle VA, Tripathy AS (2013) Altered expressions of peripheral CD11c, CD80, CD83 markers and associations of HLA class II allele and haplotypes in self-limiting Hepatitis E infection. Hum Immunol 74:277–285
Zhao J, Li Y, Jin L, Zhang S, Fan R et al (2012) Natural killer cells are characterized by the concomitantly increased interferon-γ and cytotoxicity in acute resolved hepatitis B patients. PLoS ONE 7:e49135
Kakimi K, Guidotti LG, Koezuka Y, Chisari FV (2000) Natural killer T cells activation inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vivo. J Exp Med 192:921–930
Moretta A, Bottino C, Vitale M, Pende D, Cantoni C, Mingari MC, Biassoni R, Moretta L (2001) Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediate cytolysis. Annu Rev Immunol 19:197–223
Biron CA, Nguyen KB, Pien GC, Cousens LP, Salazar-Mather TP (1999) Natural killer cells in antiviral defense: function and regulation by innate cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol 17:189–220
De Maria A, Biassoni R, Fogli M, Rizzi M, Cantoni C et al (2001) Identification, molecular cloning and functional characterization of NKp46 and NKp30 natural cytotoxicity receptors in Macaca fascicularis NK cells. Eur J Immunol 31:3546–3556
De Maria A, Fogli M, Costa P, Murdaca G, Puppo F et al (2003) The impaired NK cell cytolytic function in viremic HIV-1 infection is associated with a reduced surface expression of natural cytotoxicity receptors (NKp46, NKp30 and NKp44). Eur J Immunol 33:2410–2418
Fogli M, Costa P, Murdaca G, Setti M, Mingari MC et al (2004) Significant NK cell activation associated with decreased cytolytic function in peripheral blood of HIV-1-infected patients. Eur J Immunol 34:2313–2321
Golden-Mason L, Cox AL, Randall JA, Cheng L, Rosen HR (2010) Increased natural killer cell cytotoxicity and NKp30 expression protects against hepatitis C virus infection in high-risk individuals and inhibits replication in vitro. Hepatology 52:1581–1589
Yoon JC, Lim JB, Park JH, Lee JM (2011) Cell-to-cell contact with hepatitis C virus infected cells reduces functional capacity of natural killer cells. J Virol 85:12557–12569
Varchetta S, Mele D, Mantovani S, Oliviero B, Cremonesi E et al (2012) Impaired intrahepatic natural killer cell cytotoxic function in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 56:841–849
Pembroke T, Christian A, Jones E, Hills RK, Wang EC et al (2014) The paradox of NKp46 + natural killer cells: drivers of severe hepatitis C virus-induced pathology but in vivo resistance to interferon α treatment. Gut 63:515–524
Mao H, Tu W, Liu Y, Qin G, Zheng J et al (2010) Inhibition of human natural killer cell activity by influenza virions and hemagglutinin. J Virol 84:4148–4157
Krzewski K, Gil-Krzewska A, Nguyen V, Peruzzi G, Coligan JE (2013) LAMP1/CD107a is required for efficient perforin delivery to lytic granules and NK-cell cytotoxicity. Blood 121:4672–4683
Zhang J, Zhang XF, Zhou C, et al. (2013) Protection against hepatitis E virus infection by naturally acquired and vaccine-induced immunity. Clin Microbiol Infect. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12419
Ralainirina N, Poli A, Michel T, Poos L, Andre`s E, Hentges F, Zimmer J (2007) Control of NK cell functions by CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Leuko Biol 81:144–153
Ghiringhelli F, Ménard C, Terme M (2005) CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells inhibit natural killer cell functions in a transforming growth factor—dependent manner. J Exp Med 202:1075–1085
Castriconi R, Cantoni C, Della Chiesa M, Vitale M, Marcenaro E et al (2003) Transforming growth factor beta 1 inhibits expression of NKp30 and NKG2D receptors: consequences for the NK-mediated killing of dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:4120–4125
Rathod SB, Das R, Thanapati S, Arankalle VA, Tripathy AS (2014) Suppressive activity and altered conventional phenotype markers/mediators of regulatory T cells in patients with self-limiting Hepatitis E. J Viral Hepat 21:141–151
Acknowledgments
We thank Director, National Institute of Virology, for all the encouragements. Special thanks are due to Mr. Prasad Babbar, Mr. Vasant Walkoli, Mr. Bipin Tilekar, Mr. Sarang Kamble, Mr. Dasharath, Mr. Prakash Sarje, Mr. Prakash B. Jawalkar, Ms. Neeta Thorat and Mr. Shirish Vaidya for technical help. Contributions of Mr. Kanad Madansure, Mr. Chinmaya Mahapatra, Mr. Rishikesh Lotke and Ms. Aparna Hande are greatly acknowledged. We thank Mr. Sanjay Rathod and Mr. Subrat Thanapati for their timely help and critical reading the manuscript. We thank Dr. A. L. Kakrani (D. Y. Patil Medical College, Pune, India) and Dr. Madhuri Thakar (NARI, Pune, India) for their encouragements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, R., Tripathy, A. Increased expressions of NKp44, NKp46 on NK/NKT-like cells are associated with impaired cytolytic function in self-limiting hepatitis E infection. Med Microbiol Immunol 203, 303–314 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-014-0338-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-014-0338-1