Abstract
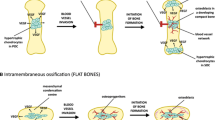
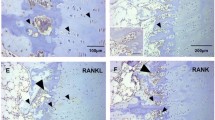
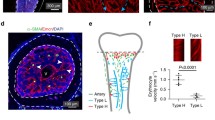
The aim of this work is to investigate the growth of the vasculature in the rat humeral head cartilage after the initial development of the secondary ossification centre until the adult organization. Rats aging from 5 weeks to 12 months were used. Histological observations on humeral heads were implemented with morphometrical analysis. Subsequently, vascular corrosion cast, that permits a three-dimensional observation of the vasculature, were prepared and observed by scanning electron microscopy. In young animals the epiphysis contains thin bone trabeculae and most of the epiphysis is occupied by bone marrow spaces. With age, the bone trabeculae progressively enlarge up to double their thickness. The percentage of bone tissue increases from 33.6 to 58.6% of the entire epiphysis, while the bone marrow spaces tend to increase very little in their mean dimension. Vascular corrosion casts show that the epiphyseal microcirculation is well distinguished from that of the diaphysis, and arises from the vessels present in the capsule and the periosteal networks. In young animals the only capillaries are bone marrow sinusoids and few subchondral capillaries. In adult animals small vessels run between the clusters of sinusoids forming the trabecular circulation. Capillary sprouts from sinusoids are always observed both in the young and adult animals. Thus, in adult rats different proper microcirculatory districts can be distinguished in the epiphysis: (a) the sinusoidal network, that supplies the hematopoiesis of the bone marrow and the adjacent osteogenic tissue; (b) the bone tissue microcirculation, limited to small vessels that supply the metabolism and the remodelling of the bone tissue. The reported microvascular organization and its adaptation to the epiphyseal growth represent the morphological basis for understanding the reciprocal interaction among the different tissues in developing and adult rat epiphysis.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguila HL, Rowe DW (2005) Skeletal development, bone remodeling, and hematopoiesis. Immunol Rev 208:7–18
Aharinejad S, Marks SC, Böck P Jr, Mackay CA, Larson Ek A Tahamtani, Mason-Savas A, Firbas W (1995) Microvascular pattern in the metaphysis during bone growth. Anat Rec 242:111–122
Briggs PI, Moran CG, Wood MB (1998) Actions of endothelin-1, 2, and 3 in the microvasculature of bone. J Orthop Res 16:340–347
Brinker MR, Lippton HL, Cook SD, Hyman AL (1990) Farmacological regulation of the circulation of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72:964–975
Carlevaro MF, Albini A, Ribatti D, Gentili C, Benelli R, Cermelli S, Cancedda R, Cancedda FD (1997) Transferrin promotes endothelial cell migration and invasion: implication in cartilage neovascularization. J Cell Biol 136:1375–1384
Casella I, Feccia T, Chelucci C, Samoggia P, Castelli G, Guerriero R, Parolini I, Petrucci E, Pelosi E, Morsilli O, Gabbianelli M, Testa U, Peschle C (2003) Autocrine-paracrine VEGF loops potentiate the maturation of megakaryocytic precursors through Flt1 receptor. Blood 101(4):1316–1323
Cecchini MG, Hofstetter W, Halasy J, Wetterwald A, Felix R (1997) Role of CSF-1 in bone and bone marrow development. Mol Reprod Dev 46(1):75–83
Dalle Carbonare L, Bertoldo F, Valenti MT, Zenari S, Zanatta M, Sella S, Giannini S, Cascio VL (2005) Histomorphometric analysis of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Micron 36(7–8):645–652
Davis TR Wood MB (1992) Endothelial control of long bone vascular resistance. J Orthop Res 10:344–349
Deckers MM, Karperien M, van der Bent C, Yamashita T, Papapoulos SE, Lowik CW (2000) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factors and their receptors during osteoblast differentiation. Endocrinology 141(5):1667–74
Doschak MR, Cooper DM, Huculak CN, Matyas JR, Hart DA, Hallgrimsson B, Zernicke RF, Bray RC (2003) Angiogenesis in the distal femoral chondroepiphysis of the rabbit during development of the secondary centre of ossification. J Anat 203(2):223–233
Ferrara N, Gerber HP (2001) The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in angiogenesis. Acta Haematol 106(4):148–156
Fiedler J, Leucht F, Waltenberger J, Dehio C, Brenner RE (2005) VEGF-A and PlGF-1 stimulate chemotactic migration of human mesenchymal progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334(2):561–568
Fleming JT, Barati MT, Beck DJ, Dodds JC, Malkani AL, Parameswaran D, Soukhova GK, Voor MJ, Feitelson JB (2001) Bone blood flow and vascular reactivity. Cells Tissues Organs 169:279–284
Floyd WE, Zaleske DJ, Schiller AL, Trahan C, Mankin HJ (1987) Vascular events associated with the appearance of the secondary center of ossification in the murine distal femoral epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69:185–190
Forriol F, Shapiro F (2005) Bone development: interaction of molecular components and biophysical forces. Clin Orthop Relat Res 432:14–33
Ganey TM, Love SM, Ogden JA (1992) Development of vascularization in the chondroepiphysis of the rabbit. J Orthop Res 10:496–510
Gaudio E, Pannarale L, Caggiati A, Marinozzi G (1990) A three-dimensional study of the morphology and topography of pericytes in the microvascular bed of skeletal muscle. Scanning Microsc 4:491–500
Gaudio E, Pannarale L, Caggiati A, Maggioni A, Marinozzi G, Motta PM (1992) Pericyte topography of the microvascular skeletal muscle: correlated analysis of corrosion casts and KOH-digested specimens. In: Motta PM, Murakami T, Fujita H (eds) Scanning Electron Microscopy of vascular casts: methods and applications. Kluwer, Boston, pp 171–180
Haines RW (1974) The pseudoepiphysis of the first metacarpal of man. J Anat 117:145–158
Harada S, Nagy JA, Sullivan KA, Thomas KA, Endo N, Rodan GA, Rodan SB (1994) Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by prostaglandin E2 and E1 in osteoblasts. J Clin Invest 93:2490–2496
Hattori K, Dias S, Heissig B, Hackett Nr, Lyden D, Tateno M, Hicklin DJ, Zhu Z, Witte L, Crystal RG, Moore MA, Rafii S (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-1 stimulate postnatal hematopoiesis by recruitment of vasculogenic and hematopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med 193:1005–1014
Heissig B, Ohki Y, Sato Y, Rafii S, Werb Z, Hattori K (2005) A role for niches in hematopoietic cell development. Hematology 10(3):247–253
Horner A, Bord S, Kemp P, Grainger D, Compston JE (1996) Distribution of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) A chain mRNA, protein, and PDGF-alpha receptor is rapidly forming human bone. Bone 19:353–362
Horner A, Bord S, Kelsall AW, Coleman N, Compston JE (2001) Tie2 ligands angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 are coexpressed with vascular endothelial cell growth factor in growing human bone. Bone 28:65–71
Hunter WL, Arsenault AL (1990) Vascular invasion of the epiphyseal growth plate: analysis of metaphyseal capillary ultrastructure and growth dynamics. Anat Rec 227:223–231
Iwaku F (1992) Microvasculature of bone and bone marrow. In: Motta PM, Murakami T, Fujita H (eds) Scanning electron microscopy of vascular cast: methods and applications. Kluwer , Boston, pp 157–169
Januszewski M, Dabrowski Z, Adamus M, Niedzwiedzki T (2003) Three-dimensional model of bone marrow stromal cell culture. Biomed Mater Eng 13(1):1–9
Kugler JH, Tomlinson A, Wagstaff A, Ward SM (1979) The role of cartilage canals in the formation of secondary centers of ossification. J Anat 129:493–506
Lametschwandtner A, Lametschwandtner U, Weiger V (1990) Scanning electron microscopy of vascular corrosion casts. Technique and applications: updated review. Scanning Microsc 4:889–941
LeCouter J, Zlot C, Tejada M, Peale F, Ferrara N (2004) Bv8 and endocrine gland-derived vascular endothelial growth factor stimulate hematopoiesis and hematopoietic cell mobilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(48):16813–16818
Lee MMC, Garn SM (1967) Pseudoepiphyses or notches in the non-epiphyseal end of metacarpal bones in healthy children. Anat Rec 159:263–272
Levene C (1964) The patterns of cartilage canals. J Anat 98:515–538
Li L, Xie T (2005) Stem cell niche: structure and function. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:605–631
Li G, Cui Y, McIlmurray L, Allen WE, Wang H (2005) rhBMP-2, rhVEGF(165), rhPTN and thrombin-related peptide, TP508 induce chemotaxis of human osteoblasts and microvascular endothelial cells. J Orthop Res 23(3):680–685
Mayer H, Bertram H, Lindenmaier W, Korff T, Weber H, Weich H (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) expression in human mesenchymal stem cells: autocrine and paracrine role on osteoblastic and endothelial differentiation. J Cell Biochem 95(4):827–839
Mayr-Wohlfart U, Waltenberger J, Hausser H, Kessler S, Gunther KP, Dehio C, Puhl W, Brenner RE (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates chemotactic migration of primary human osteoblasts. Bone 30(3):472–477
Morini S, Pannarale L, Franchitto A, Donati S, Gaudio E (1999) Microvascular features and ossification process in the femoral head of growing rats. J Anat 195:225–233
Morini S, Continenza MA, Ricciardi G, Gaudio E, Pannarale L (2004) Development of the microcirculation of the secondary ossification center in rat humeral head. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 278(1):419–427
Niida S, Kaku M, Amano H, Yoshida H, Kataoka H, Nishikawa S, Tanne K, Maeda N, Nishikawa S, Kodama H (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor can substitute for macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the support of osteoclastic bone resorption. J Exp Med 190(2):293–298
Pannarale L, Onori P, Ripani M, Gaudio E (1996) Precapillary patterns and perivascular cells in the retinal microvasculature. A scanning electron microscope study. J Anat 188:693–703
Pannarale L, Morini S, D’ubaldo E, Gaudio E, Marinozzi G (1997) S.E.M. corrosion-casts study of the microcirculation of the flat bones in the rat. Anat Rec 247:462–471
Rafii S, Avecilla S, Shmelkov S, Shido K, Tejada R, Moore MA, Heissig B, Hattori K (2003) Angiogenic factors reconstitute hematopoiesis by recruiting stem cells from bone marrow microenvironment. Ann NY Acad Sci 996:49–60
Reich A, Jaffe N, Tong A, Lavelin I, Genina O, Pines M, Sklan D, Nussinovitch A, Monsonego-Ornan E (2005) Weight loading young chicks inhibits bone elongation and promotes growth plate ossification and vascularization. J Appl Physiol 98(6):2381–2389
Roach HI, Baker JE, Clarke NM (1998) Initiation of the bone epiphysis in long bones. Chronology of interactions between the vascular system and the chondrocytes. J Bone Miner Res 13:950–961
Schmidmaier G, Wildemann B, Bail H, Lucke M, Fuchs T, Stemberger A, Flyvbjerg A, Haas NP, Raschke M (2001) Local application of growth factors (insulin-like growth factor-1 and transforming growth factor-beta1) from a biodegradable poly (d,l-lactide) coating of osteosynthetic implants accelerates fracture healing in rats. Bone 28:341–350
Skawina A, Litwin JA, Gorezyca J, Miodonski AJ (1994) Blood vessels in epiphyseal cartilage of human fetal bone: a scanning electron microscopic study of corrosion casts. Anat Embryol 189:457–462
Sundaramurthy S, Mao JJ (2006) Modulation of endochondral development of the distal femoral condyle by mechanical loading. J Orthop Res 24(2):229–241
Visco DM, Hill MA, Van Sickle DC, Kincaid SA (1990) The development of centers of ossification of bones forming elbow joints in young swine. J Anat 171:25–39
Wan C, He Q, Li G (2006) Osteoclastogenesis in the nonadherent cell population of human bone marrow is inhibited by rhBMP-2 alone or together with rhVEGF. J Orthop Res 24:29–36
Wilsman NJ, Van Sickle DC (1970) The relationship of cartilage canals to the initial osteogenesis of secondary centers of ossification. Anat Rec 168:381–392
Wirth T, Syed Ali MM, Rauer C, Suss D, Griss P, Syed Ali S (2002) The blood supply of the growth plate and the epiphysis: a comparative scanning electron microscopy and histological experimental study in growing sheep. Calcif Tissue Int 70(4):312–319
Yao Z, Lafage-Proust MH, Plouet J, Bloomfield S, Alexandre C, Vico L (2004) Increase of both angiogenesis and bone mass in response to exercise depends on VEGF. J Bone Miner Res 19(9):1471–1480
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants from Italian MURST (ex 60%, ex 40% funds).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morini, S., Pannarale, L., Conti, D. et al. Microvascular adaptation to growth in rat humeral head. Anat Embryol 211, 403–411 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-006-0092-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-006-0092-2