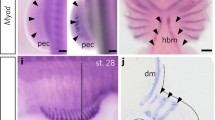
Abstract
During somite maturation, the ventral half of the epithelial somite disintegrates into the mesenchymal sclerotome, whereas the dorsal half forms a transitory epithelial sheet, the dermomyotome, lying in between the sclerotome and the surface ectoderm. The dermomyotome is the source of most of the mesodermal tissues in the body, giving rise to cell types as different as muscle, connective tissue, endothelium, and cartilage. Thus, the dermomyotome is the most important turntable of mesodermal cell fate choice in the vertebrate embryo. Here, we discuss the current knowledge on the formation of the dermomyotome and the mechanisms leading to the development of the various dermomyotomal derivatives, with special emphasis on the development of musculature and dermis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anakwe K, Robson L, Hadley J, Buxton P, Church V, Allen S, Hartmann C, Harfe B, Nohno T, Brown AM, Evans DJ, Francis-West P (2003) Wnt signaling regulates myogenic differentiation in the developing avian wing. Development 130:3503–3514
Aoyama H, Asamoto K (1988) Determination of somite cells: independence of cell differentiation and morphogenesis. Development 104:15–28
Baer V (1828) Entwickelungsgeschichte der Thiere: Beobachtung und Reflexion. Bornträger, Königsberg
Bardeen BI (1900) The development of the musculature in the body wall in the pig. Johns Hopkins Hospital Report 9:367
Ben-Yair R, Kahane N, Kalcheim C (2003) Coherent development of dermomyotome and dermis from the entire mediolateral extent of the dorsal somite. Development 130:4325–4336
Bladt F, Riethmacher D, Isenmann S, Aguzzi A, Birchmeier C (1995) Essential role for the c-met receptor in the migration of myogenic precursor cells into the limb bud. Nature 376:768–771
Borman WH, Yorde DE (1994) Barrier inhibition of a temporal neuraxial influence on early chick somitic myogenesis. Dev Dyn 200:68–78
Boyd ID (1960) Development of the striated muscle. In: Bourne GH (ed) Structure and function of muscle. Academic Press, New York
Brand-Saberi B, Ebensperger C, Wilting J, Balling R, Christ B (1993) The ventralizing effect of the notochord on somite differentiation in chick embryos. Anat Embryol (Berl) 188:239–245
Brand-Saberi B, Muller TS, Wilting J, Christ B, Birchmeier C (1996) Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor (SF/HGF) induces emigration of myogenic cells at interlimb level in vivo. Dev Biol 179:303–308
Brand-Saberi B, Christ B (2000) Evolution and development of distinct cell lineages derived from somites. Curr Top Dev Biol 48:1–42
Brennan C, Amacher SL, Currie PD (2002) Somitogenesis. Results Probl Cell Differ 40:271–297
Brent AE, Tabin CJ (2002) Developmental regulation of somite derivatives: muscle, cartilage and tendon. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:548–557
Brill G, Kahane N, Carmeli C, von Schack D, Barde YA, Kalcheim C (1995) Epithelial-mesenchymal conversion of dermatome progenitors requires neural tube-derived signals: characterization of the role of neurotrophin-3. Development 121:2583–2594
Buchner G, Broccoli V, Bulfone A, Orfanelli U, Gattuso C, Ballabio A, Franco B (2000) MAEG, an EGF-repeat containing gene, is a new marker associated with dermatome specification and morphogenesis of its derivatives. Mech Dev 98:179–182
Buckingham M, Bajard L, Chang T, Daubas P, Hadchouel J, Meilhac S, Montarras D, Rocancourt D, Relaix F (2003) The formation of skeletal muscle: from somite to limb. J Anat 202:59–68
Buffinger N, Stockdale FE (1994) Myogenic specification in somites: induction by axial structures. Development 120:1443–1452
Capdevila J, Tabin C, Johnson RL (1998) Control of dorsoventral somite patterning by Wnt-1 and beta-catenin. Dev Biol 193:182–194
Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, Young KE, Corden JL, Westphal H, Beachy PA (1996) Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature 383:407–413
Christ B, Jacob HJ, Jacob M (1972) [Experimental analysis of somitogenesis in the chick embryo]. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch 138:82–97
Christ B, Jacob HJ, Jacob M (1974) [Origin of wing musculature. Experimental studies on quail and chick embryos]. Experientia 30:1446–1449
Christ B, Jacob HJ, Jacob M (1977) Experimental analysis of the origin of the wing musculature in avian embryos. Anat Embryol (Berl) 150:171–186
Christ B, Jacob HJ, Jacob M (1978) [Regional determination of early embryonic muscle primordium. Experimental studies on quail and chick embryos (demonstration)]. Verh Anat Ges:353–357
Christ B, Jacob M, Jacob HJ (1983) On the origin and development of the ventrolateral abdominal muscles in the avian embryo. An experimental and ultrastructural study. Anat Embryol (Berl) 166:87–101
Christ B, Brand-Saberi B, Grim M, Wilting J (1992) Local signaling in dermomyotomal cell type specification. Anat Embryol (Berl) 186:505–510
Christ B, Ordahl CP (1995) Early stages of chick somite development. Anat Embryol (Berl) 191:381–396
Christ B, Huang R, Wilting J (2000) The development of the avian vertebral column. Anat Embryol (Berl) 202:179–194
Christ B, Huang R, Scaal M (2004) Formation and differentiation of the avian sclerotome. Anat Embryol, in press
Chuong CM (1998) Molecular basis of epithelial appendage morphogenesis. RG Landes, Austin, TX
Cinnamon Y, Kahane N, Kalcheim C (1999) Characterization of the early development of specific hypaxial muscles from the ventrolateral myotome. Development 126:4305–4315
Cinnamon Y, Kahane N, Bachelet I, Kalcheim C (2001) The sub-lip domain—a distinct pathway for myotome precursors that demonstrate rostral-caudal migration. Development 128:341–351
Cossu G, Kelly R, Tajbakhsh S, Di Donna S, Vivarelli E, Buckingham M (1996) Activation of different myogenic pathways: myf-5 is induced by the neural tube and MyoD by the dorsal ectoderm in mouse paraxial mesoderm. Development 122:429–437
Couly GF, Coltey PM, Le Douarin NM (1992) The developmental fate of the cephalic mesoderm in quail-chick chimeras. Development 114:1–15
Davidson D (1995) The function and evolution of Msx genes: pointers and paradoxes. Trends Genet 11:405–411
Denetclaw WF, Jr., Christ B, Ordahl CP (1997) Location and growth of epaxial myotome precursor cells. Development 124:1601–1610
Denetclaw WF, Ordahl CP (2000) The growth of the dermomyotome and formation of early myotome lineages in thoracolumbar somites of chicken embryos. Development 127:893–905
Denetclaw WF, Jr., Berdougo E, Venters SJ, Ordahl CP (2001) Morphogenetic cell movements in the middle region of the dermomyotome dorsomedial lip associated with patterning and growth of the primary epaxial myotome. Development 128:1745–1755
Dhoot GK, Gustafsson MK, Ai X, Sun W, Standiford DM, Emerson CP, Jr (2001) Regulation of Wnt signaling and embryo patterning by an extracellular sulfatase. Science 293:1663–1666
Dhouailly D (1977) Dermo-epidermal interactions during morphogenesis of cutaneous appendages in amniotes. Front Matrix Biol 4:86–121
Dietrich S, Schubert FR, Lumsden A (1997) Control of dorsoventral pattern in the chick paraxial mesoderm. Development 124:3895–3908
Dietrich S, Abou-Rebyeh F, Brohmann H, Bladt F, Sonnenberg-Riethmacher E, Yamaai T, Lumsden A, Brand-Saberi B, Birchmeier C (1999) The role of SF/HGF and c-Met in the development of skeletal muscle. Development 126:1621–1629
Duong TD, Erickson CA (2004) MMP-2 plays an essential role in producing epithelial-mesenchymal transformations in the avian embryo. Dev Dyn 229:42–53
Duprez D, Fournier-Thibault C, Le Douarin N (1998) Sonic Hedgehog induces proliferation of committed skeletal muscle cells in the chick limb. Development 125:495–505
Eloy-Trinquet S, Mathis L, Nicolas JF (2000) Retrospective tracing of the developmental lineage of the mouse myotome. Curr Top Dev Biol 47:33–80
Epstein JA, Shapiro DN, Cheng J, Lam PY, Maas RL (1996) Pax3 modulates expression of the c-Met receptor during limb muscle development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:4213–4218
Fan CM, Tessier-Lavigne M (1994) Patterning of mammalian somites by surface ectoderm and notochord: evidence for sclerotome induction by a hedgehog homolog. Cell 79:1175–1186
Fan CM, Porter JA, Chiang C, Chang DT, Beachy PA, Tessier-Lavigne M (1995) Long-range sclerotome induction by sonic hedgehog: direct role of the amino-terminal cleavage product and modulation by the cyclic AMP signaling pathway. Cell 81:457–465
Fan CM, Lee CS, Tessier-Lavigne M 1997) A role for WNT proteins in induction of dermomyotome. Dev Biol 191:160–165
Fischel A (1895) Zur Entwicklung der vertebralen Rumpf- und der Extremitätenmuskulatur der Vögel und Säugetiere Morphol Jahrb 23:544
Galli LM, Willert K, Nusse R, Yablonka-Reuveni Z, Nohno T, Denetclaw W, Burrus LW (2004) A proliferative role for Wnt-3a in chick somites. Dev Biol 269:489–504
George-Weinstein M, Gerhart J, Reed R, Flynn J, Callihan B, Mattiacci M, Miehle C, Foti G, Lash JW, Weintraub H (1996) Skeletal myogenesis: the preferred pathway of chick embryo epiblast cells in vitro. Dev Biol 173:279–291
Glücksmann A (1934) Über die Entwicklung der Amniotenextremitäten und ihre Homologie mit den Flossen. Z Anat Entwickl-gesch 102:498
Goette A (1875) Entwickelungsgeschichte der Unke (Bombinator igneus) als Grundlage einer vergleichenden Morphologie der Wirbelthiere. Leopold Voss, Leipzig
Goulding M, Lumsden A, Paquette AJ (1994) Regulation of Pax-3 expression in the dermomyotome and its role in muscle development. Development 120:957–971
Grim M (1970) Differentiation of myoblasts and the relationship between somites and the wing bud of the chick embryo. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch 132:260
Gros J, Scaal M, Marcelle C (2004) A two-step mechanism for myotome formation in chick. Dev Cell 6:875–882
Gustafsson MK, Pan H, Pinney DF, Liu Y, Lewandowski A, Epstein DJ, Emerson CP, Jr (2002) Myf5 is a direct target of long-range Shh signaling and Gli regulation for muscle specification. Genes Dev 16:114–126
Hamilton HL (1952) Lillie’s development of the chick. An introduction to embryology. Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York
He L, Papoutsi M, Huang R, Tomarev SI, Christ B, Kurz H, Wilting J (2003) Three different fates of cells migrating from somites into the limb bud. Anat Embryol (Berl) 207:29–34
His W (1868) Untersuchungen über die erste Anlage des Wirbelthierleibes. Die erste Entwicklung des Hühnchens im Ei. Leipzig, Vogel
Holtzer H, Schultheiss T, Dilullo C, Choi J, Costa M, Lu M, Holtzer S (1990) Autonomous expression of the differentiation programs of cells in the cardiac and skeletal myogenic lineages. Ann N Y Acad Sci 599:158–169
Houzelstein D, Auda-Boucher G, Cheraud Y, Rouaud T, Blanc I, Tajbakhsh S, Buckingham ME, Fontaine-Perus J, Robert B (1999) The homeobox gene Msx1 is expressed in a subset of somites, and in muscle progenitor cells migrating into the forelimb. Development 126:2689–2701
Houzelstein D, Cheraud Y, Auda-Boucher G, Fontaine-Perus J, Robert B (2000) The expression of the homeobox gene Msx1 reveals two populations of dermal progenitor cells originating from the somites. Development 127:2155–2164
Huang R, Zhi Q, Izpisua-Belmonte JC, Christ B, Patel K (1999) Origin and development of the avian tongue muscles. Anat Embryol 200:137
Huang R, Zhi Q, Patel K, Wilting J, Christ B (2000) Dual origin and segmental organisation of the avian scapula. Development 127:3789–3794
Huang R, Lang E, Otto WR, Christ B, Patel K (2001) Molecular and cellular analysis of embryonic avian tongue development. Anat Embryol 204:179
Ikeya M, Takada S (1998) Wnt signaling from the dorsal neural tube is required for the formation of the medial dermomyotome. Development 125:4969–4976
Kahane N, Cinnamon Y, Kalcheim C (1998a) The cellular mechanism by which the dermomyotome contributes to the second wave of myotome development. Development 125:4259–4271
Kahane N, Cinnamon Y, Kalcheim C (1998b) The origin and fate of pioneer myotomal cells in the avian embryo. Mech Dev 74:59–73
Kahane N, Cinnamon Y, Bachelet I, Kalcheim C (2001) The third wave of myotome colonization by mitotically competent progenitors: regulating the balance between differentiation and proliferation during muscle development. Development 128:2187–2198
Kahane N, Cinnamon Y, Kalcheim C (2002) The roles of cell migration and myofiber intercalation in patterning formation of the postmitotic myotome. Development 129:2675–2687
Kardon G, Campbell JK, Tabin CJ (2002) Local extrinsic signals determine muscle and endothelial cell fate and patterning in the vertebrate limb. Dev Cell 3:533–545
Kölliker A (1879) Entwicklungsgeschichte des Menschen und der höheren Thiere. Engelmann, Leipzig
Krenn V, Gorka P, Wachtler F, Christ B, Jacob HJ (1988) On the origin of cells determined to form skeletal muscle in avian embryos. Anat Embryol (Berl) 179:49–54
Le Douarin NM (1969) Particularites du noyau interphasique chez la caille japonaise (Coturnix c. japonica). Utilisation de ses particularites comme “marquage biologique” dans les recherches sur les interactions tissulaires et les migrations cellulairs au cours de l’ontogenese. Bull Biol Fr Bel 103:435–452
Le Douarin NM (1973) A biological cell labeling technique and its use in experimental embryology. Dev Biol 30:217–222
Le Lievre CS, Le Douarin NM (1975) Mesenchymal derivatives of the neural crest: analysis of chimaeric quail and chick embryos. J Embryol Exp Morph 34:125–154
Lee CS, Buttitta LA, May NR, Kispert A, Fan CM (2000) SHH-N upregulates Sfrp2 to mediate its competitive interaction with WNT1 and WNT4 in the somitic mesoderm. Development 127:109–118
Lee CS, Buttitta L, Fan CM (2001) Evidence that the WNT-inducible growth arrest-specific gene 1 encodes an antagonist of sonic hedgehog signaling in the somite. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:11347–11352
Li L, Cserjesi P, Olson EN (1995) Dermo-1: a novel twist-related bHLH protein expressed in the developing dermis. Dev Biol 172:280–292
Linker C, Lesbros C, Stark MR, Marcelle C (2003) Intrinsic signals regulate the initial steps of myogenesis in vertebrates. Development 130:4797–4807
Marcelle C, Eichmann A, Halevy O, Breant C, Le Douarin NM (1994) Distinct developmental expression of a new avian fibroblast growth factor receptor. Development 120:683–694
Marcelle C, Wolf J, Bronner-Fraser M (1995) The in vivo expression of the FGF receptor FREK mRNA in avian myoblasts suggests a role in muscle growth and differentiation. Dev Biol 172:100–114
Marcelle C, Stark MR, Bronner-Fraser M (1997) Coordinate actions of BMPs, Wnts, Shh and noggin mediate patterning of the dorsal somite. Development 124:3955–3963
Marcelle C, Ahlgren S, Bronner-Fraser M (1999) In vivo regulation of somite differentiation and proliferation by Sonic Hedgehog. Dev Biol 214:277–287
Marcelle C, Lesbros C, Linker C (2002) Somite patterning: a few more pieces of the puzzle. Results Probl Cell Differ 38:81–108
Marics I, Padilla F, Guillemot JF, Scaal M, Marcelle C (2002) FGFR4 signaling is a necessary step in limb muscle differentiation. Development 129:4559–4569
Maroto M, Reshef R, Munsterberg AE, Koester S, Goulding M, Lassar AB (1997) Ectopic Pax-3 activates MyoD and Myf-5 expression in embryonic mesoderm and neural tissue. Cell 89:139–148
Mauger A (1972) [The role of somitic mesoderm in the development of dorsal plumage in chick embryos. I. Origin, regulative capacity and determination of the plumage-forming mesoderm]. J Embryol Exp Morphol 28:313–341
Mestres P, Hinrichsen K (1976) The histogenesis of somites in the chick. J Embryol Exp Morphol 36:669
Minot CS (1892) Human embryology. Wood and Co., New York
Münsterberg AE, Kitajewski J, Bumcrot DA, McMahon AP, Lassar AB (1995) Combinatorial signaling by Sonic hedgehog and Wnt family members induces myogenic bHLH gene expression in the somite. Genes Dev 9:2911–2922
Münsterberg AE, Lassar AB (1995) Combinatorial signals from the neural tube, floor plate and notochord induce myogenic bHLH gene expression in the somite. Development 121:651–660
Murray PDF (1928a) The origin of the dermis. Nature 122:609
Murray PDF (1928b) Chorio-allantoic grafts of fragments of the two-day chick, with special reference to the development of the limbs, intestine, and skin. Austr J Exper Biol Med Sci 5:237–256
Nicolas JF, Mathis L, Bonnerot C, Saurin W (1996) Evidence in the mouse for self-renewing stem cells in the formation of a segmented longitudinal structure, the myotome. Development 122:2933–2946
Noden DM (1983) The role of the neural crest in patterning of avian cranial skeletal, connective, and muscle tissues. Dev Biol 96:144–165
Olivera-Martinez I, Coltey M, Dhouailly D, Pourquié O (2000) Mediolateral somitic origin of ribs and dermis determined by quail-chick chimeras. Development 127:4611–4617
Olivera-Martinez I, Thelu J, Teillet MA, Dhouailly D (2001) Dorsal dermis development depends on a signal from the dorsal neural tube, which can be substituted by Wnt-1. Mech Dev 100:233–244
Olivera-Martinez I, Missier S, Fraboulet S, Thelu J, Dhouailly D (2002) Differential regulation of the chick dorsal thoracic dermal progenitors from the medial dermomyotome. Development 129:4763–4772
Olivera-Martinez I, Thelu J, Dhouailly D (2004) Molecular mechanisms controlling dorsal dermis generation from the somitic dermomyotome. Int J Dev Biol 48:93–101
Ordahl CP, Berdougo E, Venters SJ, Denetclaw WF, Jr (2001) The dermomyotome dorsomedial lip drives growth and morphogenesis of both the primary myotome and dermomyotome epithelium. Development 128:1731–1744
Ott MO, Bober E, Lyons G, Arnold H, Buckingham M (1991) Early expression of the myogenic regulatory gene, myf-5, in precursor cells of skeletal muscle in the mouse embryo. Development 111:1097–1107
Pardanaud L, Luton D, Prigent M, Bourcheix LM, Catala M, Dieterlen-Lievre F (1996) Two distinct endothelial lineages in ontogeny, one of them related to hemopoiesis. Development 122:1363–1371
Pinot M (1970) The role of somitic mesoderm in the early morphogenesis of the limbs in the fowl embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol 23:109
Pispa J, Thesleff I (2003) Mechanisms of ectodermal organogenesis. Dev Biol 262:195–205
Pourquié O, Fan CM, Coltey M, Hirsinger E, Watanabe Y, Breant C, Francis-West P, Brickell P, Tessier-Lavigne M, Le Douarin NM (1996) Lateral and axial signals involved in avian somite patterning: a role for BMP4. Cell 84:461–471
Pourquié O (2001) Vertebrate somitogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:311–350
Pownall ME, Emerson CP, Jr (1992) Sequential activation of three myogenic regulatory genes during somite morphogenesis in quail embryos. Dev Biol 151:67–79
Psychoyos D, Stern CD (1996) Fates and migratory routes of primitive streak cells in the chick embryo. Development 122:1523–1534
Raff RA (1994) Developmental mechanisms in the evolution of animal form: Origins and evolvability of body plans. In: Early life on earth. Columbia University Press, New York, pp 489–500
Reichert CB (1838) Das Entwickelungsleben im Wirbelthierreich
Remak R (1850) Untersuchungen über die Entwickelung der Wirbelthiere. Reimer, Berlin
Reshef R, Maroto M, Lassar AB (1998) Regulation of dorsal somitic cell fates: BMPs and Noggin control the timing and pattern of myogenic regulator expression. Genes Dev 12:290–303
Rong PM, Teillet MA, Ziller C, Le Douarin NM (1992) The neural tube/notochord complex is necessary for vertebral but not limb and body wall striated muscle differentiation. Development 115:657–672
Rudnicki MA, Schnegelsberg PN, Stead RH, Braun T, Arnold HH, Jaenisch R (1993) MyoD or Myf-5 is required for the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell 75:1351–1359
Saunders JW (1948) Do the somites contribute to the formation of the chick wing? Anat Rec 100:756
Scaal M, Bonafede A, Dathe V, Sachs M, Cann G, Christ B, Brand-Saberi B (1999) SF/HGF is a mediator between limb patterning and muscle development. Development 126:4885–4893
Scaal M, Fuchtbauer EM, Brand-Saberi B (2001) cDermo-1 expression indicates a role in avian skin development. Anat Embryol (Berl) 203:1–7
Scaal M, Prols F, Fuchtbauer EM, Patel K, Hornik C, Kohler T, Christ B, Brand-Saberi B (2002) BMPs induce dermal markers and ectopic feather tracts. Mech Dev 110:51–60
Scaal M, Gros J, Lesbros C, Marcelle C (2004) In ovo electroporation of avian somites. Dev Dyn 229:643–650
Schäfer K, Braun T (1999) Early specification of limb muscle precursor cells by the homeobox gene Lbx1 h. Nat Genet 23:213–216
Schemainda H (1981) Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Entwicklung der Zungenmuskulatur beim Hühnerembryo. Verh Ana. Ges 75:501
Schmidt C, Bladt F, Goedecke S, Brinkmann V, Zschiesche W, Sharpe M, Gherardi E, Birchmeier C (1995) Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor is essential for liver development. Nature 373:699–702
Selleck MA, Stern CD (1991) Fate mapping and cell lineage analysis of Hensen’s node in the chick embryo. Development 112:615–626
Sengel P (1976) Morphogenesis of skin. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p. 277
Sengel P (1990) Pattern formation in skin development. Int J Dev Biol 34:33–50
Song K, Wang Y, Sassoon D (1992) Expression of Hox-7.1 in myoblasts inhibits terminal differentiation and induces cell transformation. Nature 360:477–481
Sorrell JM, Caplan AI (2004) Fibroblast heterogeneity: more than skin deep. J Cell Sci 117:667–675
Spence MS, Yip J, Erickson CA (1996) The dorsal neural tube organizes the dermamyotome and induces axial myocytes in the avian embryo. Development 122:231–241
Stern HM, Brown AM, Hauschka SD (1995) Myogenesis in paraxial mesoderm: preferential induction by dorsal neural tube and by cells expressing Wnt-1. Development 121:3675–3686
Stern HM, Hauschka SD (1995) Neural tube and notochord promote in vitro myogenesis in single somite explants. Dev Biol 167:87–103
Tajbakhsh S, Buckingham ME (1994) Mouse limb muscle is determined in the absence of the earliest myogenic factor myf-5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:747–751
Tajbakhsh S, Rocancourt D, Cossu G, Buckingham M (1997) Redefining the genetic hierarchies controlling skeletal myogenesis: Pax-3 and Myf-5 act upstream of MyoD. Cell 89:127–138
Teboul L, Hadchouel J, Daubas P, Summerbell D, Buckingham M, Rigby PW (2002) The early epaxial enhancer is essential for the initial expression of the skeletal muscle determination gene Myf5 but not for subsequent, multiple phases of somitic myogenesis. Development 129:4571–4580
Teillet M, Watanabe Y, Jeffs P, Duprez D, Lapointe F, Le Douarin NM (1998) Sonic hedgehog is required for survival of both myogenic and chondrogenic somitic lineages. Development 125:2019–2030
Venters SJ, Ordahl CP (2002) Persistent myogenic capacity of the dermomyotome dorsomedial lip and restriction of myogenic competence. Development 129:3873–3885
Wagner J, Schmidt C, Nikowits W, Jr., Christ B (2000) Compartmentalization of the somite and myogenesis in chick embryos are influenced by wnt expression. Dev Biol 228:86–94
Wessells NK (1965) Morphology and proliferation during early feather development. Dev Biol 12:131–153
Wilson-Rawls J, Hurt CR, Parsons SM, Rawls A (1999) Differential regulation of epaxial and hypaxial muscle development by paraxis. Development 126:5217–5229
Wilting J, Brand-Saberi B, Kurz H, Christ B (1995) Development of the embryonic vascular system. Cell Mol Biol Res 41:219–232
Wilting J, Christ B, Yuan L, Eichmann A (2003) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of embryonic haemangiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Naturwissenschaften 90:433–448
Acknowledgements
We thank the colleagues and members of our laboratory who have contributed to this work, and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft for continuous financial support.