Abstract
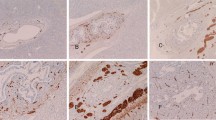
The autonomic nervous system plays a role in a variety of liver regenerative and metabolic functions, including modulating bile secretion and cholangiocyte and hepatobiliary progenitors of the canals of Hering. However, the nature and location of nerves which link to the proximal biliary tree have remained uncertain. We investigate the anatomic relationship of nerves to the proximal biliary tree including the putative stem/progenitor cell niche of the canal of Hering. Using double immunostaining (fluorescence, histochemistry) to highlight markers of cholangiocytes (biliary-type keratins), nerves (S100, neurofilament protein, PGP9.5, tyrosine hydroxylase), and stellate cells (CRBP-1), we examined sections from normal adult livers from autopsy or surgical resections. There is extensive contact between nerves and interlobular bile ducts, bile ductules, and canals of Hering (CoH). In multiple serial sections from 4 normal livers, biliary-nerve contacts were seen in all of these structures and were more common in the interlobular bile ducts (78/137; 57%) than in the ductules and CoH (95/294; 33%) (p < 0.001). Contacts appear to consist of nerves in juxtaposition to the biliary basement membrane, though crossing through basement membrane to interface directly with cholangiocytes is also present. These nerves are positive for tyrosine hydroxylase and are, thus, predominately adrenergic. Electron microscopy confirms nerves closely approximating ductules. Nerve fiber–hepatic stellate cell juxtaposition is observed but without stellate cell approximation to cholangiocytes. We present novel findings of biliary innervation, perhaps mediated in part, by direct cholangiocyte-nerve interactions. The implications of these findings are protean for studies of neuromodulation of biliary physiology and hepatic stem/progenitor cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HSPC:
-
Hepatic stem/progenitor cells
- PBS:
-
Proximal biliary structures
- CoH:
-
Canal of Hering
- NF:
-
Neurofilament protein
- TH:
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase
- HSC:
-
Hepatic stellate cell
References
Mizuno K, Ueno Y (2017) Autonomic nervous system and the liver. Hepatol Res 47:160–165
Theise ND, Saxena R, Portmann BP, Thung SN, Yee H, Chiriboga L, Kumar A, Crawford JM (1999) The canals of Hering and hepatic stem cells in humans. Hepatology 30:1425–1433
Factor VM, Radaeva SA, Thorgeirsson SS (1994) Origin and fate of oval cells in dipin-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in the mouse. Am J Pathol 145:409–422
Kuwahara R, Kofman AV, Landis CS, Swenson ES, Barendswaard E, Theise ND (2008) The hepatic stem cell niche: identification by label retaining cell assay. Hepatology 47:1994–2002
Tiniakos DG, Lee JA, Burt AD (1996) Innervation of the liver: morphology and function. Liver 16:151–160
Cucchiaro G, Branum GD, Farouk M et al (1992) The effects of liver denervation on the regulation of hepatic biliary secretion. Transplant 54:129–136
Fava G, Marzioni M, Francis H, Glaser S, Demorrrow S, Ueno Y, Benedetti A, Alpini G (2007) Novel interaction of bile acid and neural signaling in the regulation of cholangiocyte function. Hepatol Res 37(Suppl 3):S420–S429
LeSage G, Glaser S, Alpini G (2000) Regulatory mechanisms of ductal bile secretion. Dig Liver Dis 32:563–566
Theise ND (2006) Gastrointestinal stem cells. III. Emergent themes of liver stem cell biology: niche, quiescence, self-renewal, and plasticity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G189–G193
LeSage G, Alvaro D, Benedetti A et al (1999) Cholinergic system modulates growth, apoptosis, and secretion of cholangiocytes from bile duct-ligated rats. Gastroenterology. 117:191–199
Cassiman D, Libbrecht L, Sinelli N, Desmet V, Denef C, Roskams T (2002) The vagal nerve stimulates activation of the hepatic progenitor cell compartment via muscarinic acetylcholine receptor type 3. Am J Pathol 161:521–530
Oben JA, Roskams T, Yang S, Lin H, Sinelli N, Li Z, Torbenson M, Huang J, Guarino P, Kafrouni M, Diehl AM (2003) Sympathetic nervous system inhibition increases hepatic progenitors and reduces liver injury. Hepatology 38:664–673
Soyama A, Eguchi S, Hamada T et al (2012) The impact of hepatic denervation on the accumulation of hepatic progenitor cells during liver regeneration in rats. Hepatogastroenterology 59:1577–1579
Tanimizu N, Ichinohe N, Mitaka T (2018) Intrahepatic bile ducts guide establishment of the intrahepatic nerve network in developing and regenerating mouse liver. Development 145:dev159095
Terada T (2015) Ontogenic development of nerve fibers in human fetal livers: an immunohistochemical study using neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) and neuron-specific enolase (NSE). Histochem Cell Biol 143:421–429
Tiniakos DG, Mathew J, Kittas C, Burt AD (2008) Ontogeny of human intrahepatic innervation. Virchows Arch 452:435–442
Gershon MD (2005) Nerves, reflexes, and the enteric nervous system: pathogenesis of the irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol 39:S184–S193
Bioulac-Sage P, Lafon ME, Saric J, Balabaud C (1990) Nerves and perisinusoidal cells in human liver. J Hepatol 10:105–112
Uchio K, Tuchweber B, Manabe N, Gabbiani G, Rosenbaum J, Desmouliere A (2002) Cellular retinol-binding protein-1 expression and modulation during in vivo and in vitro myofibroblastic differentiation of rat hepatic stellate cells and portal fibroblasts. Lab Investig 82:619–628
Lepreux S, Bioulac-Sage P, Gabbiani G, Sapin V, Housset C, Rosenbaum J, Balabaud C, Desmoulière A (2004) Cellular retinol-binding protein-1 expression in normal and fibrotic/cirrhotic human liver: different patterns of expression in hepatic stellate cells and (myo)fibroblast subpopulations. J Hepatol 40:774–780
Crawford AR, Lin XZ, Crawford JM (1998) The normal adult human liver biopsy: a quantitative reference standard. Hepatology 28:323–331
Saxena R, Theise ND, Crawford JM (1999) Microanatomy of the human liver -- exploring the hidden interfaces. Hepatology 30:1339–1346
Ludwig J, Ritman EL, LaRusso NF, Sheedy PF, Zume G (1998) Anatomy of the human biliary system studied by quantitative computer-aided three-dimensional imaging techniques. Hepatology 27:893–899
McCuskey RS (2004) Anatomy of efferent hepatic nerves. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 280:821–826
Burt AD, Tiniakos D, MacSween RN, Griffiths MR, Wisse E, Polak JM (1989) Localization of adrenergic and neuropeptide tyrosine-containing nerves in the mammalian liver. Hepatology 9:839–845
Roskams T, Cassiman D, De Vos R, Libbrecht L (2004) Neuroregulation of the neuroendocrine compartment of the liver. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 280:910–923
Oben JA, Diehl AM (2004) Sympathetic nervous system regulation of liver repair. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 280:874–883
Kandilis AN, Papadopoulou IP, Koskinas J, Sotiropoulos G, Tiniakos DG (2015) Liver innervation and hepatic function: new insights. J Surg Res 194:511–519
Cassiman D, Sinelli N, Bockx I et al (2007) Human hepatic progenitor cells express vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor type 2 and receive nerve endings. Liver Int 27:323–328
Paku S, Schnur J, Nagy P, Thorgeirsson SS (2001) Origin and structural evolution of the early proliferating oval cells in rat liver. Am J Pathol 158:1313–1323
Omenetti A, Yang L, Gainetdinov RR et al (2011) Paracrine modulation of cholangiocyte serotonin synthesis orchestrates biliary remodeling in adults. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300:303–315
Boon AP, Hubscher SG, Lee JA, Hines JE, Burt AD (1992) Hepatic reinnervation following orthotopic liver transplantation in man. J Pathol 167:217–222
Dhillon AP, Sankey EA, Wang JH, Wightman K, Mathur S, Burroughs AK, Scheuer PJ (1992) Immunohistochemical studies on the innervation of human transplanted livers. J Pathol 167:211–216
Kjaer M, Jurlander J, Keiding S, Galbo H, Kirkegaard P, Hage E (1994) No reinnervation of hepatic sympathetic nerves after liver transplantation in human subjects. J Hepatol 20:97–100
Colle I, Van Vlierberghe H, Troisi R, De Hemptinne B (2004) Transplanted liver: Consequences of denervation for liver functions. Anat Rec 280A(1):924–931
Navez J, Golce N, Bancel B, Rode A, Ducerf C, Mezoughi S, Mokram K, Mabrut JY (2016) Traumatic biliary neuroma after orthotopic liver transplantation: possible cause of “unexplained” anastomotic biliary strictures. Clin Transpl 30:1366–1369
Katayama Y, Battista M, Kao W-M, Hidalgo A, Peired AJ, Thomas SA, Frenette PS (2006) Signals from the sympathetic nervous system regulate hematopoietic stem cell egress from bone marrow. Cell 124:407–421
Bohórquez DV, Shahid RA, Erdmann A et al (2015) Neuroepithelial circuit formed by innervation of sensory enteroendocrine cells. J Clin Invest 125:782–786
Loesch A, Unwin R, Gandhi V, Burnstock G (2009) Sympathetic nerve varicosities in close apposition to basolateral membranes of collecting duct epithelial cells of rat kidney. Nephron Physiol 113:15–21
Guthoff RF, Wienss H, Hahnel C, Wree A (2005) Epithelial innervation of human cornea: a three-dimensional study using confocal laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Cornea 24:608–613
Knox SM, Lombaert IM, Reed X, Vitale-Cross L, Gutkind JS, Hoffman MP (2010) Parasympathetic innervation maintains epithelial progenitor cells during salivary organogenesis. Science 329:1645–1647
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Liliane Dubuisson (SERCOMI, University Bordeaux 2, France) for her help in electron microscopic observation and Mr. Zong-Shi Wang (Histology, Dept. of Pathology, Beth Israel Medical Center, New York, NY, USA) for his careful preparation of serial tissue sections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AZ: experiments and procedures, data analysis, JR: experiments and procedures, HJF: experiments and procedures, data analysis, manuscript preparation, JQ: experiments and procedures, ASG: study design and concept, manuscript preparation, JO: experiments and procedures, AK: experiments and procedures, CB: study design and concept, experiments and procedures, PB-S: study design and concept, data analysis, manuscript preparation, DGT: study design and concept, experiments and procedures, data analysis, manuscript preparation, NDT: study design and concept, experiments and procedures, data analysis, manuscript preparation
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zanchi, A., Reidy, J., Feldman, H.J. et al. Innervation of the proximal human biliary tree. Virchows Arch 477, 385–392 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-020-02761-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-020-02761-4