Abstract
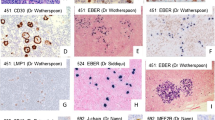
According to the WHO classification, anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a distinct T-cell lymphoma entity with a number of morphological variants. The characteristic feature of lymphohistiocytic variant of ALCL according to the WHO classification is the abundance of histiocytes that exceed and mask the tumour cell population. In the current, study we reanalysed a historical series of 17 lymphomas, diagnosed as lymphohistiocytic lymphoma according to the criteria of the Kiel classification, with the presence of large purple macrophages (LPM) as the decisive finding for diagnosing this lymphoma subtype. We assessed the cellular composition of the tumour and correlated the results with the definition of lymphohistiocytic variant of ALCL given in the WHO classification. Although all cases in our cohort matched the criteria of ALCL according to the WHO, in 30% of the cases, the total amount of macrophages did not exceed the number of CD30-positive tumour cells. Our results indicate that the presence of LPM might be helpful to identify this subgroup of ALCL. Because the distinction of morphological subtypes of ALCL is of clinical relevance, improved criteria for subtyping ALCL are urgently needed that might include the presence LPM as one criteria.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Bonzheim I, Geissinger E, Roth S, Zettl A, Marx A, Rosenwald A, Muller-Hermelink HK, Rudiger T (2004) Anaplastic large cell lymphomas lack the expression of T-cell receptor molecules or molecules of proximal T-cell receptor signaling. Blood 104:3358–3360
Cordell JL, Falini B, Erber WN, Ghosh AK, Abdulaziz Z, MacDonald S, Pulford KA, Stein H, Mason DY (1984) Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem 32:219–229
Damm-Welk C, Busch K, Burkhardt B, Schieferstein J, Viehmann S, Oschlies I, Klapper W, Zimmermann M, Harbott J, Reiter A, Woessmann W (2007) Prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in bone marrow or peripheral blood as detected by qualitative and quantitative PCR in pediatric NPM–ALK positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood 110:670–677
Geissinger E, Odenwald T, Lee SS, Bonzheim I, Roth S, Reimer P, Wilhelm M, Muller-Hermelink HK, Rudiger T (2004) Nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas and, in particular, their lymphoepithelioid (Lennert’s) variant are often derived from CD8(+) cytotoxic T-cells. Virchows Arch 445:334–343
Jaffe E, Harris N, Stein H, Vardiman JW (2001) Pathology and genetics of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC, Lyon
Kinney MC, Collins RD, Greer JP, Whitlock JA, Sioutos N, Kadin ME (1993) A small-cell-predominant variant of primary Ki-1 (CD30)+ T-cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol 17:859–868
Lennert K, Feller A (1981) Histopathologie der Non-Hodgkin-Lymphome. Springer, Berlin
Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL, Look AT (1994) Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 263:1281–1284
Passoni L, Gallo B, Biganzoli E, Stefanoni R, Massimino M, Di Nicola M, Gianni AM, Gambacorti-Passerini C (2006) In vivo T-cell immune response against anaplastic lymphoma kinase in patients with anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Haematologica 91:48–55
Pileri S, Falini B, Delsol G, Stein H, Baglioni P, Poggi S, Martelli MF, Rivano MT, Mason DY, Stansfeld AG (1990) Lymphohistiocytic T-cell lymphoma (anaplastic large cell lymphoma CD30+/Ki-1+ with a high content of reactive histiocytes). Histopathology 16:383–391
Pileri SA, Pulford K, Mori S, Mason DY, Sabattini E, Roncador G, Piccioli M, Ceccarelli C, Piccaluga PP, Santini D, Leone O, Stein H, Falini B (1997) Frequent expression of the NPM–ALK chimeric fusion protein in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, lymphohistiocytic type. Am J Pathol 150:1207–1211
Pulford K, Falini B, Banham AH, Codrington D, Roberton H, Hatton C, Mason DY (2000) Immune response to the ALK oncogenic tyrosine kinase in patients with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 96:1605–1607
Pulford K, Lamant L, Espinos E, Jiang Q, Xue L, Turturro F, Delsol G, Morris SW (2004) The emerging normal and disease-related roles of anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:2939–2953
Pulford K, Lamant L, Morris SW, Butler LH, Wood KM, Stroud D, Delsol G, Mason DY (1997) Detection of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and nucleolar protein nucleophosmin (NPM)–ALK proteins in normal and neoplastic cells with the monoclonal antibody ALK1. Blood 89:1394–1404
Salaverria I, Bea S, Lopez-Guillermo A, Lespinet V, Pinyol M, Burkhardt B, Lamant L, Zettl A, Horsman D, Gascoyne R, Ott G, Siebert R, Delsol G, Campo E (2008) Genomic profiling reveals different genetic aberrations in systemic ALK-positive and ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Br J Haematol 140:516–526
Stein H, Foss HD, Durkop H, Marafioti T, Delsol G, Pulford K, Pileri S, Falini B (2000) CD30(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a review of its histopathologic, genetic, and clinical features. Blood 96:3681–3695
Zettl A, Rudiger T, Konrad MA, Chott A, Simonitsch-Klupp I, Sonnen R, Muller-Hermelink HK, Ott G (2004) Genomic profiling of peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified, and anaplastic large T-cell lymphoma delineates novel recurrent chromosomal alterations. Am J Pathol 164:1837–1848
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Olivera Batic, Monika Hauberg, Michael Weiss, Charlotte von Drathen and Christiane Stange for their excellent technical assistance and Kay Dege for editing the manuscript. This work was supported by the Kinder-Krebs-Initiative Buchholz, Holm-Seppensen.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klapper, W., Böhm, M., Siebert, R. et al. Morphological variability of lymphohistiocytic variant of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (former lymphohistiocytic lymphoma according to the Kiel classification). Virchows Arch 452, 599–605 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-008-0616-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-008-0616-7