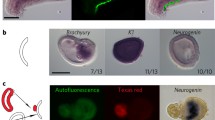
Abstract
The core molecular mechanisms of dorsal organizer formation during gastrulation are highly conserved within the chordate lineage. One of the key characteristics is that Nodal signaling is required for the organizer-specific gene expression. This feature appears to be ancestral, as evidenced by the presence in the most basally divergent chordate amphioxus. To provide a better understanding of the evolution of organizer-specific gene regulation in chordates, we analyzed the cis-regulatory sequence of amphioxus Chordin in the context of the vertebrate embryo. First, we generated stable zebrafish transgenic lines, and by using light-sheet fluorescent microscopy, characterized in detail the expression pattern of GFP driven by the cis-regulatory sequences of amphioxus Chordin. Next, we performed a 5′deletion analysis and identified an enhancer sufficient to drive the expression of the reporter gene into a chordate dorsal organizer. Finally, we found that the identified enhancer element strongly depends on Nodal signaling, which is consistent with the well-established role of this pathway in the regulation of the expression of dorsal organizer–specific genes across chordates. The enhancer identified in our study may represent a suitable simple system to study the interplay of the evolutionarily conserved regulatory mechanisms operating during early chordate development.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials will be available upon request.
References
Agius E, Oelgeschlager M, Wessely O, Kemp C, De Robertis EM (2000) Endodermal Nodal-related signals and mesoderm induction in Xenopus. Development 127:1173–1183
Bessa J, Tena JJ, de la Calle-Mustienes E, Fernandez-Minan A, Naranjo S, Fernandez A, Montoliu L, Akalin A, Lenhard B, Casares F, Gomez-Skarmeta JL (2009) Zebrafish enhancer detection (ZED) vector: a new tool to facilitate transgenesis and the functional analysis of cis-regulatory regions in zebrafish. Dev Dyn 238:2409–2417
Cannavo E, Khoueiry P, Garfield DA, Geeleher P, Zichner T, Gustafson EH, Ciglar L, Korbel JO, Furlong EE (2016) Shadow enhancers are pervasive features of developmental regulatory networks. Curr Biol 26:38–51
DaCosta Byfield S, Major C, Laping NJ, Roberts AB (2004) SB-505124 is a selective inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta type I receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Mol Pharmacol 65(3):744–52. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.65.3.744.
Demagny H, Araki T, De Robertis EM (2014) The tumor suppressor Smad4/DPC4 is regulated by phosphorylations that integrate FGF, Wnt, and TGF-beta signaling. Cell Rep 9:688–700
Hagos EG, Dougan ST (2007) Time-dependent patterning of the mesoderm and endoderm by Nodal signals in zebrafish. BMC Dev Biol 7:22
Houston DW (2017) Vertebrate axial patterning: from egg to asymmetry. Adv Exp Med Biol 953:209–306
Jones CM, Kuehn MR, Hogan BL, Smith JC, Wright CV (1995) Nodal-related signals induce axial mesoderm and dorsalize mesoderm during gastrulation. Development 121:3651–3662
Kawakami K, Takeda H, Kawakami N, Kobayashi M, Matsuda N, Mishina M (2004) A transposon-mediated gene trap approach identifies developmentally regulated genes in zebrafish. Dev Cell 7:133–144
Kozmikova I, Kozmik Z (2015) Gene regulation in amphioxus: an insight from transgenic studies in amphioxus and vertebrates. Mar Genomics 24(Pt 2):159–166
Kozmikova I, Yu JK (2017) Dorsal-ventral patterning in amphioxus: current understanding, unresolved issues, and future directions. Int J Dev Biol 61:601–610
Kozmikova I, Smolikova J, Vlcek C, Kozmik Z (2011) Conservation and diversification of an ancestral chordate gene regulatory network for dorsoventral patterning. PLoS One 6:e14650
Kozmikova I, Candiani S, Fabian P, Gurska D, Kozmik Z (2013) Essential role of Bmp signaling and its positive feedback loop in the early cell fate evolution of chordates. Dev Biol 382:538–554
Kozmikova I, Kozmik Z (2020) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is an evolutionarily conserved determinant of chordate dorsal organizer. Elife 9:e56817
Kumar V, Umair Z, Kumar S, Lee U, Kim J (2021) Smad2 and Smad3 differentially modulate chordin transcription via direct binding on the distal elements in gastrula Xenopus embryos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 559:168–175
Kuroda H, Wessely O, De Robertis EM (2004) Neural induction in Xenopus: requirement for ectodermal and endomesodermal signals via Chordin, Noggin, beta-Catenin, and Cerberus. PLoS Biol 2:E92
Le Petillon Y, Luxardi G, Scerbo P, Cibois M, Leon A, Subirana L, Irimia M, Kodjabachian L, Escriva H, Bertrand S (2017) Nodal/activin pathway is a conserved neural induction signal in chordates. Nat Ecol Evol 1:1192–1200
Marletaz F, Firbas PN, Maeso I, Tena JJ, Bogdanovic O, Perry M, Wyatt CDR, de la Calle-Mustienes E, Bertrand S, Burguera D, Acemel RD, van Heeringen SJ, Naranjo S, Herrera-Ubeda C, Skvortsova K, Jimenez-Gancedo S, Aldea D, Marquez Y, Buono L, Kozmikova I, Permanyer J, Louis A, Albuixech-Crespo B, Le Petillon Y, Leon A, Subirana L, Balwierz PJ, Duckett PE, Farahani E, Aury JM, Mangenot S, Wincker P, Albalat R, Benito-Gutierrez E, Canestro C, Castro F, D’Aniello S, Ferrier DEK, Huang S, Laudet V, Marais GAB, Pontarotti P, Schubert M, Seitz H, Somorjai I, Takahashi T, Mirabeau O, Xu A, Yu JK, Carninci P, Martinez-Morales JR, Crollius HR, Kozmik Z, Weirauch MT, Garcia-Fernandez J, Lister R, Lenhard B, Holland PWH, Escriva H, Gomez-Skarmeta JL, Irimia M (2018) Amphioxus functional genomics and the origins of vertebrate gene regulation. Nature 564:64–70
Miller-Bertoglio VE, Fisher S, Sanchez A, Mullins MC, Halpern ME (1997) Differential regulation of chordin expression domains in mutant zebrafish. Dev Biol 192:537–550
Minguillon C, Gibson-Brown JJ, Logan MP (2009) Tbx4/5 gene duplication and the origin of vertebrate paired appendages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:21726–21730
Morov AR, Ukizintambara T, Sabirov RM, Yasui K (2016) Acquisition of the dorsal structures in chordate amphioxus. Open Biol 6:160062
Onai T, Yu JK, Blitz IL, Cho KW, Holland LZ (2010) Opposing Nodal/Vg1 and BMP signals mediate axial patterning in embryos of the basal chordate amphioxus. Dev Biol 344:377–389
Sasai Y, Lu B, Steinbeisser H, Geissert D, Gont LK, De Robertis EM (1994) Xenopus chordin: a novel dorsalizing factor activated by organizer-specific homeobox genes. Cell 79:779–790
Scott IC, Blitz IL, Pappano WN, Imamura Y, Clark TG, Steiglitz BM, Thomas CL, Maas SA, Takahara K, Cho KW, Greenspan DS (1999) Mammalian BMP-1/Tolloid-related metalloproteinases, including novel family member mammalian Tolloid-like 2, have differential enzymatic activities and distributions of expression relevant to patterning and skeletogenesis. Dev Biol 213:283–300
Shi C, Huang J, Chen S, Li G, Wang Y (2018) Generation of two transgenic amphioxus lines using the Tol2 transposon system. J Genet Genomics 45:513–516
Streit A, Lee KJ, Woo I, Roberts C, Jessell TM, Stern CD (1998) Chordin regulates primitive streak development and the stability of induced neural cells, but is not sufficient for neural induction in the chick embryo. Development 125:507–519
Tam PP, Behringer RR (1997) Mouse gastrulation: the formation of a mammalian body plan. Mech Dev 68:3–25
Van Otterloo E, Li W, Garnett A, Cattell M, Medeiros DM, Cornell RA (2012) Novel Tfap2-mediated control of soxE expression facilitated the evolutionary emergence of the neural crest. Development 139:720–730
Yasuoka Y (2020) Enhancer evolution in chordates: lessons from functional analyses of cephalochordate cis-regulatory modules. Dev Growth Differ 62:279–300
Yasuoka Y, Tando Y, Kubokawa K, Taira M (2019) Evolution of cis-regulatory modules for the head organizer gene goosecoid in chordates: comparisons between Branchiostoma and Xenopus. Zoological Lett 5:27
Yoshida M, Kajikawa E, Kurokawa D, Noro M, Iwai T, Yonemura S, Kobayashi K, Kiyonari H, Aizawa S (2016) Conserved and divergent expression pat- terns of markers of axial development in reptilian embryos: Chinese soft-shell turtle and Madagascar ground gecko. Dev Biol 415:122–142
Yu JK, Satou Y, Holland ND, Shin IT, Kohara Y, Satoh N, Bronner-Fraser M, Holland LZ (2007) Axial patterning in cephalochordates and the evolution of the organizer. Nature 445:613–617
Yu JK, Meulemans D, McKeown SJ, Bronner-Fraser M (2008) Insights from the amphioxus genome on the origin of vertebrate neural crest. Genome Res 18:1127–1132
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Veronika Noskova for the amphioxus facility maintenance and Dr. Sarka Takacova for proofreading the manuscript. We acknowledge the Light Microscopy Core Facility, IMG CAS, supported by RVO – 68378050-KAV-NPUI, for help with the light-sheet microscopy presented herein.
Funding
This work was supported by the Czech Science Foundation grant 20-25377S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I.K. and Z.K. conceived the study. S.M. and Z.K. performed experiments. I.K. wrote the main manuscript text. S.M. prepared Figs. 1, 2, 3, and 4, that were supervised/corrected by I.K.Z.K. prepared Supplementary Figure 1. S.M. prepared all videos. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Ildiko Somorjai.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Fig. 5
Supplementary Figure 1 Epigenetic data from B. lanceolatum embryos indicating regions of open chromatin. Region used for reporter gene assays is shown by green line. Blue box indicates the enhancer region. Putative Smad-binding elements are highlighted within the nucleotide sequence of B. floridae enhancer.170 KB

Fig. 6
Supplementary Figure 2 Scheme of the vector used for zebrafish transgenesis27.7 KB
Supplementary video 1 Stable zebrafish transgenic line containing the BfChrd::eGFP (- 1.5kb) construct was imaged with a Zeiss Light Sheet Z.1 microscope. The embryo is in the dorsal view. (AVI 975 KB)
Supplementary video 2 Stable zebrafish transgenic line containing the BfChrd::eGFP (- 1.5kb) construct was imaged with a Zeiss Light Sheet Z.1 microscope. The embryo is in the lateral view. The reporter gene expression starts in the ectoderm and is then much stronger in the involuting mesoderm. (AVI 869 KB)
Supplementary video 3 Stable zebrafish transgenic line containing the BfChrd::eGFP (- 1.5kB/-1.0kb) construct was imaged with a Zeiss Light Sheet Z.1 microscope. The embryo is in the dorsal view. (AVI 1481 KB)
Supplementary video 4 Stable zebrafish transgenic line containing the BfChrd::eGFP (- 1.5kB/-1.0kb) construct was imaged with a Zeiss Light Sheet Z.1 microscope. The embryo is in the lateral view. The reporter gene expression starts in the ectoderm and is then much stronger in the involuting mesoderm. (AVI 2028 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Machacova, S., Kozmik, Z. & Kozmikova, I. Identification of Nodal-dependent enhancer of amphioxus Chordin sufficient to drive gene expression into the chordate dorsal organizer. Dev Genes Evol 232, 137–145 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-022-00698-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-022-00698-z