Abstract
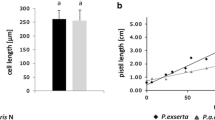
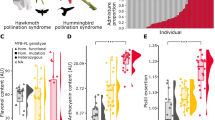
The two related Petunia species, P. axillaris and P. integrifolia, are sympatric at various locations in South America but do not hybridise. Divergent pollinator preferences are believed to be in part responsible for their reproductive isolation. The volume of nectar produced and several components of flower morphology might contribute to pollinator-dependant reproductive isolation. In this study, we aimed to identify the genetic changes underlying the quantitative differences observed between these two Petunia species in flower size and nectar volume. We mapped quantitative trait loci (QTL) responsible for the different phenotypes of P. axillaris and P. integrifolia in an inter-specific backcross population. QTL of small to moderate effect control the differences in flower size and volume of nectar. In addition, we observed strong suppression of meiotic recombination in Petunia, even between closely related species, which precluded a fine resolution of QTL mapping. Thus, our data suggest that flower size and nectar volume are highly polygenic. They are likely to have evolved gradually through pollinator-mediated adaptation or reinforcement, and are not likely to have been primary factors in early steps of pollinator isolation of P. axillaris and P. integrifolia.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- PVE:
-
Percent variance explained
- BC1 :
-
Backcross 1
- BIL:
-
Backcross inbred line
- NIL:
-
Near isogenic line
References
Abiracheddarmency M, Tarenghi E, Dejong JH (1992) The effect on meiotic synapsis of a recombination modulator in Petunia hybrida. Genome 35:443–453
Ando T, Nomura M, Tsukahara J, Watanabe H, Kokubun H, Tsukamoto T, Hashimoto G, Marchesi E, Kitching IJ (2001) Reproductive isolation in a native population of Petunia sensu Jussieu (Solanaceae). Ann Bot 88:403–413
Bradshaw HD, Schemske DW (2003) Allele substitution at a flower colour locus produces a pollinator shift in monkeyflowers. Nature 426:176–178
Bradshaw HD, Wilbert SM, Otto KG, Schemske DW (1995) Genetic mapping of floral traits associated with reproductive isolation in monkeyflowers (Mimulus). Nature 376:762–765
Bradshaw HD, Otto KG, Frewen BE, McKay JK, Schemske DW (1998) Quantitative trait loci affecting differences in floral morphology between two species of monkeyflower (Mimulus). Genetics 149:367–382
Cornu A, Farcy E, Mousset C (1988) A genetic basis for variations in meiotic recombination in Petunia hybrida. Genome 32:46–53
Coyne JA, Orr HA (2004) Speciation. Library of congress cataloging-in-publication data, Sunderland
De Vicente MC, Tanksley SD (1993) QTL analysis of transgressive segregation in an interspecific tomato cross. Genetics 134:585–596
Doerge RW, Churchill GA (1996) Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics 142:285–294
Fenster CB, Armbruster WS, Wilson P, Dudash MR, Thomson JD (2004) Pollination syndromes and floral specialization. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 35:375–403
Galen C (1996) Rates of floral evolution: Adaptation to bumblebee pollination in an alpine wildflower, Polemonium viscosum. Evolution 50:120–125
Galliot C, Stuurman J, Kuhlemeier C (2006) The genetic dissection of floral pollination syndromes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:78–82
Gerats T, Vandenbussche M (2005) A model system for comparative research: Petunia. Trends Plant Sci 10:251–256
Grant V (1994) Modes and origins of mechanical and ethological isolation in angiosperms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3–10
Hall MC, Willis JH (2005) Transmission ratio distortion in intraspecific hybrids of Mimulus guttatus: implications for genomic divergence. Genetics 170:375–386
Hoballah ME, Stuurman J, Turlings TCJ, Guerin PM, Connétable S, Kuhlemeier C (2005) The composition and timing of flower odour emission by wild Petunia axillaris coincide with the antennal perception and nocturnal activity of the pollinator Manduca sexta. Planta 222:141–150
Manly KF, Cudmore RHJ, Meer JM (2001) Map Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome 12:930–932
Mitchell RJ (2004) Heritability of nectar traits: why do we know so little? Ecology 85:1527–1533
Proctor M, Yeao P, Lack A (1996) The natural history of pollination. Harper Collins Publishers, London
Quattrocchio F, Wing JF, van der Woude K, Mol JN, Koes R (1998) Analysis of bHLH and MYB domain proteins: species-specific regulatory differences are caused by divergent evolution of target anthocyanin genes. Plant J 13:475–488
Quattrocchio F, Wing J, van der Woude K, Souer E, de Vetten N, Mol J, Koes R (1999) Molecular analysis of the anthocyanin2 gene of Petunia and its role in the evolution of flower color. Plant Cell 11:1433–1444
Robbins TP, Gerats AGM, Fiske H, Jorgensen RA (1995) Suppression of recombination in wide hybrids of Petunia hybrida as revealed by genetic mapping of marker transgenes. Theor Appl Genet 90:957–968
Robert N, Farcy E, Cornu A (1991) Genetic control of meiotic recombination in Petunia hybrida—dosage effect of gene Rm1 on segments Hf1-Lg1 and An2-Rt—Role of modifiers. Genome 34:515–523
Stehmann JR (1987) Petunia exserta (Solanaceae): Uma nova espécie do Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Napaea Rev Bot 2:19–21
Strommer J, Gerats AGM, Sanago M, Molnar SJ (2000) A gene-based RFLP map of Petunia. Theor Appl Genet 100:899–905
Strommer J, Peters J, Zethof J, De Keukeleire P, Gerats T (2002) AFLP maps of Petunia hybrida: building maps when markers cluster. Theor Appl Genet 105:1000–1009
Stuurman J, Hoballah ME, Broger L, Moore J, Basten C, Kuhlemeier C (2004) Dissection of floral pollination syndromes in Petunia. Genetics 168:1585–1599
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de-Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton TM, Giovannoni JJ, Grandillo S, Martin GB, Messeguer R, Miller JC, Miller L, Paterson AH, Pineda O, Roder MS, Wing RA, Wu W, Young ND (1992) High density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Torgerson WS (1965) Multidimensional scaling of similarity. Psychometrika 30:379–393
Verdonk JC, Haring MA, van Tunen AJ, Schuurink RC (2005) ODORANT1 regulates fragrance biosynthesis in Petunia flowers. Plant Cell 17:1612–1624
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng Z-B (2005) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC (http://www.statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Larissa Broger for technical assistance, Alexandre Dell’Olivo for helpful discussions, and Christopher Ball and Rebecca Alder for their care of a large plant population.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galliot, C., Hoballah, M.E., Kuhlemeier, C. et al. Genetics of flower size and nectar volume in Petunia pollination syndromes. Planta 225, 203–212 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0342-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0342-9